Difference between revisions of "Projects:UtahAtlasSegmentation"
Hjmjohnson (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | = Atlas Based Brain | + | = Atlas Based Classification (ABC) for Healthy Brain MRI = |
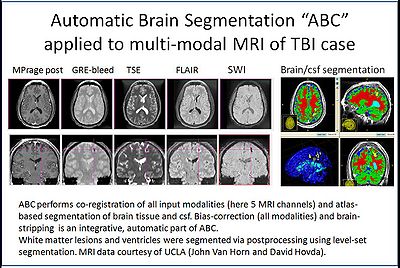
| − | Automatic segmentation can be performed reliably using priors from brain atlases and an image generative model. We have developed a tool that provides an automatic segmentation pipeline in a modular framework. | + | Automatic segmentation of brain MR images can be performed reliably using priors from brain atlases and an image generative model. We have developed a tool called ABC that provides an automatic segmentation pipeline in a modular framework. |
| − | The processing pipeline is composed tasks such as filtering the input images, registering the multimodal input images and the brain atlas to a common space, followed by iterative steps which interleave segmentation, inhomogeneity correction, and atlas warping. | + | The processing pipeline is composed of tasks such as filtering the input images, registering the multimodal input images and the brain atlas to a common space, followed by iterative steps which interleave segmentation, inhomogeneity correction, and atlas warping. |
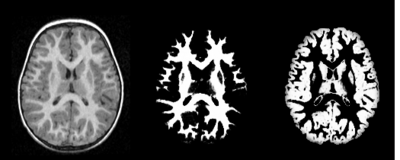
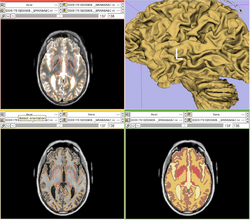
Our tool generates bias corrected images, fuzzy classification maps, and discrete segmentation labels. The tool has been used to automatically segment thousands of adult and toddler images from the University of North Carolina (UNC), and is also being used as a skull stripping mechanism for DTI processing at UNC and Utah. An example of the output of the tool is shown below. | Our tool generates bias corrected images, fuzzy classification maps, and discrete segmentation labels. The tool has been used to automatically segment thousands of adult and toddler images from the University of North Carolina (UNC), and is also being used as a skull stripping mechanism for DTI processing at UNC and Utah. An example of the output of the tool is shown below. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| − | The tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc . | + | The ABC tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc . |
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == External | + | == External Use and Modifications of ABC == |
| − | + | An earlier version of ABC has been distributed to a large number of other research groups associated with ongoing image analysis projects at the University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill and the University of Utah, and to research groups linked to these investigators. High profile projects include the Silvio Conte Center (http://www.psychiatry.unc.edu/conte/, PI John H. Gilmore, UNC) involving the processing of over 1000 infant MRI, and the Autism Centers of Excellence Project IBIS (http://www.ibis-network.org/, PI Joseph Piven, UNC) where over 650 infant brain MRI will be processed with this tool. In order to segment infant brains with age range of 6 months to 2 years as part of this longitudinal study, new age-specific atlases have been developed to be used as spatial priors for ABC. | |
| − | The ABC method has also been modified and extensively used by the University of Iowa, | + | The ABC method has also been modified and extensively used by the Hans Johnson from University of Iowa, as part of a large, multi-center Huntington Disease study. Experience with a couple of hundred datasets at Iowa demonstrated the excellent robustness and reliability of the methodology. |
{| | {| | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
|} | |} | ||
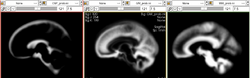
| − | The probability maps for the atlas were created from a set of 729 3T multi-modal image data sets ( | + | The probability maps for the atlas were created from a set of 729 3T multi-modal image data sets (Iowa, Hans Johnson). Improvements made were to include a measure of Venus Blood as a part of the model, and to add explicit tissue regions outside the head for tissue types that are not part of the brain. This atlas definitions are available from |
svn co https://www.nitrc.org/svn/brains/BRAINS/trunk/BRAINSTools/BRAINSABC/Atlas_20100510 | svn co https://www.nitrc.org/svn/brains/BRAINS/trunk/BRAINSTools/BRAINSABC/Atlas_20100510 | ||
| − | Under guidance of Hans Johnson, a branch of the ABC NITRC code has been modified to meet the needs of the | + | Under guidance of Hans Johnson, a branch of the ABC NITRC code has been modified to meet the needs of the Iowa group. This includes integration of a new Bspline-based registration from BRAINSFit, integration of BRAINSROIAuto, and to make it work with data with arbitrary orientation, and modifications of the interface (svn to https://www.nitrc.org/svn/brains/BRAINS/trunk/BRAINSTools/BRAINSABC). |
