Difference between revisions of "2009 Summer Project Week 3DGRASE"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Matthias Gunther, Koichi Oshio, and David A Feinberg. Single-shot 3D imaging techniques improve arterial spin labeling perfusion measurements. Magn Reson Med, 54(2):491-8, 2005. [[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20580|DOI]] | ||
| + | # James G. Pipe. Motion correction with PROPELLER MRI: Application to head motion and free-breathing cardiac imaging. 42(5):963-969, 1999. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:14, 26 June 2009
Home < 2009 Summer Project Week 3DGRASE
Key Investigators
- BWH: Scott Hoge
- WFU: Bob Kraft, Huan Tan
- Mediri: Mattias Guenther
Objective
The objective of this project is to port Dr Guenther's 3D GRASE pulse sequence for perfusion imaging to the GE 3T scanner. Once ported, we will seek to integrate the pulse sequence with image reconstruction routines from the NCIGT fast imaging library.
Approach, Plan
Our goals for the project week are:
1. Complete development of GE EPIC version of 3D GRASE
2. Perform and evaluate performance on 3T short bore
Progress
3D GRASE ported to GE scanner platform, and integrated with PROPELLER EPI with NCIGT fast imaging library used for parallel imaging stage of Nyquist ghost correction step.
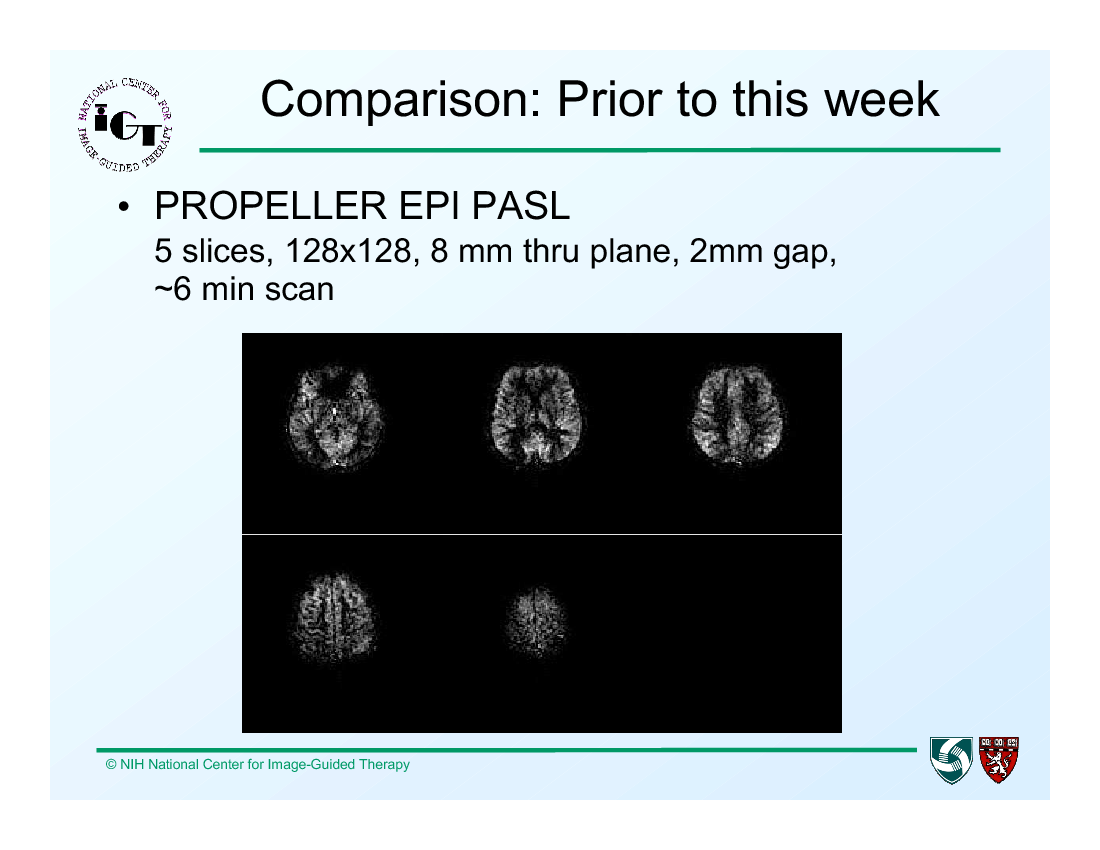
Prior to IGT Week:
- Perfusion ASL using PROPELLER EPI at WFU gave 5 slices, 128x128 image size, 8mm through plane resolution, with 2mm gap in roughly 6 minutes
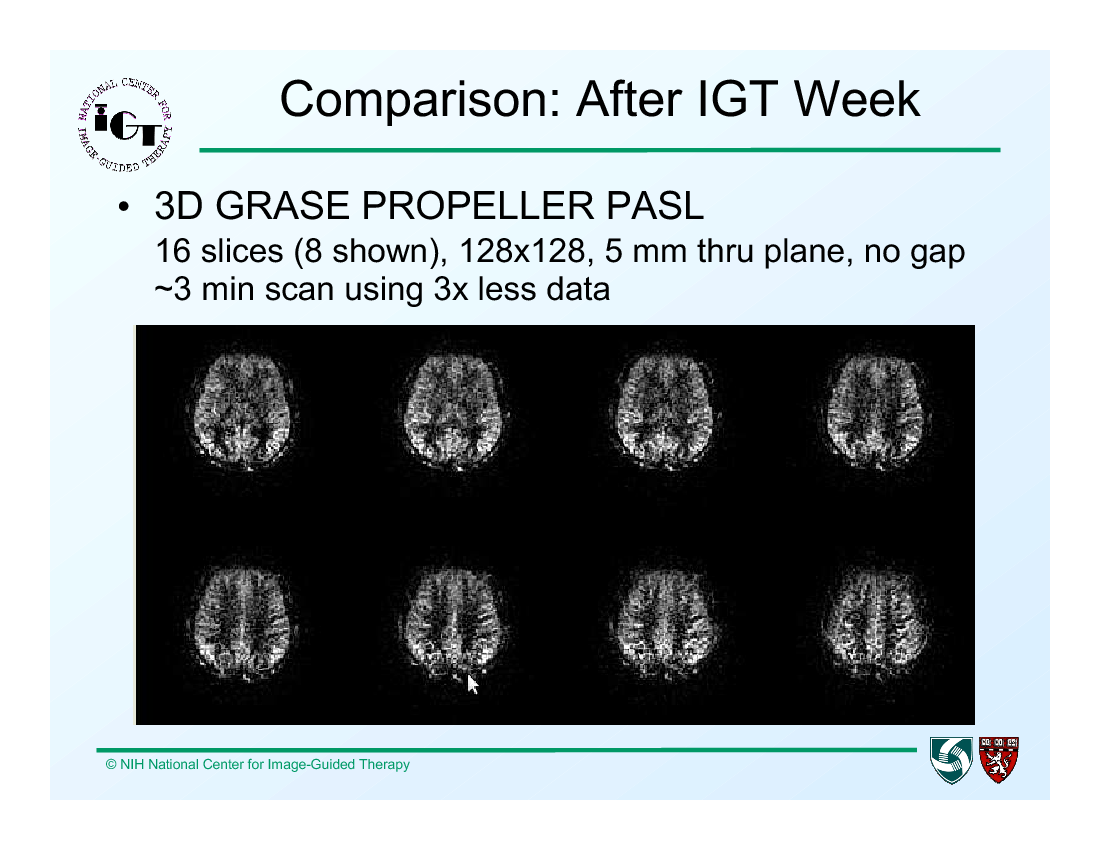
After IGT Week:
- 3D GRASE PROPELLER PASL gives 16 slices, 128x128 image size, 5 mm through plane, with no gap, in around a 3 min scan.
References
- Matthias Gunther, Koichi Oshio, and David A Feinberg. Single-shot 3D imaging techniques improve arterial spin labeling perfusion measurements. Magn Reson Med, 54(2):491-8, 2005. [[1]]
- James G. Pipe. Motion correction with PROPELLER MRI: Application to head motion and free-breathing cardiac imaging. 42(5):963-969, 1999.