Difference between revisions of "Projects:UtahAtlasSegmentation"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
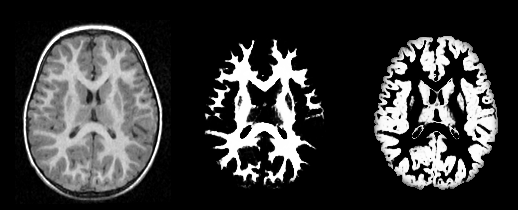
[[Image:UtahSegPlugin_result.png|thumb|center|600px|Output of the segmentation plugin, showing the bias corrected image and the probabilities for white and gray matter.]] | [[Image:UtahSegPlugin_result.png|thumb|center|600px|Output of the segmentation plugin, showing the bias corrected image and the probabilities for white and gray matter.]] | ||
| − | The tool | + | The tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc |
| − | [[Image:UtahSegPlugin_screen.png|thumb|center|400px|Screen shot of the segmentation plugin in Slicer.]] | + | {| |
| + | |- | ||
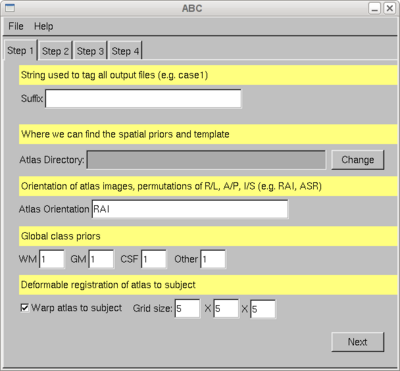
| + | | [[Image:UtahSegPlugin_screen.png|thumb|center|400px|Screen shot of the segmentation plugin in Slicer.]] | ||
| + | | [[Image:UtahSegGUI_screen.png|thumb|center|400px|Screen shot of the stand-alone segmentation GUI.]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
The bias correction module that we develop as part of our tool is available separately from NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/probbiascor. | The bias correction module that we develop as part of our tool is available separately from NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/probbiascor. | ||
Revision as of 00:28, 6 May 2010
Home < Projects:UtahAtlasSegmentationBack to Utah 2 Algorithms
Atlas Based Brain Segmentation
Automatic segmentation can be performed reliably using priors from brain atlases and an image generative model. We have developed a tool that provides an automatic segmentation pipeline in a modular framework. The processing pipeline is composed tasks such as filtering the input images, registering the multimodal input images and the brain atlas to a common space, followed by iterative steps which interleave segmentation, inhomogeneity correction, and atlas warping.
Our tool generates bias corrected images, fuzzy classification maps, and discrete segmentation labels. The tool has been used to automatically segment thousands of adult and toddler images from the University of North Carolina (UNC), and is also being used as a skull stripping mechanism for DTI processing at UNC and Utah. An example of the output of the tool is shown below.
The tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc
The bias correction module that we develop as part of our tool is available separately from NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/probbiascor.
Key Investigators
- Utah Algorithms: Marcel Prastawa, Guido Gerig