Difference between revisions of "2009 Summer Project Week Prostate Robotics"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| − | During IGT Workshop in 2008 (Boston, December 2008), we successfully tested communication among the navigation software (3D Slicer / RadVision), robot control software, and 3T MRI at BWH. Since then, we have been working on two | + | During IGT Workshop in 2008 (Boston, December 2008), we successfully tested communication among the navigation software (3D Slicer / RadVision), robot control software, and 3T MRI at BWH. Since then, we have been working on two tasks: improvement of the pneumatic mechanism at JHU and volunteer studies to analyze the workspace in the 3T MRI at BWH. |
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 15:36, 22 May 2009
Home < 2009 Summer Project Week Prostate RoboticsKey Investigators
- BWH: Junichi Tokuda, Nobuhiko Hata
- JHU: Sam Song, Nathan Cho
- AMS: Jack Blevins, Clif Burdette
- WPI: Gregory Fischer
- Queen's: Andras Lasso
Objective
We will perform a mock-up procedure to validate our software / hardware system for MRI-guided transperineal prostate intervention.
Approach, Plan
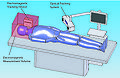
The software system consists of three sub-components: a) control software for the needle placement robot, b) software to control a closed-bore whole body 3T MRI scanner (GE Excite HD 3T, GE Healthcare), and c) open-source surgical navigation software (3D Slicer, http://www.slicer.org/). The core component of the software system is 3D Slicer, running on a Linux-based workstation, that serves as an integrated environment for calibration, surgical planning, image guidance and device monitoring and control. The 3D Slicer communicates with the other components through 100 Base-T Ethernet to exchange data and commands using an open network communication protocol, OpenIGTLink. We developed a software module in 3D Slicer that offers all features uniquely required for MR-guided robotic prostate intervention, as follows: 1) management of the ‘workphase’ of the all components in the system; 2) treatment planning by placing target points on the pre-operative 3D images loaded on the 3D Slicer and robot control based on the plan; 3) registration of the robot and patient coordinate systems; 4) integrated visualization of real-time 2D image, preoperative 3D image, and visualization of the current needle position on the 3D viewer of 3D Slicer.
Progress
During IGT Workshop in 2008 (Boston, December 2008), we successfully tested communication among the navigation software (3D Slicer / RadVision), robot control software, and 3T MRI at BWH. Since then, we have been working on two tasks: improvement of the pneumatic mechanism at JHU and volunteer studies to analyze the workspace in the 3T MRI at BWH.
References
- DiMaio S.P., Fischer G.S., Haker S.J., Hata N., Iordachita I., Tempany C.M., Kikinis R., Fichtinger G. A system for MRI-guided Prostate Interventions. Proceedings of IEEE RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics 2006 Feb.
- Fischer G.S., Iordachita I., Csoma C., Tokuda J., Mewes P.W., Tempany C.M., Hata N., Fichtinger G. Pneumatically Operated MRI Compatible Needle Placement Robot for Prostate Interventions. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2008;2489-2495.
- Mewes P., Tokuda J., DiMaio S., Fischer G., Csoma C., Gobbi D., Tempany C., Fichtinger G., Hata N. Integrated System for Robot-Assisted in Prostate Biopsy in Closed MRI Scanner. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2008; 2959-2962.
- Fischer G.S., Iordachita I., Csoma C., Tokuda J., DiMaio S.P., Tempany C.M., Hata N., Fichtinger G. MRI-Compatible Pneumatic Robot for Transperineal Prostate Needle Placement. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics June 2008; 13(3):295-305.
- Tokuda J., Fischer G.S., Csoma C., DiMaio S.P., Gobbi D.G., Fichtinger G., Tempany C.M., Hata N. Software Strategy for Robotic Transperineal Prostate Therapy in Closed-Bore MRI. Int Conf Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008;11(Pt 2):701-709. PMID: 18982666.