Difference between revisions of "RobustStatisticsSegmentation"
m (→Usage) |
|||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
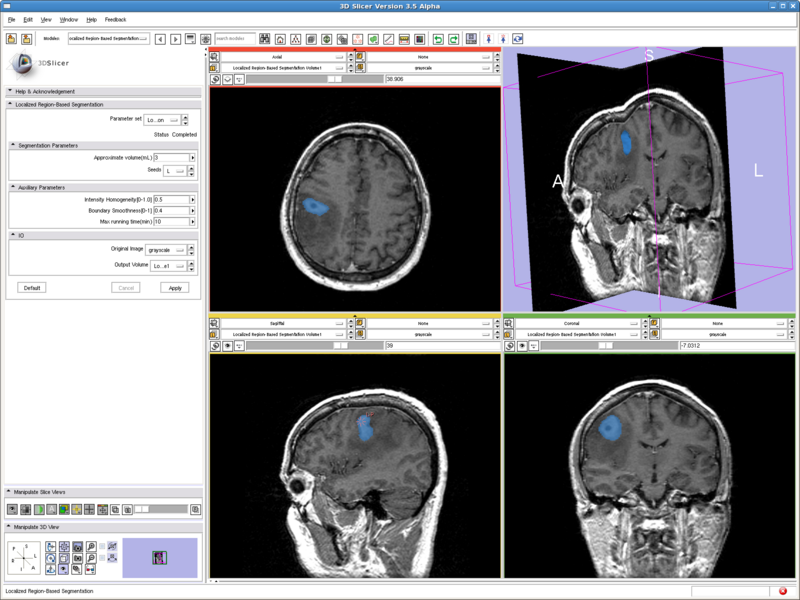
In the figure below we show the position of the two seeds. They are both in the cortex region. And it can be seen in the segmentation result, the renal cortex got segmented and the pelvis is not. | In the figure below we show the position of the two seeds. They are both in the cortex region. And it can be seen in the segmentation result, the renal cortex got segmented and the pelvis is not. | ||
| − | [[Image:RobustStatisticsSegmentation_RightKidney.png | Segmentation of | + | [[Image:RobustStatisticsSegmentation_RightKidney.png | Segmentation of right kidney | 800px]] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Testing case: spleen == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Data set: http://wiki.na-mic.org/Wiki/images/8/8d/Patient1.tar.gz | ||
| + | * Approximate volume: 300 mL | ||
| + | * Intensity homogeneity: 1 | ||
| + | * Boundary smoothness: 0.3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the figure below we show the position of the two seeds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:RobustStatisticsSegmentation_Spleen.png | Segmentation of spleen | 800px]] | ||
== Testing case: tumor == | == Testing case: tumor == | ||
Revision as of 16:58, 21 November 2009
Home < RobustStatisticsSegmentationRobust Statistics Based Segmentation
Description
How to get the module
- start Slicer 3.5
- open View->Extension Manager
- check "Find & Install", click "Next"
- in the list, select "LocalRegionalSegModule", then "Download & Install", and "Next"
- Slicer will ask to restart, confirm.
- after restarts, the module is in Module category: "Segmentation-->Localized Region-based Segmentation"
Usage
General guideline
- First run:
- Give a rough estimate of the object volume and put fiducial points (preferred to be 2 or more) in the object.
- Run the module using the default parameters.
- Note:
- The Approximate volume is just a rough upper limit for the volume. It should be at least the size of the object. This is because when the volume reaches that, the program must stop. However, other criteria may stop the algorithm before the volume reaches this value.
- The fiducial points can be thrown into the object. What I do is I just add two fiducial points and move them into the object within one slice.
- Troubleshooting
- Surface is too rough. Try:
- Increase "Boundary smoothness"
- Leakage into thin/narrow regions. Try:
- Increase "Boundary smoothness"
- leakage into similar (but still different) intensity regions (which is not necessarily thin), Try:
- Increase "Intensity homogeneity"
- Some regions are missed: Try (either one):
- Increase "Max volume"
- Decrease"Intensity homogeneity"
- Decrease "Boundary smoothness"
- Some regions are missed, at the same time leakages to some other regions. Try (either one)
- Increase "Intensity homogeneity"
- Add another fiducial point
- Surface is too rough. Try:
Testing
Several tests are conducted and shown here along with the parameters used to get the results.
