Difference between revisions of "Mapped Hexahedral Meshing"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
*[http://www.ccad.uiowa.edu/mimx Musculoskeletal Imaging, Modeling and Experimentation (MIMX)] | *[http://www.ccad.uiowa.edu/mimx Musculoskeletal Imaging, Modeling and Experimentation (MIMX)] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Figures:''' | '''Figures:''' | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 28 February 2010
Home < Mapped Hexahedral MeshingObjective:
- Develop a tool for mapped meshing that will warp a template mesh onto a surface for a new subject
- Determine the limits that the warping algorithm will succeed and fail
- Apply these techniques to a sample of data to determine the reliability of the algorithm with respect to mesh quality
Progress:
- Previous work on this project was performed at the 2007 AHM - Mapped Mesh 4 Block
- Warped meshing framework has been developed using VTK and ITK using a finite element approach
- VTK
- Support the reading and writing of meshes (vtkUnstructuredGrid) and surfaces (vtkPolyData)
- Distance measures between the deforming mesh and the subject surface
- Initial registration - Iterative Closest Point or Procrustes
- ITK
- Finite element framework used to warped the template mesh onto the subject surface
- VTK
- Registration made hierarchical to speed up the registration process
- Requires multiple template meshes to exist
- This is readily supported using the interactive meshing tools by changing the average edge length
- Subsequent meshes are initialized using a thin plate splines
- Parameters allowed to vary at each level of the registration
- Iterations
- Young's Modulus
- Convergence based on distance between the warped template and the subject surface
- User specified convergence threshold in mm
- Convergence can be based on average or maximum distance
- Boundary conditions can be applied
- Center of the mesh - Holds the eight nodes closest to the center of the mesh fixed
- External - Applies boundary conditions to the mesh as they fall within a user specified tolerance of the subject surface
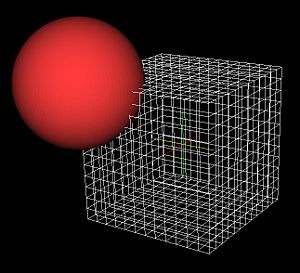
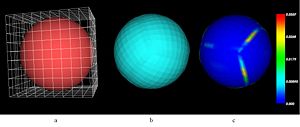
- Initial testing done by warping a cube mesh onto a sphere
- Evaluation:
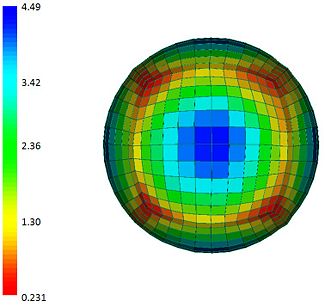
- Distance between warped mesh and subject surface
- Mesh quality
- Evaluation:
Publications:
- Grosland NM, Bafna R, Magnotta VA. Automated hexahedral meshing of anatomic structures using deformable registration. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 12(1):35-43, 2009.
Key Investigators:
- Iowa: Nicole Grosland, Vincent Magnotta, Ritesh Bafna
Links:
Figures: