Difference between revisions of "2014 Summer Project Week:Stroke-SuperResolution"
From NAMIC Wiki
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:PW-MIT2014.png|[[2014_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | Image:PW-MIT2014.png|[[2014_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | ||
| + | Image:WMH_T1.png|Clinical Stroke Image | ||
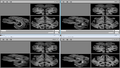
Image:STROKE_SR1.png|Super-Resolution initial results -- top-left is a 'real' image, from which we simulate a 1x1x7mm clinical image. The bottom images are state of the art interpolations. The top right is our current result. | Image:STROKE_SR1.png|Super-Resolution initial results -- top-left is a 'real' image, from which we simulate a 1x1x7mm clinical image. The bottom images are state of the art interpolations. The top right is our current result. | ||
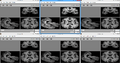
| + | Image:STROKE_SR2.png|Super-Resolution results on Thursday evening -- top-left is a 'real' image, from which we simulate a 1x1x7mm clinical image (top-center). The bottom row are all our results, with slight variations. | ||
| + | Image:STROKE_SR3.png| Top: Original, downsampled(input); Bottom results: NLM, us (before), us (now) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
==Project Description== | ==Project Description== | ||
<div style="margin: 20px;"> | <div style="margin: 20px;"> | ||
| − | To improve results for | + | Due to the low quality of clinical images (often with many artifacts, 7mm thick slices, etc), most standard algorithms, such as those for registration, segmentation, analysis, will fail. To improve results for large datasets of clinical-quality data, we are investigating super-resolution methods. Here, we are using a patch-based approach with MRF priors and utilizing only the current dataset, without an external training dataset. |
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
<div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | <div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| − | * | + | * Several improvements (i.e. bug fixes :) ) as well as an implementation of scale-space has been done |
| + | * Changes helped significantly on simulated data. See result image. | ||
| + | * Trying to apply algorithm to new datasets: [http://slicer.kitware.com/midas3/folder/2182 Sample prostate MRI dataset to evaluate applicability] (see 3-SAG, 4-COR and 5-AX series of the same subject/prostate in sagittal coronal and axial planes) | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:40, 27 June 2014
Home < 2014 Summer Project Week:Stroke-SuperResolutionKey Investigators
- Adrian Dalca, Ramesh Sridharan, Polina Golland, MIT
Project Description
Due to the low quality of clinical images (often with many artifacts, 7mm thick slices, etc), most standard algorithms, such as those for registration, segmentation, analysis, will fail. To improve results for large datasets of clinical-quality data, we are investigating super-resolution methods. Here, we are using a patch-based approach with MRF priors and utilizing only the current dataset, without an external training dataset.
Objective
- We will investigate/implement a scale-space MRF inference based on patch search results.
Approach, Plan
- We are developing a patch library in MATLAB, and need to apply it in a scale-space framework to the T2-FLAIR dataset.
Progress
- Several improvements (i.e. bug fixes :) ) as well as an implementation of scale-space has been done
- Changes helped significantly on simulated data. See result image.
- Trying to apply algorithm to new datasets: Sample prostate MRI dataset to evaluate applicability (see 3-SAG, 4-COR and 5-AX series of the same subject/prostate in sagittal coronal and axial planes)