Difference between revisions of "2014 Summer Project Week:Slicer Murin Shape Analysis"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Investigators== | ==Key Investigators== | ||
| − | * Murat Maga | + | * Murat Maga (Seattle Children's Research Institute & University of Washington Dept. of Pediatrics) |
| − | * Ryan Young | + | * Ryan Young (Seattle Children's Research Institute) |
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li> Face is the major diagnostic feature to identify | <li> Face is the major diagnostic feature to identify | ||
| − | <li> But brain and the CNS are affected primarily( | + | <li> But brain and the CNS are affected primarily() |
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| − | <li> Modalities: Optical Projection Tomography | + | <li> Modalities: <b> Optical Projection Tomography</b> [[File:Sample OPT Mouse embryo.zip]] <br>[[Image:OPT Crossection.PNG|100px]]<br> |
| + | <B> Micro Computed Tomography </b> ([[File:Stained registered sample mCT.zip]]) | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>We use landmarks to identify the anatomical regions across our samples which vary hugely in development. | <li>We use landmarks to identify the anatomical regions across our samples which vary hugely in development. | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 24 June 2014
Home < 2014 Summer Project Week:Slicer Murin Shape AnalysisKey Investigators
- Murat Maga (Seattle Children's Research Institute & University of Washington Dept. of Pediatrics)
- Ryan Young (Seattle Children's Research Institute)
Project Description
- Face is the major diagnostic feature to identify
- But brain and the CNS are affected primarily()
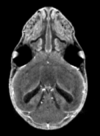
Micro Computed Tomography (File:Stained registered sample mCT.zip)
- Meet the community and learn
- Implement the landmark based Procrustes Analysis in Slicer
Objective
- Create a GPA/PCA shape analysis and visualization module for Slicer.
Approach, Plan
- Impliment GPA/PCA shape analysis in python
- Visualize the deformation of a reference volume along the principle components using thin plate splines(
 )
) - Ability to create semi-landmarks to increase spatial coverage.
- User will a uniformly sampled point cloud by entering the number of semi-landmarks. Existing “hard” landmarks will be used for their distribution. This will serve as the template to be transferred to all remaining volumes (atlas)
- The template will be transferred to a new surface. Existing “hard” landmarks will allow for correspondence. The transferred points will then be moved along the surface of the volume by optimizing the bending energy function.
- The coordinates of the slid landmarks will be saved into a new fiducial list, from which the GPA analysis can be conducted.
Progress
- Generalized Procrustes Alignment
- Principal Component and Singular Value Decomposition of the Procrustes aligned coordinates
- Thin Plate Spline visualization of the shape variables from PCA and/or SVD (by either morphing a reference volume along the shape variable, or visualizing the TPS grid using Transformation Visualizer module).