Difference between revisions of "2012 Summer Project Week:DTIRegistration"
(Created page with '__NOTOC__ <gallery> Image:PW-MIT2012.png|Projects List Image:genuFAp.jpg|Scatter plot of the original FA data through the genu of the corpus…') |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:PW-MIT2012.png|[[2012_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | Image:PW-MIT2012.png|[[2012_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | ||
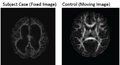
| − | Image: | + | Image:Subject Control1.png|EnlargedLV Reg |
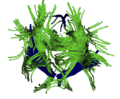
| − | Image: | + | Image:View ant before.png|Fiber Geometry Registration Before. |
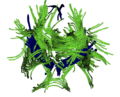
| + | Image:View ant after.png|Fiber Geometry Registration After. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
| − | We are developing methods for fiber feature map based landmark initialization for highly deformable DTI registration. The goal is to register | + | We are developing methods for fiber feature map based landmark initialization for highly deformable DTI registration. The goal is to register diffusion tensor images with large pathological variations as compared to normal controls with the use of a feature map based on white matter (WM) fiber tracts. Our final objective is to have an accurate registration to enable analysis of properties such as fractional anisotropy even on cases with large pathological variations. |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
<h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | <h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | ||
| − | Our approach is to develop a novel feature map that represents | + | Our approach is to develop a novel feature map that represents fiber geometry and is robust against variations in WM fiber tract integrity. From this novel feature map, we plan to develop |
| − | landmark correspondence using a 3D point correspondence algorithm. This correspondence forms the basis of a deformation | + | landmark correspondence using a 3D point correspondence algorithm. This correspondence forms the basis of a deformation field computed using Gaussian radial basis functions(RBF) or a registration defined by landmarks and intensity. |
Our plan for the project week is to first try to improve our current feature map by taking into consideration the features most useful to develop strong correspondence. Having determined strong correspondence points, we would look into methods that would best give us a strong initialization field, so that any scalar registration and DTI registration can then be used for these highly deformable cases. | Our plan for the project week is to first try to improve our current feature map by taking into consideration the features most useful to develop strong correspondence. Having determined strong correspondence points, we would look into methods that would best give us a strong initialization field, so that any scalar registration and DTI registration can then be used for these highly deformable cases. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<div style="width: 97%; float: left;"> | <div style="width: 97%; float: left;"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Data== | ||
| + | * [http://wiki.na-mic.org/Wiki/index.php/File:Tractography.zip Full brain tractography of normal control and Krabbe vtk files] | ||
| + | * [http://wiki.na-mic.org/Wiki/index.php/File:11067_012511_FullBrainTractography_New.vtk.zip Full brain tractography of Krabbe subject regenerated vtk files] | ||
| + | * [[File:Test-output-test2.zip]] test output of tractography registration | ||
| + | * [[File:Neo-0011-2-1-1year dwi 35 all DTI AffTrans deformed wFA Y01 OutputFiberBundle.vtk.zip]] Fiber bundle of intermediate output. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Updates== | ||
| + | Discussed and initial work on different methods to obtain registration: | ||
| + | * Geometric Metamorphosis - worked on implementation of Matlab code. | ||
| + | * Fiber geometry based registration with Lauren Donnell. Figures before and after registration attached on top of page. | ||
| + | * Feature Map improvements: | ||
| + | - Crossing Fibers. | ||
| + | - Fiber Density. | ||
| + | - Weighting Function. | ||
| + | * TumorSim. | ||
==Delivery Mechanism== | ==Delivery Mechanism== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 69: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
