Difference between revisions of "Engineering:Isomics"
m (Fix MediaWiki table formatting issue discovered while converting to GitHub Flavored Markdown using pandoc (via https://github.com/outofcontrol/mediawiki-to-gfm)) Tag: 2017 source edit |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Back to [[Engineering:Main|NA-MIC Engineering]] | Back to [[Engineering:Main|NA-MIC Engineering]] | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | |||
= Overview of Isomics Projects (PI: Steve Pieper) = | = Overview of Isomics Projects (PI: Steve Pieper) = | ||
| − | + | [[image:Isomics-logo-text-horizontal-700.png|thumb|right|400px]] | |
At Isomics, we are responsible for the end-user application software | At Isomics, we are responsible for the end-user application software | ||
| − | that serves as vehicle for translating | + | that serves as vehicle for translating algorithms and engineering infrastructure directly |
| − | engineering infrastructure directly into the hands | + | into the hands biological scientists. Primary effort goes into the 3D Slicer software, |
| − | biological scientists. Primary effort goes into the 3D Slicer software, | ||
the reference implementation of NA-MIC Kit technologies. In close | the reference implementation of NA-MIC Kit technologies. In close | ||
collaboration with our Engineering Core colleagues and cooperative | collaboration with our Engineering Core colleagues and cooperative | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
The 3D Slicer platform has been completely reworked through the joint | The 3D Slicer platform has been completely reworked through the joint | ||
| − | efforts of the NA-MIC community and the | + | efforts of the NA-MIC community and the |
[http://nac.spl.harvard.edu NAC], [http://www.ncigt.org NCIGT], and | [http://nac.spl.harvard.edu NAC], [http://www.ncigt.org NCIGT], and | ||
other cooperative grants that leverage the common infrastructure. | other cooperative grants that leverage the common infrastructure. | ||
Isomics is pleased to serve as the chief architects and major | Isomics is pleased to serve as the chief architects and major | ||
| − | + | implementers of this package. In this role, we help coordinate group | |
development activities to ensure interoperability and cross platform | development activities to ensure interoperability and cross platform | ||
support. [http://slicer.org More...] | support. [http://slicer.org More...] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
access to software tools. This productive collaboration is resulting in | access to software tools. This productive collaboration is resulting in | ||
the development of a | the development of a | ||
| − | [ | + | [https://www.slicer.org/wiki/Slicer3:Loadable_Modules |
loadable module infrastructure] for the Slicer3 platform through which | loadable module infrastructure] for the Slicer3 platform through which | ||
dedicated neuroimaging modules can have a project-focused web presence | dedicated neuroimaging modules can have a project-focused web presence | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
| | | | | | ||
| − | == [[NA-MIC_NCBC_Collaboration:Automated_FE_Mesh_Development | Finite | + | == [[NA-MIC_NCBC_Collaboration:Automated_FE_Mesh_Development | Finite Element Meshing from Image Segmentations]] == |
| − | Element Meshing from Image Segmentations]] == | ||
Funded through the NCBC collaboration grant mechanism, this projects | Funded through the NCBC collaboration grant mechanism, this projects | ||
| Line 64: | Line 63: | ||
quality finite element meshes to support biomechanical research. | quality finite element meshes to support biomechanical research. | ||
[[NA-MIC_NCBC_Collaboration:Automated_FE_Mesh_Development | More...]] | [[NA-MIC_NCBC_Collaboration:Automated_FE_Mesh_Development | More...]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | [[Image:Virtual Colonoscopy Auto Detection - Yoshida.png|100px]] | ||
| + | | | | ||
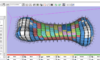
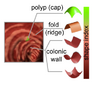
| + | ==[[NA-MIC_NCBC_Collaboration:NA-MIC virtual colonoscopy|PAR-07-249: R01CA131718 NA-MIC Virtual Colonoscopy]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This project is funded under an NCBC collaboration grant to PI Hiroyuki Yoshida. The goal of this project is to [[NA-MIC_NCBC_Collaboration:NA-MIC virtual colonoscopy|More...]] | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
| Line 81: | Line 89: | ||
areas. These include pediatric cardiology research with Boston | areas. These include pediatric cardiology research with Boston | ||