Testing case: left kidney
- Data set: http://wiki.na-mic.org/Wiki/images/8/8d/Patient1.tar.gz
- Approximate volume: 200 mL
- Intensity homogeneity: 0.1
- Boundary smoothness: 0.5
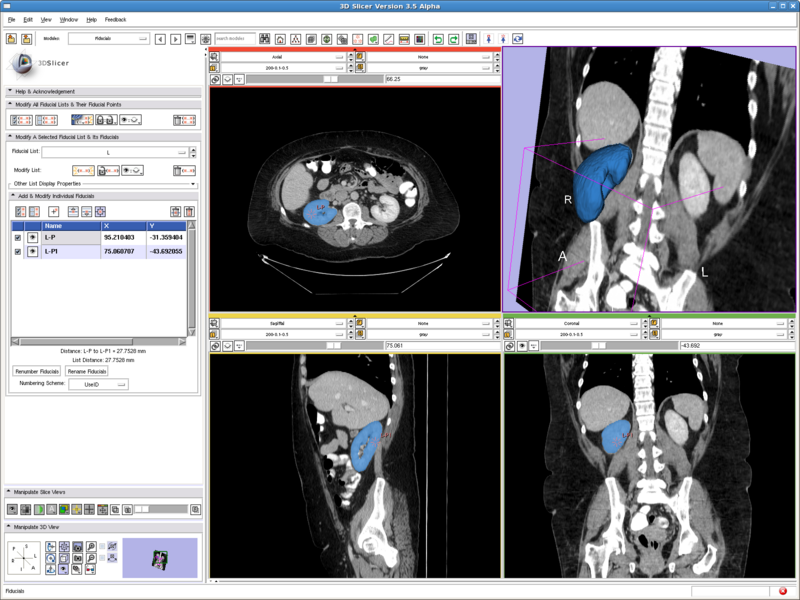
Testing case: right kidney
- Data set: http://wiki.na-mic.org/Wiki/images/8/8d/Patient1.tar.gz
- Approximate volume: 200 mL
- Intensity homogeneity: 0.1
- Boundary smoothness: 0.5
In the figure below we show the position of the two seeds. They are both in the cortex region. And it can be seen in the segmentation result, the renal cortex got segmented and the pelvis is not.
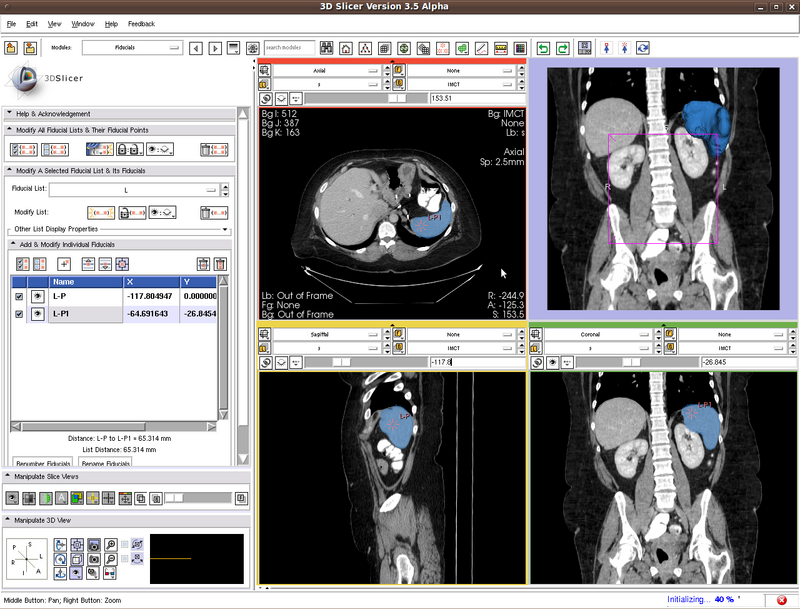
Testing case: spleen
- Data set: http://wiki.na-mic.org/Wiki/images/8/8d/Patient1.tar.gz
- Approximate volume: 300 mL
- Intensity homogeneity: 1
- Boundary smoothness: 0.3
In the figure below we show the position of the two seeds.