1. Fornefett, M., Rohr, K., Stiehl, H.S.: Elastic registration of medical images using radial basis functions with compact support. Proc. Computer Vison and Pattern Recognition (1999) 402407 | 1. Fornefett, M., Rohr, K., Stiehl, H.S.: Elastic registration of medical images using radial basis functions with compact support. Proc. Computer Vison and Pattern Recognition (1999) 402407 | ||
| − | 2. Escolar, M., Poe, M., Smith, J., Gilmore, J., Kurtzberg, J., Lin, W., Styner, M.: | + | 2. Escolar, M., Poe, M., Smith, J., Gilmore, J., Kurtzberg, J., Lin, W., Styner, M.: Diffusion tensor imaging detects abnormalities in the corticospinal tracts of neonates with infantile krabbe disease. American Journal of Neuroradiology 30(5) (May 2009) 1017-1021. |
3. Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. IJCV 60(2) (2004) 91-110. | 3. Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. IJCV 60(2) (2004) 91-110. | ||
| − | 4. Allaire, S., Kim, J., Breen, S., | + | 4. Allaire, S., Kim, J., Breen, S., Jaray, D., Pekar, V.: Full orientation invariance and improved feature selectivity of 3d sift with application to medical image analysis. In: MMBIA. (2008) |
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:00, 22 June 2012
Home < 2012 Summer Project Week:DTIRegistrationContents
Key Investigators
- UNC: Aditya Gupta, Martin Styner
- MIT: Matthew Toes
Objective
We are developing methods for fiber feature map based landmark initialization for highly deformable DTI registration. The goal is to register diffusion tensor images with large pathological variations as compared to normal controls with the use of a feature map based on white matter (WM) fiber tracts. Our final objective is to have an accurate registration to enable analysis of properties such as fractional anisotropy even on cases with large pathological variations.
Approach, Plan
Our approach is to develop a novel feature map that represents fiber geometry and is robust against variations in WM fiber tract integrity. From this novel feature map, we plan to develop landmark correspondence using a 3D point correspondence algorithm. This correspondence forms the basis of a deformation field computed using Gaussian radial basis functions(RBF) or a registration defined by landmarks and intensity.
Our plan for the project week is to first try to improve our current feature map by taking into consideration the features most useful to develop strong correspondence. Having determined strong correspondence points, we would look into methods that would best give us a strong initialization field, so that any scalar registration and DTI registration can then be used for these highly deformable cases.
Progress
We have developed a novel feature map that is partially immune to WM fiber tract integrity. The landmarks from this feature map used with gaussian radial basis function gives us an initial vector field which when used with demons gives us a good registration. But there is need for a more robust and more accurate method of deriving landmarks and generating a strong initialization field.
Data
- Full brain tractography of normal control and Krabbe vtk files
- Full brain tractography of Krabbe subject regenerated vtk files
- File:Test-output-test2.zip test output of tractography registration
- File:Neo-0011-2-1-1year dwi 35 all DTI AffTrans deformed wFA Y01 OutputFiberBundle.vtk.zip Fiber bundle of intermediate output.
Updates
Discussed and initial work on different methods to obtain registration:
- Geometric Metamorphosis - worked on implementation of Matlab code.
- Fiber geometry based registration with Lauren Donnell. Figures before and after registration attached on top of page.
- Feature Map improvements:
- Crossing Fibers. - Fiber Density. - Weighting Function.
- TumorSim.
Delivery Mechanism
This work will be delivered to the NA-MIC Kit as a (please select the appropriate options by noting YES against them below)
- ITK Module - YES
- Slicer Module - YES
- Built-in
- Extension -- commandline - YES
- Extension -- loadable
- Other (Please specify)
References
1. Fornefett, M., Rohr, K., Stiehl, H.S.: Elastic registration of medical images using radial basis functions with compact support. Proc. Computer Vison and Pattern Recognition (1999) 402407 2. Escolar, M., Poe, M., Smith, J., Gilmore, J., Kurtzberg, J., Lin, W., Styner, M.: Diffusion tensor imaging detects abnormalities in the corticospinal tracts of neonates with infantile krabbe disease. American Journal of Neuroradiology 30(5) (May 2009) 1017-1021. 3. Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. IJCV 60(2) (2004) 91-110. 4. Allaire, S., Kim, J., Breen, S., Jaray, D., Pekar, V.: Full orientation invariance and improved feature selectivity of 3d sift with application to medical image analysis. In: MMBIA. (2008)