Children's Hospital and University of Utah; radiation treatment planning | Children's Hospital and University of Utah; radiation treatment planning | ||
| − | research with | + | research with Massachusetts General Hospital; vascular modeling with the |
Mario Negri Institute; whole-body segmentation with Washington | Mario Negri Institute; whole-body segmentation with Washington | ||
University, St. Louis, and Stanford University; surgical robotics with | University, St. Louis, and Stanford University; surgical robotics with | ||
| Line 90: | Line 98: | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Isomics Personnel Activities == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Architects, active contributors and organizers for the 3D Slicer version 3 project. | ||
| + | * Participants in many Project Week activities related to image analysis, software engineering, user interface, and other topics. | ||
| + | * Presenters at scientific conferences on medical image analysis. | ||
| + | * Instructors at NA-MIC training and dissemination events. | ||
| + | * Active participants in NA-MIC organizational events. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:30, 11 April 2023
Home < Engineering:IsomicsBack to NA-MIC Engineering
Overview of Isomics Projects (PI: Steve Pieper)
At Isomics, we are responsible for the end-user application software that serves as vehicle for translating algorithms and engineering infrastructure directly into the hands biological scientists. Primary effort goes into the 3D Slicer software, the reference implementation of NA-MIC Kit technologies. In close collaboration with our Engineering Core colleagues and cooperative development with other NIH funded efforts, we work to provide usable, documented, and efficient application software that enables world class science.
Isomics Projects

|
3D SlicerThe 3D Slicer platform has been completely reworked through the joint efforts of the NA-MIC community and the NAC, NCIGT, and other cooperative grants that leverage the common infrastructure. Isomics is pleased to serve as the chief architects and major implementers of this package. In this role, we help coordinate group development activities to ensure interoperability and cross platform support. More... |
The Neuroimaging Tools and Resources Clearinghouse (NITRC)Isomics has taken the lead in NA-MIC interactions with our sister effort at NITRC. Where NA-MIC provides algorithms and software infrastructure, NITRC is dedicated to hosting an active community of neuroimaging researchers and supporting them with information and well structured access to software tools. This productive collaboration is resulting in the development of a [https://www.slicer.org/wiki/Slicer3:Loadable_Modules loadable module infrastructure] for the Slicer3 platform through which dedicated neuroimaging modules can have a project-focused web presence using NITRC, while integrating tightly with the Slicer3 application for usability. More... | |
|
Finite Element Meshing from Image SegmentationsFunded through the NCBC collaboration grant mechanism, this projects brings together researchers at Isomics and University of Iowa to create a fully open source pipeline to go from CT scanned cadaver hands to high quality finite element meshes to support biomechanical research. More...
|
|
PAR-07-249: R01CA131718 NA-MIC Virtual ColonoscopyThis project is funded under an NCBC collaboration grant to PI Hiroyuki Yoshida. The goal of this project is to More... |
|
Outreach and Collaboration EffortsAs Co-PI for the NA-MIC Dissemination Core in addition to his engineering role, Dr. Pieper serves as the engineering contact for many external contacts with groups that may benefit from NA-MIC technology development. Productive technical interchanges are actively underway with a diverse group of sites and in an wide variety of application areas. These include pediatric cardiology research with Boston Children's Hospital and University of Utah; radiation treatment planning research with Massachusetts General Hospital; vascular modeling with the Mario Negri Institute; whole-body segmentation with Washington University, St. Louis, and Stanford University; surgical robotics with Johns Hopkins University and the Japanese government; microscopy image analysis with UCSD and Ohio State; cardiovascular image informatics with Johns Hopkins University; biomechanical simulation of blast dynamics with MIT and the US Army. Isomics Personnel Activities
|
