Difference between revisions of "2011 Winter Project Week:SegEye"
From NAMIC Wiki
Ivan.kolesov (talk | contribs) (Created page with '==Key Investigators== * Georgia Tech: Ivan Kolesov and Allen Tannenbaum * MGH: Gregory Sharp <div style="margin: 20px;"> <div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"…') |
Ivan.kolesov (talk | contribs) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | |||
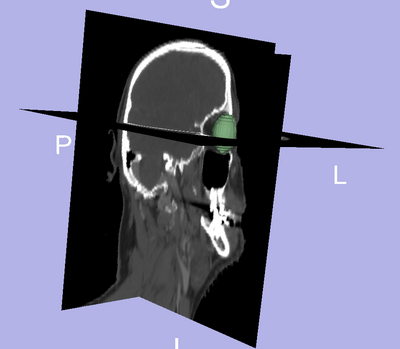
| + | [[File:3D_eye.png|400px|thumb|left|Segmentation of the eye ball.]] | ||
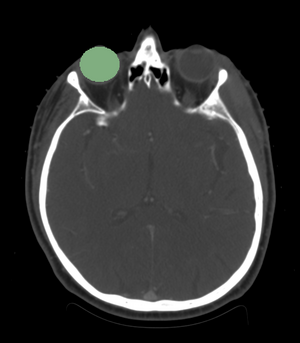
| + | [[File:2D_eye.png|300px|thumb|left|Axial view of the eye ball segmentation.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Key Investigators== | ==Key Investigators== | ||
* Georgia Tech: Ivan Kolesov and Allen Tannenbaum | * Georgia Tech: Ivan Kolesov and Allen Tannenbaum | ||
| Line 5: | Line 11: | ||
<div style="margin: 20px;"> | <div style="margin: 20px;"> | ||
<div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | <div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | ||
| − | |||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
| + | *We are interested in segmenting the eye ball, lens, optic nerve, and the optic chiasm. | ||
| + | *Anatomical structures are highly sensitive to radiation. | ||
| + | *We are creating a framework to perform these segmentations, which is likely to require a different approach for each structures due to the proximity of multiple structures to each other. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 22: | ||
<div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | <div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | ||
| + | <h3>Approach</h3> | ||
| + | *The eye ball is considered to be the pivotal organ since its segmentation will localize the region of interest when looking for other structures. | ||
| + | *We will reduce the dimensionality of this problem by performing model based segmentation for each structure. | ||
| + | *Once the eye is segmented, we use this knowledge to locate the lens/ initialize optic nerve segmentation. | ||
| + | *We would like to leverage the information provided by a CT scan with additional data from an MRI -- we have to consider this registration problem. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div style="width: 40%; float: left;"> | ||
| − | |||
| − | </ | + | <h3>Progress</h3> |
| − | + | *We segmented the eye ball. | |
| − | + | *Experiments: | |
| + | #VMTK Modules in Slicer for optic nerve segmentation. | ||
| + | #The particle filtering based approach for nerve segmentation. | ||
| + | #Ellipse constrained segmentation of optic lens. | ||
| − | + | *There remain a number of future experiments: | |
| + | #Incorporate constraints on Hounsfield units for segmentation of CT imagery. | ||
| + | #Use atlas for more robust localization of eye ball. | ||
| + | #Add prior anatomical knowledge for optic nerve segmentation (surrounding bone easily visible). | ||
| Line 33: | Line 53: | ||
<div style="width: 97%; float: left;"> | <div style="width: 97%; float: left;"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:47, 13 January 2011
Home < 2011 Winter Project Week:SegEye
Key Investigators
- Georgia Tech: Ivan Kolesov and Allen Tannenbaum
- MGH: Gregory Sharp
Objective
- We are interested in segmenting the eye ball, lens, optic nerve, and the optic chiasm.
- Anatomical structures are highly sensitive to radiation.
- We are creating a framework to perform these segmentations, which is likely to require a different approach for each structures due to the proximity of multiple structures to each other.
Approach
- The eye ball is considered to be the pivotal organ since its segmentation will localize the region of interest when looking for other structures.
- We will reduce the dimensionality of this problem by performing model based segmentation for each structure.
- Once the eye is segmented, we use this knowledge to locate the lens/ initialize optic nerve segmentation.
- We would like to leverage the information provided by a CT scan with additional data from an MRI -- we have to consider this registration problem.
Progress
- We segmented the eye ball.
- Experiments:
- VMTK Modules in Slicer for optic nerve segmentation.
- The particle filtering based approach for nerve segmentation.
- Ellipse constrained segmentation of optic lens.
- There remain a number of future experiments:
- Incorporate constraints on Hounsfield units for segmentation of CT imagery.
- Use atlas for more robust localization of eye ball.
- Add prior anatomical knowledge for optic nerve segmentation (surrounding bone easily visible).