Difference between revisions of "NA-MIC/Projects/Collaboration/SBIA UPenn"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|[[Image:ProjectWeek-2008.png|thumb|360px|Return to [[2008_Summer_Project_Week|Project Week Main Page]] ]] | |[[Image:ProjectWeek-2008.png|thumb|360px|Return to [[2008_Summer_Project_Week|Project Week Main Page]] ]] | ||
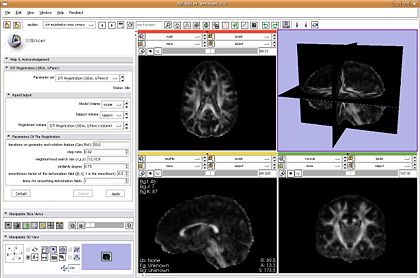
| − | |[[Image:DTIReg.JPG|thumb|420px| The | + | |[[Image:DTIReg.JPG|thumb|420px|The non-linear DTI registration plugin.]] |
|} | |} | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
Revision as of 15:19, 18 June 2008
Home < NA-MIC < Projects < Collaboration < SBIA UPenn Return to Project Week Main Page |
Key Investigators
- Ragini Verma, SBIA, UPenn <Ragini.Verma@uphs.upenn.edu>
- Christos Davatzikos <Christos.Davatzikos@uphs.upenn.edu>
- Yang Li <Yang.Li@uphs.upenn.edu>
- Luke Bloy <lbloy@seas.upenn.edu>
Objective
To incorporate into Slicer, processing and analysis methods for DTI and HARDI being developed at the Section of Biomedical Image Analysis (SBIA), UPenn [1]. The main components will be plugins for DTI registration and manifold-based statistics followed by methods for HARDI registration and statistics.
Approach, Plan
- DTI registration: has been developed in SBIA over a period of 2 years, mainly using in-house code (not in ITK). This will be incorporated as a plugin.
- DTI Statistics: SPM-like package for statistics on the full tensor. The proposed format is again a plugin as it is based on code already existing in SBIA in C, C++.
- HARDI registration: This is being developed in ITK, building on HARDI representation format currently under development
- HARDI statistics: being developed in ITK
Progress
- DTI Registration: plugin is ready and will be demonstrated
To do: Replace the affine registration component, help file, speed, version control
- Need help with:
1. General representation for registration in ITK
2. Code for Demons DTI registration for comparison
3. Visualization: tensor glyphs and ODFs
References
This work was supported in part by NIH grants .
- Link to SBIA web site:
- J. Yang, D. Shen, C. Davatzikos and R. Verma, Diffusion Tensor Image Registration Using Tensor Geometry and Orientation Features, in MICCAI 2008, New York.
- J. Yang, D. Shen, C. Davatzikos and R. Verma, Spatial Normalization of Diffusion Tensor Images Based on Anisotropic Segmentation, in SPIE Medical Imaging 2008, San Diego.
- R. Verma, P. Khurd, C. Davatzikos, On Analyzing Diffusion Tensor Images by Identifying Manifold Structure using Isomaps, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 772-778, Vol. 26, No. 6, 2007 (need access to IEEE explore to view papers)
- P. Khurd, R. Verma and C. Davatzikos, Kernel-based Manifold Learning for Statistical Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Images, Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), 581-593, Vol. 4584, 2007