Testing case: tumor
- Data set: http://wiki.na-mic.org/Wiki/images/0/0f/MayExperiments.zip (DiffusionEditorBaselineNode.nrrd)
- Approximate volume: 30 mL
- Intensity homogeneity: 0.1
Testing case: tumor
- Data set: http://www.spl.harvard.edu/publications/bitstream/download/4217 (case3/grayscale.nrrd)
- Approximate volume: 30 mL
- Intensity homogeneity: 0.4
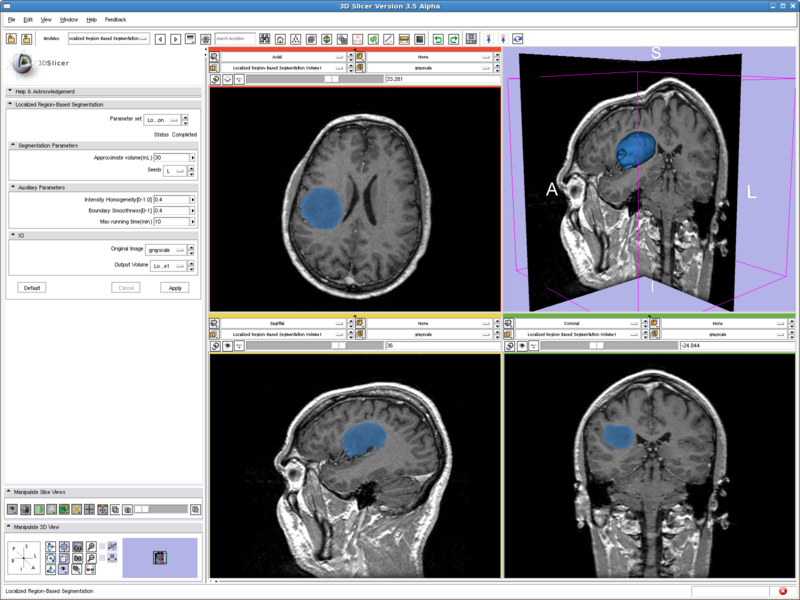
Testing case: tumor
- Data set: http://www.spl.harvard.edu/publications/bitstream/download/4217 (case5/grayscale.nrrd)
- Approximate volume: 3 mL
- Intensity homogeneity: 0.5
- Boundary smoothness: 0.4
This is a difficult case. All the other methods tested either captures only the middle dark spot, or leaks out of the tumor. But the method here nicely capture both the dark core and the bright shell, without leaking out to regions with intensities in the middle.
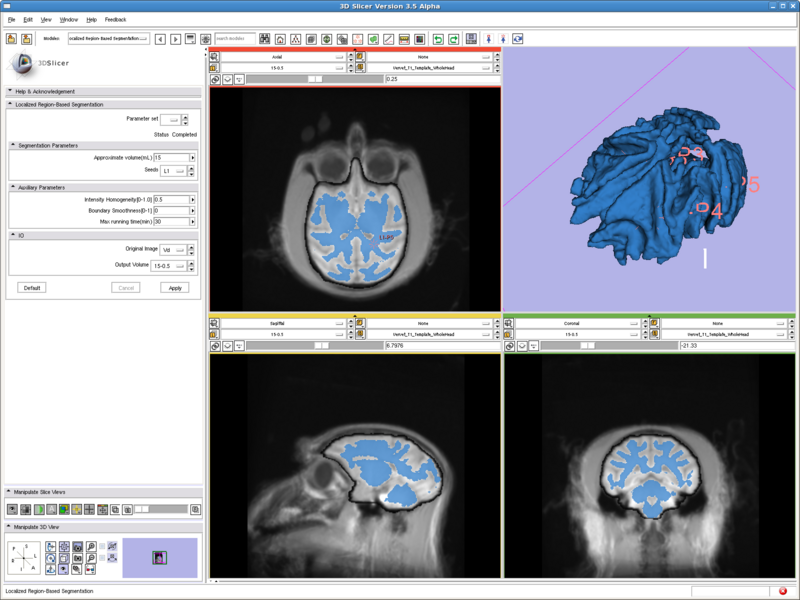
Testing case: vervet brain
- Data set: http://www.na-mic.org/Wiki/index.php/Vervet_MRI_registration (http://www.bsl.ece.vt.edu/data/vervet_atlas/VPA-10-1.1.zip Vervet_T1_Template_WholeHead.nii)
- Approximate volume: 15 mL
- Intensity homogeneity: 0.5
Previous tests all run with two fiducial points, and running time are all less than 10 seconds. This case has 6 points and runs for 15min to get the result shown.
Key Investigators
Georgia Tech: Yi Gao and Allen Tannenbaum
BWH: Katie Hayes, Andriy Fedorov, and Ron Kikinis
Publications
The method is based on:
- NA-MIC Publications Database
- Yang, Y. and Tannenbaum, A. and Giddens, D. and Coulter, WH, "Knowledge-based 3D segmentation and reconstruction of coronary arteries using CT images", in IEEE EMBS 2004, pp1664--1666