Difference between revisions of "EM Segmentation For Orthopaedic Applications"
From NAMIC Wiki
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
* We have utilized the Slicer2.7 EM Segmentation Module for segmentation of the phalanx bones | * We have utilized the Slicer2.7 EM Segmentation Module for segmentation of the phalanx bones | ||
| − | *# Registration was performed outside of | + | *# Registration was performed outside of Slicer using ITK registration algorithms that are available in the IaFeMesh software. This includes Thin plate spline, B-Spline and rigid registration algorithms. |
*# Probability map information was created from a single subject used as the atlas image and filtered using a Gaussian filter. | *# Probability map information was created from a single subject used as the atlas image and filtered using a Gaussian filter. | ||
| − | * Initial evaluation has been | + | * Initial evaluation has been performed |
| − | * Work is underway to develop a Slicer2.7 tutorial for this segmentation ([[Image: | + | **Reliability assessed on fourteen specimens that also had the index finger segmented, and two specimens that had the index, middle, ring and little fingers manually segmented |
| + | **Validation assessed using the laser scanning of the index finger (proximal, middle, and distal) phalanx bones in five specimens | ||
| + | * Work is underway to develop a Slicer2.7 tutorial for this segmentation ([[Image:Draft_EM_Segment_Tutorial_9_12.pdf|Draft Copy]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Results:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| + | |+Relative Overlap with Manual Rater | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Finger !! Phalanx Segment !! Average Relative Overlap | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Index (14 subjects) | ||
| + | | Proximal || 0.87 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Medial || 0.80 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Distal || 0.70 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Middle (2 subjects) | ||
| + | | Proximal || 0.79 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Medial || 0.77 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Distal || 0.71 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Ring (2 subjects) | ||
| + | | Proximal || 0.76 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Medial || 0.82 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Distal || 0.80 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Pinky (2 subjects) | ||
| + | | Proximal || 0.70 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Medial || 0.73 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | | Distal || 0.72 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Example of Validation Results is shown below in the figures | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
'''To Do:''' | '''To Do:''' | ||
| − | + | *Update the the tutorial to support the Slicer3 Workflow | |
| − | * Update the the tutorial to support the Slicer3 Workflow | + | **Tutorial will be developed by Austin Ramme - In progress |
| − | * | + | *Slicer3 Segmentation applied to the femur |
| + | **Using BRAINSFit for mapping of probability information to the subject images | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Manuscript:''' | ||
| + | *Ramme AJ, Devries N, Kallemyn NA, Magnotta VA, Grosland NM. [http://www.springerlink.com/content/h972u63630311g78/ Semi-automated Phalanx Bone Segmentation Using the Expectation Maximization Algorithm]. J Digit Imaging. 2008. | ||
| + | |||
'''Key Investigators:''' | '''Key Investigators:''' | ||
| Line 21: | Line 78: | ||
'''Links:''' | '''Links:''' | ||
| − | *[http://www.ccad.uiowa.edu/mimx Musculoskeletal Imaging, | + | *[http://www.ccad.uiowa.edu/mimx Musculoskeletal Imaging, Modeling and Experimentation (MIMX)] |
| Line 28: | Line 85: | ||
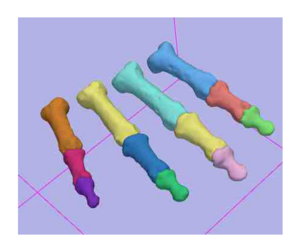
[[Image:EM-Segment-Phalanx.png|left|thumb|300px|Surface models from EM Segmentation generated via Slicer3]] | [[Image:EM-Segment-Phalanx.png|left|thumb|300px|Surface models from EM Segmentation generated via Slicer3]] | ||
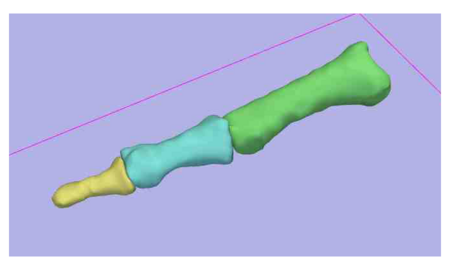
| − | [[Image:EM-Segment-Proximal.png|left|thumb| | + | [[Image:EM-Segment-Proximal.png|left|thumb|450px|Results of the EM Segmentation for the Proximal Pahalanx]] |
| + | |||
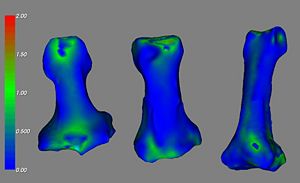
| + | [[Image:EMSegment-Phalanx-DistanceMap.jpg|left|thumb|300px|Validation of EM Segmentation for the phalanx bones of the hand. Distance of automated segmentation versus physical laser surface scanning]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:30, 20 January 2010
Home < EM Segmentation For Orthopaedic ApplicationsObjective:
- To utilize the Slicer3 Expectation Maximization Algorithm for segmentation of the phalanx bones of the hand.
Progress:
- We have utilized the Slicer2.7 EM Segmentation Module for segmentation of the phalanx bones
- Registration was performed outside of Slicer using ITK registration algorithms that are available in the IaFeMesh software. This includes Thin plate spline, B-Spline and rigid registration algorithms.
- Probability map information was created from a single subject used as the atlas image and filtered using a Gaussian filter.
- Initial evaluation has been performed
- Reliability assessed on fourteen specimens that also had the index finger segmented, and two specimens that had the index, middle, ring and little fingers manually segmented
- Validation assessed using the laser scanning of the index finger (proximal, middle, and distal) phalanx bones in five specimens
- Work is underway to develop a Slicer2.7 tutorial for this segmentation (File:Draft EM Segment Tutorial 9 12.pdf)
Results:
| Finger | Phalanx Segment | Average Relative Overlap |
|---|---|---|
| Index (14 subjects) | Proximal | 0.87 |
| Medial | 0.80 | |
| Distal | 0.70 | |
| Middle (2 subjects) | Proximal | 0.79 |
| Medial | 0.77 | |
| Distal | 0.71 | |
| Ring (2 subjects) | Proximal | 0.76 |
| Medial | 0.82 | |
| Distal | 0.80 | |
| Pinky (2 subjects) | Proximal | 0.70 |
| Medial | 0.73 | |
| Distal | 0.72 |
- Example of Validation Results is shown below in the figures
To Do:
- Update the the tutorial to support the Slicer3 Workflow
- Tutorial will be developed by Austin Ramme - In progress
- Slicer3 Segmentation applied to the femur
- Using BRAINSFit for mapping of probability information to the subject images
Manuscript:
- Ramme AJ, Devries N, Kallemyn NA, Magnotta VA, Grosland NM. Semi-automated Phalanx Bone Segmentation Using the Expectation Maximization Algorithm. J Digit Imaging. 2008.
Key Investigators:
- Iowa: Austin Ramme, Nicole Grosland, and Vincent Magnotta
Links:
Figures: