Difference between revisions of "2011 Summer Project Week Segmentation TBI"
(Created page with '__NOTOC__ <gallery> Image:PW-MIT2011.png|Projects List Image:notfound.png|Interesting picture to be added... </gallery> '''Full Title of P…') |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:PW-MIT2011.png|[[2011_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | Image:PW-MIT2011.png|[[2011_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | ||
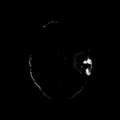
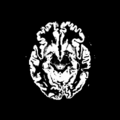
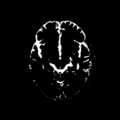
| − | Image: | + | Image:ain1_69-tile_baseline.png | Result of supervised segmentation - acute images |
| + | Image:ain1_69-tile_followup.png | Result of supervised segmentation - follow-up images | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
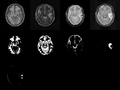
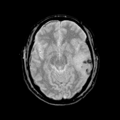
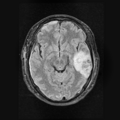
| + | <gallery widths=120px heights=120px perrow=4 caption="Figure 1. Acute and follow-up images"> | ||
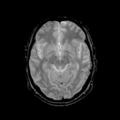
| + | File: Ori_base_Channel1_Slice_69.png| T1 - acute | ||
| + | File: Ori_base_Channel2_Slice_69.png| T2 - acute | ||
| + | File: Ori_base_Channel3_Slice_69.png| GRE - acute | ||
| + | File: Ori_base_Channel4_Slice_69.png| Flair - acute | ||
| + | |||
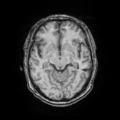
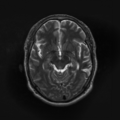
| + | File: Ori_follow_Channel1_Slice_69.png | T1 - follow-up | ||
| + | File: Ori_follow_Channel2_Slice_69.png | T2 - follow-up | ||
| + | File: Ori_follow_Channel3_Slice_69.png | GRE - follow-up | ||
| + | File: Ori_follow_Channel4_Slice_69.png | Flair - follow-up | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
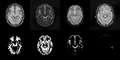
| + | <gallery widths=120px heights=120px perrow=5 caption="Figure 2. Supervised segmentation"> | ||
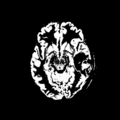
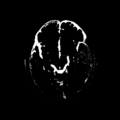
| + | File: Posterior_base_1_class.png | Posterior of WM - acute | ||
| + | File: Posterior_base_2_class.png | Posterior of GM - acute | ||
| + | File: Posterior_base_3_class.png | Posterior of CSF - acute | ||
| + | File: Posterior_base_4_class.png | Posterior of Non-hemorrhagic lesion - acute | ||
| + | File: Posterior_base_5_class.png | Posterior of Hemorrhagic lesion - acute | ||
| + | |||
| + | File: Posterior_follow_class_1.png | Posterior of WM - follow-up | ||
| + | File: Posterior_follow_class_2.png | Posterior of GM - follow-up | ||
| + | File: Posterior_follow_class_3.png | Posterior of CSF - follow-up | ||
| + | File: Posterior_follow_class_4.png | Posterior of lesion - follow-up | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
'''Full Title of Project''' | '''Full Title of Project''' | ||
| Line 17: | Line 47: | ||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
| − | Traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults. | + | Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a driving biological problem (DBP) in NA-MIC. It occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults. |
| + | |||
| + | We're working on the supervised segmentation and atlas optimization of longitudinal TBI data. | ||
On anatomical MRI scans, to quantitatively analyze the cortical thickness, white matter changes, we need to have a good segmentation on TBI images. However, for TBI data, standard automated image analysis methods are not robust with respect to the TBI-related changes in image contrast, changes in brain shape, cranial fractures, white matter fiber alterations, and other signatures of head injury. | On anatomical MRI scans, to quantitatively analyze the cortical thickness, white matter changes, we need to have a good segmentation on TBI images. However, for TBI data, standard automated image analysis methods are not robust with respect to the TBI-related changes in image contrast, changes in brain shape, cranial fractures, white matter fiber alterations, and other signatures of head injury. | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 60: | ||
<h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | <h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | ||
| − | + | Our plan for the project week: | |
| − | + | * Test our preliminary code | |
| − | + | * Discuss with collaborators and try to refine the algorithm | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 70: | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| − | + | * We applied the preliminary algorithm to current data and fixed some bugs in the code. | |
| + | * Our collaborators helped us to validate our current results of supervised segmentation. We got some comments and feedback from our collaborators, which are very important for us to improve the current algorithm. | ||
| + | * After discussing with Andrei and Micah about the TBI data, we know more clearly about what the clinicians need. | ||
| + | |||
Latest revision as of 14:30, 24 June 2011
Home < 2011 Summer Project Week Segmentation TBI- Figure 1. Acute and follow-up images
- Figure 2. Supervised segmentation
Full Title of Project
Key Investigators
- Utah: Bo Wang, Marcel Prastawa, Guido Gerig
- UCLA: Jack Van Horn, Andrei Irimia, Micah Chambers
Objective
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a driving biological problem (DBP) in NA-MIC. It occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults.
We're working on the supervised segmentation and atlas optimization of longitudinal TBI data.
On anatomical MRI scans, to quantitatively analyze the cortical thickness, white matter changes, we need to have a good segmentation on TBI images. However, for TBI data, standard automated image analysis methods are not robust with respect to the TBI-related changes in image contrast, changes in brain shape, cranial fractures, white matter fiber alterations, and other signatures of head injury.
Approach, Plan
Our plan for the project week:
- Test our preliminary code
- Discuss with collaborators and try to refine the algorithm
Progress
- We applied the preliminary algorithm to current data and fixed some bugs in the code.
- Our collaborators helped us to validate our current results of supervised segmentation. We got some comments and feedback from our collaborators, which are very important for us to improve the current algorithm.
- After discussing with Andrei and Micah about the TBI data, we know more clearly about what the clinicians need.