Difference between revisions of "Mapped Hexahedral Meshing"
From NAMIC Wiki
m (Text replacement - "[http://www.na-mic.org/Wiki/images/" to "[https://na-mic.org/w/images/") |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
'''Progress:''' | '''Progress:''' | ||
| − | + | * Previous work on this project was performed at the 2007 AHM - [https://na-mic.org/w/images/3/34/2007_AHM_Programming_Half_Week_MappedMesh.ppt Mapped Mesh 4 Block] | |
* Warped meshing framework has been developed using VTK and ITK using a finite element approach | * Warped meshing framework has been developed using VTK and ITK using a finite element approach | ||
**VTK | **VTK | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
***Mesh quality | ***Mesh quality | ||
| − | + | '''Publications:''' | |
| − | ''' | + | *Grosland NM, Bafna R, Magnotta VA. [http://www.informaworld.com/smpp/content~db=all?content=10.1080/10255840802136143 Automated hexahedral meshing of anatomic structures using deformable registration]. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 12(1):35-43, 2009. |
| − | * | ||
'''Key Investigators:''' | '''Key Investigators:''' | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
'''Links:''' | '''Links:''' | ||
| − | *[http://www.ccad.uiowa.edu/mimx Musculoskeletal Imaging, | + | *[http://www.ccad.uiowa.edu/mimx Musculoskeletal Imaging, Modeling and Experimentation (MIMX)] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Figures:''' | |
| − | |||
| − | ''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
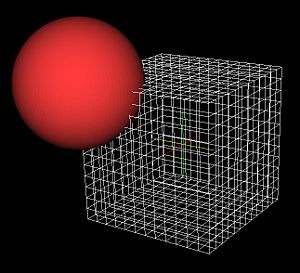
| − | + | [[Image:MappedHexMeshSquareSphereInit.jpg|left|thumb|300px|Initial position of the cube template mesh and the sphere surface prior to registration using the itk::FEM mapped meshing algorithm]] | |
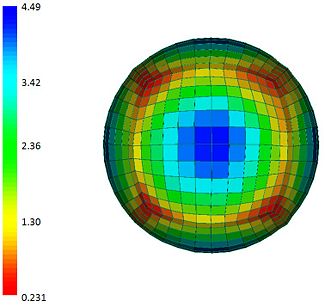
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:MappedMeshCubeSphereQuality.jpg|left|thumb|325px|Mesh quality evaluation of the warped cube]] |
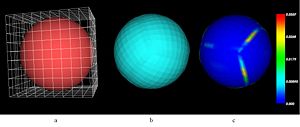
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:MappedMeshSquareSphere.jpg|left|thumb|300px|a)Position of the template cube mesh and surface after ICP registration. b) Resulting warped cube after itk::FEM mapped meshing. c) Distance map between the warped cube and the sphere surface]] |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:MappedMeshProximalPhalanxTrial.jpg|left|thumb|300px|Initial attempt to apply mapped meshing algorithm to the proximal phalanx]] |
Latest revision as of 18:27, 10 July 2017
Home < Mapped Hexahedral MeshingObjective:
- Develop a tool for mapped meshing that will warp a template mesh onto a surface for a new subject
- Determine the limits that the warping algorithm will succeed and fail
- Apply these techniques to a sample of data to determine the reliability of the algorithm with respect to mesh quality
Progress:
- Previous work on this project was performed at the 2007 AHM - Mapped Mesh 4 Block
- Warped meshing framework has been developed using VTK and ITK using a finite element approach
- VTK
- Support the reading and writing of meshes (vtkUnstructuredGrid) and surfaces (vtkPolyData)
- Distance measures between the deforming mesh and the subject surface
- Initial registration - Iterative Closest Point or Procrustes
- ITK
- Finite element framework used to warped the template mesh onto the subject surface
- VTK
- Registration made hierarchical to speed up the registration process
- Requires multiple template meshes to exist
- This is readily supported using the interactive meshing tools by changing the average edge length
- Subsequent meshes are initialized using a thin plate splines
- Parameters allowed to vary at each level of the registration
- Iterations
- Young's Modulus
- Convergence based on distance between the warped template and the subject surface
- User specified convergence threshold in mm
- Convergence can be based on average or maximum distance
- Boundary conditions can be applied
- Center of the mesh - Holds the eight nodes closest to the center of the mesh fixed
- External - Applies boundary conditions to the mesh as they fall within a user specified tolerance of the subject surface
- Initial testing done by warping a cube mesh onto a sphere
- Evaluation:
- Distance between warped mesh and subject surface
- Mesh quality
- Evaluation:
Publications:
- Grosland NM, Bafna R, Magnotta VA. Automated hexahedral meshing of anatomic structures using deformable registration. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 12(1):35-43, 2009.
Key Investigators:
- Iowa: Nicole Grosland, Vincent Magnotta, Ritesh Bafna
Links:
Figures: