Difference between revisions of "Mbirn: MBIRN Pipeline Arquitecture concept"
m (Update from Wiki) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Processing_pipeline_overview.gif|thumb|right|182px|Processing Pipeline Overview]] | |
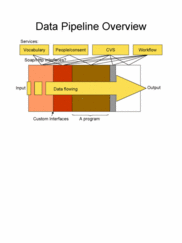
The pipeline architecture will allow loose coupling to existing programs. It will be possible to run existing applications locally if they exist on the client machine with the appropriate API’s to the pipeline core application. However, through a Service Oriented Architecture (SOA), applications will be able to run on distant machines using a SOAP interface. Polling of specific unified resource locations for available applications (resource discovery) will be part of the core pipeline architecture. With this architecture, mBIRN will provide a specification for building an application for data analysis that can be run as a service. These applications could then be discovered and run by the pipeline. This provides a good way to enable concurrent development of resources in this loosely coupled framework. More details can be found in . There will be four core services that will be maintained by mBIRN on which the pipeline will rely. The first is the CVS service which is the repository where the code that runs the core pipeline application will be obtained, as well as applications that can be fetched as the pipeline directs a specific (helper) application to run locally. The second is the Workflow service that will store the XML representation of the workflow and the data provenance information as well as provide services where client viewers can attach to follow the progression of the workflow. It will also provide the URL’s for the discovery of available applications at various locations. The Vocabulary service will be used to look up and register enumerated values of controlled vocabularies. Its important function is to provide tables to map similar terms to one another, and contain lists of acceptable elements for various data elements used in the data and metadata of the pipeline. Finally, the research subjects of the experiments will have their aliases and consent process managed by a service. The People/consent service will provide lookups during the data processing to map together aliases of a research subject, and assure that permission exists in the form of consent to proceed with the movement of data. | The pipeline architecture will allow loose coupling to existing programs. It will be possible to run existing applications locally if they exist on the client machine with the appropriate API’s to the pipeline core application. However, through a Service Oriented Architecture (SOA), applications will be able to run on distant machines using a SOAP interface. Polling of specific unified resource locations for available applications (resource discovery) will be part of the core pipeline architecture. With this architecture, mBIRN will provide a specification for building an application for data analysis that can be run as a service. These applications could then be discovered and run by the pipeline. This provides a good way to enable concurrent development of resources in this loosely coupled framework. More details can be found in . There will be four core services that will be maintained by mBIRN on which the pipeline will rely. The first is the CVS service which is the repository where the code that runs the core pipeline application will be obtained, as well as applications that can be fetched as the pipeline directs a specific (helper) application to run locally. The second is the Workflow service that will store the XML representation of the workflow and the data provenance information as well as provide services where client viewers can attach to follow the progression of the workflow. It will also provide the URL’s for the discovery of available applications at various locations. The Vocabulary service will be used to look up and register enumerated values of controlled vocabularies. Its important function is to provide tables to map similar terms to one another, and contain lists of acceptable elements for various data elements used in the data and metadata of the pipeline. Finally, the research subjects of the experiments will have their aliases and consent process managed by a service. The People/consent service will provide lookups during the data processing to map together aliases of a research subject, and assure that permission exists in the form of consent to proceed with the movement of data. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:08, 20 December 2006
Home < Mbirn: MBIRN Pipeline Arquitecture conceptThe goal is for a workflow analysis pipeline application suite to evolve that will encapsulate the mBIRN image processing requirements. Ongoing and future work involves:
- Definition of specifications: The application suite should be open source and highly conducive to loosely coupled development between teams of programmers. The core applications should be platform independent to the extent that they should run on Windows and Linux platforms. To that end, the programming languages used in the core of the program will be Java and C++. However, the architecture will be primarily based upon the use of web services, and these web services can access programming in any language and on any platform that has a web server available.
- Definition of pipeline architecture: The resulting analysis pipeline will be defined in the context of 4 available services. Data such as images and patient demographics will stream though the pipeline. This data is processed through a series of programs, which constitute the analysis pipeline. The core pipeline management software application will manage theses applications, and be responsible for directing the data to the applications in a secure manner, recording the application versions that are used, providing uniform error trapping, providing a quality assurance strategy, providing a standard recovery on failure, and providing a central metadata repository for tracking the jobs. Data provenance will be recorded through the pipeline services.
The pipeline architecture will allow loose coupling to existing programs. It will be possible to run existing applications locally if they exist on the client machine with the appropriate API’s to the pipeline core application. However, through a Service Oriented Architecture (SOA), applications will be able to run on distant machines using a SOAP interface. Polling of specific unified resource locations for available applications (resource discovery) will be part of the core pipeline architecture. With this architecture, mBIRN will provide a specification for building an application for data analysis that can be run as a service. These applications could then be discovered and run by the pipeline. This provides a good way to enable concurrent development of resources in this loosely coupled framework. More details can be found in . There will be four core services that will be maintained by mBIRN on which the pipeline will rely. The first is the CVS service which is the repository where the code that runs the core pipeline application will be obtained, as well as applications that can be fetched as the pipeline directs a specific (helper) application to run locally. The second is the Workflow service that will store the XML representation of the workflow and the data provenance information as well as provide services where client viewers can attach to follow the progression of the workflow. It will also provide the URL’s for the discovery of available applications at various locations. The Vocabulary service will be used to look up and register enumerated values of controlled vocabularies. Its important function is to provide tables to map similar terms to one another, and contain lists of acceptable elements for various data elements used in the data and metadata of the pipeline. Finally, the research subjects of the experiments will have their aliases and consent process managed by a service. The People/consent service will provide lookups during the data processing to map together aliases of a research subject, and assure that permission exists in the form of consent to proceed with the movement of data.