Difference between revisions of "2016 Winter Project Week/Projects/DSCAnalysis"
Stevedaxiao (talk | contribs) |
Stevedaxiao (talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
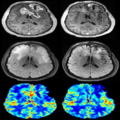
Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC) MRI imaging is an important functional imaging method that enables quantitative assessment of tissue hemodynamic patterns. Abnormality of blood flow, volume and permeability is frequently observed during tumor growth, and characterization of these perfusion attributes has become clinically important for both diagnosis and therapy planning. In the context of glial neoplasms, perfusion characteristics have been shown to correlate with tumor type and grade and hence influence treatment decisions. | Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC) MRI imaging is an important functional imaging method that enables quantitative assessment of tissue hemodynamic patterns. Abnormality of blood flow, volume and permeability is frequently observed during tumor growth, and characterization of these perfusion attributes has become clinically important for both diagnosis and therapy planning. In the context of glial neoplasms, perfusion characteristics have been shown to correlate with tumor type and grade and hence influence treatment decisions. | ||
| − | DSC MRI imaging is based on the principle that flow of a paramagnetic contrast agent through a capillary bed will transiently change the magnetic susceptibility of the given tissue. Decreased signal intensity on spin-echo or gradient-echo images after the first pass of the contrast agent, frequently described as susceptibility-induced T2* shortening, is the result of this temporal change in magnetic susceptibility. This signal time curve is then converted into a concentration time curve, and use of tracer kinetic analysis various hemodynamic variables, such as cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow, and mean transit time, as well as metrics that address vessel leakage may be estimated. Combined, these metrics enable microvascular imaging, providing a visual correlate of blood flow, volume, and vessel permeability. | + | DSC MRI imaging is based on the principle that flow of a paramagnetic contrast agent through a capillary bed will transiently change the magnetic susceptibility of the given tissue. Decreased signal intensity on spin-echo or gradient-echo images after the first pass of the contrast agent, frequently described as susceptibility-induced T2* shortening, is the result of this temporal change in magnetic susceptibility. This signal time curve is then converted into a concentration time curve, and use of tracer kinetic analysis various hemodynamic variables, such as cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow, and mean transit time, as well as metrics that address vessel leakage may be estimated. Combined, these metrics enable microvascular imaging, providing a visual correlate of blood flow, volume, and vessel permeability. |
| + | [[File:DSC_GUI_New.png|300px|thumb|left|GUI of DSC Analysis Module]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSC_Framework_New.png|500px|thumb|left|Framework of DSC Analysis]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSC_Comparison.png|600px|thumb|left|Comparison with the Commercial Software]] | ||
| + | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! style="text-align: left; width:27%" | Objective | ! style="text-align: left; width:27%" | Objective | ||
| Line 36: | Line 40: | ||
| | | | ||
<!-- Progress and Next steps bullet points (fill out at the end of project week --> | <!-- Progress and Next steps bullet points (fill out at the end of project week --> | ||
| − | * | + | * Finalized the source code |
| + | * Finished the DSC analysis module packaging | ||
| + | * Moved repository to QIICR on Github | ||
| + | * Picked up few MGH GBM cases and ran commercial software for comparison | ||
| + | * Updated the Slicer wiki page for DSC analysis module (http://slicer.org/slicerWiki/index.php/Documentation/Nightly/Modules/DSC_MRI_Analysis) | ||
| + | * Released the module | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 45: | Line 54: | ||
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4208985/pdf/nihms596683.pdf Other method to investigate DSC MRI] | * [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4208985/pdf/nihms596683.pdf Other method to investigate DSC MRI] | ||
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16611779 Leakage correction for DSC MRI] | * [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16611779 Leakage correction for DSC MRI] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Source Code== | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/QIICR/DSC_Analysis Source code for analysis of DSC MRI] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:55, 7 January 2016
Home < 2016 Winter Project Week < Projects < DSCAnalysisKey Investigators
- Xiao Da (MGH)
- Yangming Ou (MGH)
- Andriy Fedorov (BWH)
- Steve Pieper (Isomics)
- Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer (MGH)
Project Description
Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC) MRI imaging is an important functional imaging method that enables quantitative assessment of tissue hemodynamic patterns. Abnormality of blood flow, volume and permeability is frequently observed during tumor growth, and characterization of these perfusion attributes has become clinically important for both diagnosis and therapy planning. In the context of glial neoplasms, perfusion characteristics have been shown to correlate with tumor type and grade and hence influence treatment decisions.
DSC MRI imaging is based on the principle that flow of a paramagnetic contrast agent through a capillary bed will transiently change the magnetic susceptibility of the given tissue. Decreased signal intensity on spin-echo or gradient-echo images after the first pass of the contrast agent, frequently described as susceptibility-induced T2* shortening, is the result of this temporal change in magnetic susceptibility. This signal time curve is then converted into a concentration time curve, and use of tracer kinetic analysis various hemodynamic variables, such as cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow, and mean transit time, as well as metrics that address vessel leakage may be estimated. Combined, these metrics enable microvascular imaging, providing a visual correlate of blood flow, volume, and vessel permeability.
| Objective | Approach and Plan | Progress and Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Background and References
- Introduction of DSC MRI from Siemens
- Equations for conversion of signal to concentration for DSC
- Other method to investigate DSC MRI
- Leakage correction for DSC MRI