== ABC Bias Correction Module == | == ABC Bias Correction Module == | ||
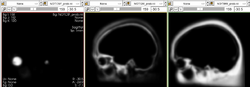
| − | + | In order to meet existing strong demands for a stand-alone MRI bias correction method with FLASH images, part of the ABC code has been made available as a separate module and distributed via NITRC (http://www.nitrc.org/projects/probbiascor) by the MIND Institute group lead by Mark Skully and Jeremy Bockholt. | |
| − | = Publications | + | = Publications = |
| − | + | * [http://www.na-mic.org/publications/pages/display/?search=Projects%3AUtahAtlasSegmentation NA-MIC Publications Database on Atlas Based Classification (ABC) for Healthy Brain MRI] | |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Key Investigators = | = Key Investigators = | ||
| Line 57: | Line 52: | ||
*Utah Algorithms: Marcel Prastawa, Guido Gerig | *Utah Algorithms: Marcel Prastawa, Guido Gerig | ||
*UNC Algorithms: Martin Styner | *UNC Algorithms: Martin Styner | ||
| − | *External research collaboration: Hans Johnson, MIND Institute | + | *External research collaboration: Hans Johnson, The University of Iowa |
| + | *External research collaboration: Jeremy Bockholt, MIND Institute | ||
Latest revision as of 13:25, 14 May 2010
Home < Projects:UtahAtlasSegmentationBack to Utah 2 Algorithms
Atlas Based Classification (ABC) for Healthy Brain MRI
Automatic segmentation of brain MR images can be performed reliably using priors from brain atlases and an image generative model. We have developed a tool called ABC that provides an automatic segmentation pipeline in a modular framework. The processing pipeline is composed of tasks such as filtering the input images, registering the multimodal input images and the brain atlas to a common space, followed by iterative steps which interleave segmentation, inhomogeneity correction, and atlas warping.
Our tool generates bias corrected images, fuzzy classification maps, and discrete segmentation labels. The tool has been used to automatically segment thousands of adult and toddler images from the University of North Carolina (UNC), and is also being used as a skull stripping mechanism for DTI processing at UNC and Utah. An example of the output of the tool is shown below.
The ABC tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc .
External Use and Modifications of ABC
An earlier version of ABC has been distributed to a large number of other research groups associated with ongoing image analysis projects at the University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill and the University of Utah, and to research groups linked to these investigators. High profile projects include the Silvio Conte Center (http://www.psychiatry.unc.edu/conte/, PI John H. Gilmore, UNC) involving the processing of over 1000 infant MRI, and the Autism Centers of Excellence Project IBIS (http://www.ibis-network.org/, PI Joseph Piven, UNC) where over 650 infant brain MRI will be processed with this tool. In order to segment infant brains with age range of 6 months to 2 years as part of this longitudinal study, new age-specific atlases have been developed to be used as spatial priors for ABC.
The ABC method has also been modified and extensively used by the Hans Johnson from University of Iowa, as part of a large, multi-center Huntington Disease study. Experience with a couple of hundred datasets at Iowa demonstrated the excellent robustness and reliability of the methodology.
The probability maps for the atlas were created from a set of 729 3T multi-modal image data sets (Iowa, Hans Johnson). Improvements made were to include a measure of Venus Blood as a part of the model, and to add explicit tissue regions outside the head for tissue types that are not part of the brain. This atlas definitions are available from svn co https://www.nitrc.org/svn/brains/BRAINS/trunk/BRAINSTools/BRAINSABC/Atlas_20100510
Under guidance of Hans Johnson, a branch of the ABC NITRC code has been modified to meet the needs of the Iowa group. This includes integration of a new Bspline-based registration from BRAINSFit, integration of BRAINSROIAuto, and to make it work with data with arbitrary orientation, and modifications of the interface (svn to https://www.nitrc.org/svn/brains/BRAINS/trunk/BRAINSTools/BRAINSABC).
ABC Bias Correction Module
In order to meet existing strong demands for a stand-alone MRI bias correction method with FLASH images, part of the ABC code has been made available as a separate module and distributed via NITRC (http://www.nitrc.org/projects/probbiascor) by the MIND Institute group lead by Mark Skully and Jeremy Bockholt.
Publications
Key Investigators
- Utah Algorithms: Marcel Prastawa, Guido Gerig
- UNC Algorithms: Martin Styner
- External research collaboration: Hans Johnson, The University of Iowa
- External research collaboration: Jeremy Bockholt, MIND Institute