Difference between revisions of "Driving Biological Projects"
From NAMIC Wiki
m (Update from Wiki) |
m (1 revision imported: "pages" articles) |
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 23:53, 1 June 2017
Home < Driving Biological ProjectsDriving Biological Projects

|
| Overview |
To ensure that, at the end of the day, demonstrable healthcare improvements are achieved, Driving Biological Projects (DBPs) are selected to guide research development. The role of a NA-MIC DBP is to:
- define a clinical problem
- provide a clinical dataset (individual or population)
- collaborate with algorithms scientists to develop a solution
- work with software engineers to create end-to-end applications for clinical users
|
|
|
|
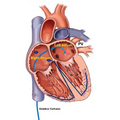
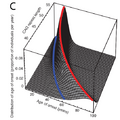
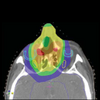
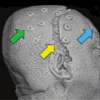
| Atrial Fibrillation | Huntington's Disease | Head and Neck Cancer | Traumatic Brain Injury |
| At the inception of NA-MIC, the focus of biological project development was centered on schizophrenia. Schizophrenia provided a rich resource of neuroimaging data and a pressing need for new imaging technologies to unlock the white matter regions of the brain. The DBPs contributing to this effort were based at Harvard Medical School, University of California at Irvine, Dartmouth College, Indiana University, and University of Toronto. In the ensuing years, the scope of project development expanded to include a broader range of diseases. Links are provided to disease-specific datasets, tutorials, software, representative peer review publications, and notes maintained by the individual DBPs on NA-MIC's interactive Wiki. | |||
|
|
|
|
| Schizophrenia | Lupus | Prostate Cancer | Autism |