Difference between revisions of "2009 Winter Project Week Slicer VMTK"
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | The | + | The current version of the module which can<br> |
| − | + | be seen as an example to use the latest<br> | |
| − | + | Slicer-Python interaction techniques and<br> | |
| − | + | callbacks is always available at the following<br> | |
| + | NITRC repository: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/slicervmtklvlst/ | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 22:23, 2 March 2009
Home < 2009 Winter Project Week Slicer VMTK Return to Project Week Main Page |
Key Investigators
- Daniel Haehn (Student of Medical Informatics, University of Heidelberg)
- Luca Antiga (Medical Imaging Unit, Biomedical Engineering Department, Mario Negri Institute)
- Ron
Objective
The Vascular Modeling Toolkit (VMTK) is a collection of libraries and tools for 3D reconstruction, geometric analysis, mesh generation and surface data analysis for image-based modeling of blood vessels. It should be very interesting to offer such techniques in Slicer3.
Approach, Plan
VMTK provides Python pipeable scripts (PypeS) to connect various commands and/or scripts. An automated mechanism to generate non-interactive Slicer modules has already been implemented.
The plan is to write a python scripted module for Slicer3 that connects to VMTK pipes and provides the same user interaction style found in VMTK. This is necessary for interactive segmentation.
In addition, a collection of non-interactive modules relevant to segmentation and characterization of vascular networks will be generated.
Finally, Slicer-vmtk packaging issues will be tackled.
Progress
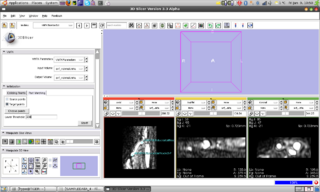
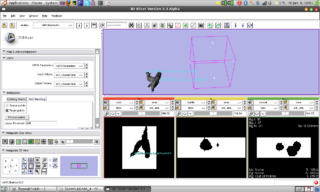
An interactive python module
skeleton has been created. Through
a workaround the VMTK classes are
already accessible in Slicer through a
compiled library. Since
now techniques like observers and
callbacks are available in Slicer-Python
we could add the first algorithm of VMTK
to slicer: Fast Marching Initialization.
The current version of the module which can
be seen as an example to use the latest
Slicer-Python interaction techniques and
callbacks is always available at the following
NITRC repository: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/slicervmtklvlst/