Difference between revisions of "Multimodality Image Registration for TBI"
From NAMIC Wiki
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Image:PW-MIT2011.png|[[2011_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | Image:PW-MIT2011.png|[[2011_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | ||
Image::BRAINSCutFigure.png|BRAINSCut Result Example | Image::BRAINSCutFigure.png|BRAINSCut Result Example | ||
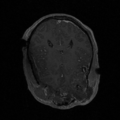
| − | Image: | + | Image:t1e1.png|T1 exam1 |
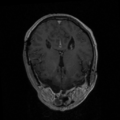
| − | Image: | + | Image:t1e2.png|T1 exam2 |
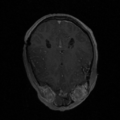
| − | Image: | + | Image:t1e1deformedM.png|T1 deformed |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Key Investigators== | ==Key Investigators== | ||
* Georgia Tech: Yifei Lou and Allen Tannenbaum | * Georgia Tech: Yifei Lou and Allen Tannenbaum | ||
| − | * Micah Chambers | + | * UCLA: Micah Chambers, Andrei Irimia |
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
* Understanding brain injury using (multimodal) deformable image registration | * Understanding brain injury using (multimodal) deformable image registration | ||
* Robust registrations inspire of topological changes (enforcing zero flow?) | * Robust registrations inspire of topological changes (enforcing zero flow?) | ||
| + | * The algorithm is based on a viscous fluid model, which can handle larger deformable as compared to the B-spline type of methods | ||
* CUDA-based implementation, which takes 1 min for 256x256x60 | * CUDA-based implementation, which takes 1 min for 256x256x60 | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
* Integration into Slicer3 Module | * Integration into Slicer3 Module | ||
| − | * | + | * Learn more about TBI and our data set from Micah (UCLA NA-MIC TBI DBP team member) |
| − | * Validate algorithm on | + | * Validate algorithm on additional TBI datasets from UCLA |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 41: | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Learn more about TBI and ITK/Slicer | ||
| + | * Demonstrate the efficiency of my algorithm on TBI data | ||
| + | * Its failure in one registration case suggests us dividing 12 modalities into 2 subgroups and co-register within group | ||
| + | * plan to write a paper and integrate my algorithm into ITK/Slicer | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<!-- Fill this out before Friday's summary presentations - list what you did and how well it worked. --> | <!-- Fill this out before Friday's summary presentations - list what you did and how well it worked. --> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:28, 24 June 2011
Home < Multimodality Image Registration for TBIMultimodality Image Registration for Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Key Investigators
- Georgia Tech: Yifei Lou and Allen Tannenbaum
- UCLA: Micah Chambers, Andrei Irimia
Objective
- Understanding brain injury using (multimodal) deformable image registration
- Robust registrations inspire of topological changes (enforcing zero flow?)
- The algorithm is based on a viscous fluid model, which can handle larger deformable as compared to the B-spline type of methods
- CUDA-based implementation, which takes 1 min for 256x256x60
Approach, Plan
- Integration into Slicer3 Module
- Learn more about TBI and our data set from Micah (UCLA NA-MIC TBI DBP team member)
- Validate algorithm on additional TBI datasets from UCLA
Progress
- Learn more about TBI and ITK/Slicer
- Demonstrate the efficiency of my algorithm on TBI data
- Its failure in one registration case suggests us dividing 12 modalities into 2 subgroups and co-register within group
- plan to write a paper and integrate my algorithm into ITK/Slicer
References
1 Yifei Lou and Allen Tannenbaum. Multimodal Deformable Image Registration via the Bhattacharyya Distance. Submitted to IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011
2 Yifei Lou, Xun Jia, Xuejun Gu and Allen Tannenbaum. A GPU-based Implementation of Multimodal Deformable Image Registration Based on Mutual Information or Bhattacharyya Distance. Insight Journal, 2011. [[1]]
Delivery Mechanism
This work will be delivered to the NAMIC Kit as a
- NITRIC distribution
- Slicer Module
- Built-in: NO
- Extension -- commandline: NO
- Extension -- loadable: NO