Difference between revisions of "2008 Winter Project Week:IGT IGSTK Slicer"
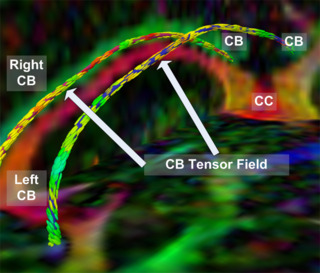
(New page: {| |thumb|320px|Return to [[2008_Winter_Project_Week ]] |valign="top"|thumb|320px|The Cingulum Bundle Anchor Tract |} __...) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<h1>Objective</h1> | <h1>Objective</h1> | ||
| − | + | The overall goal of this proposal is to develop and validate an integrated system based on open source software for improved visualization and probe placement during radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of liver tumors. While radiofrequency ablation is becoming an increasingly important treatment option for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and liver metastases, the procedure has several technical limitations. These limitations are mostly related to the difficulty of precisely placing the RFA needle to ablate the entire tumor and achieve adequate margins. In particular, larger tumors require multiple overlapping needle placements, which can be difficult to achieve. The specific aims of the project are to: 1) Develop an open source software architecture for a liver RFA planning/treatment workstation that builds on existing open source projects at the two collaborating institutions 2) Develop and evaluate semi-automatic segmentation techniques for the liver, liver vasculature, and liver tumors. These techniques will be integrated with a graphical user interface and the segmentation results will be evaluated by comparison with expert radiologists. 3) Based on the segmented liver data set, develop a path planning module for evaluating alternative paths to the liver tumor and incorporating multiple overlapping placements as needed. 4) Integrate the two capabilities developed above along with electromagnetic tracking of the RFA probe to provide a complete software environment for liver tumor planning, visualization, and execution. This software environment will merge ongoing work at Georgetown and Brigham and Women's Hospital in developing open source software for image-guided procedures. 5) Validate the clinical feasibility of the system in a swine animal model. Agar nodules will be created in the swine liver and the ability of the system to segment and provide path planning for these nodules will be assessed. The accuracy of the system will also be evaluated. This research is important in advancing the technology for treatment of liver cancer that presently can not be treated well with current available therapies. This technology would also enable a modern, individualized therapy, which relies on integration of high power computers and innovations in medical science. It would have a contribution to public health by developing liver cancer treatments without the need for more invasive surgeries. | |
| − | |||
| − | The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 27: | ||
====June 2007 Project Week==== | ====June 2007 Project Week==== | ||
| − | During | + | During the June 2007 Project Week, we designed communication framework for MRI-robot for Transperineum Prostate Brachytherapy (BRP Project/ PI: Dr. Clare Tempany), based on vtkIGTOpenTrackerStream. |
====Jan 2007 Project Half Week==== | ====Jan 2007 Project Half Week==== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 45: | Line 41: | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 21:07, 13 December 2007
Home < 2008 Winter Project Week:IGT IGSTK Slicer Return to 2008_Winter_Project_Week |
Key Investigators
- BWH: Nobuhiko Hata, Haiying Liu, Junichi Tokuda
Objective
The overall goal of this proposal is to develop and validate an integrated system based on open source software for improved visualization and probe placement during radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of liver tumors. While radiofrequency ablation is becoming an increasingly important treatment option for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and liver metastases, the procedure has several technical limitations. These limitations are mostly related to the difficulty of precisely placing the RFA needle to ablate the entire tumor and achieve adequate margins. In particular, larger tumors require multiple overlapping needle placements, which can be difficult to achieve. The specific aims of the project are to: 1) Develop an open source software architecture for a liver RFA planning/treatment workstation that builds on existing open source projects at the two collaborating institutions 2) Develop and evaluate semi-automatic segmentation techniques for the liver, liver vasculature, and liver tumors. These techniques will be integrated with a graphical user interface and the segmentation results will be evaluated by comparison with expert radiologists. 3) Based on the segmented liver data set, develop a path planning module for evaluating alternative paths to the liver tumor and incorporating multiple overlapping placements as needed. 4) Integrate the two capabilities developed above along with electromagnetic tracking of the RFA probe to provide a complete software environment for liver tumor planning, visualization, and execution. This software environment will merge ongoing work at Georgetown and Brigham and Women's Hospital in developing open source software for image-guided procedures. 5) Validate the clinical feasibility of the system in a swine animal model. Agar nodules will be created in the swine liver and the ability of the system to segment and provide path planning for these nodules will be assessed. The accuracy of the system will also be evaluated. This research is important in advancing the technology for treatment of liver cancer that presently can not be treated well with current available therapies. This technology would also enable a modern, individualized therapy, which relies on integration of high power computers and innovations in medical science. It would have a contribution to public health by developing liver cancer treatments without the need for more invasive surgeries.
Approach, Plan
Our approach is described by the references below. Our challenge is to build the ITK infrastructure (such as new ITK iterators) to support this algorithm. Our main purpose at the Project Week is to collaborate on new algorithms and clinical data to provide the best solutions for our DBP partners.
Progress
June 2007 Project Week
During the June 2007 Project Week, we designed communication framework for MRI-robot for Transperineum Prostate Brachytherapy (BRP Project/ PI: Dr. Clare Tempany), based on vtkIGTOpenTrackerStream.
Jan 2007 Project Half Week