Difference between revisions of "NA-MIC Internal Collaborations:StructuralImageAnalysis"
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
<font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Zhao Z., Taylor W., Styner M., Steffens D., Krishnan R., Macfall J. , Hippocampus shape analysis and late-life depression. PLoS ONE. 2008 Mar 19;3(3):e1837. | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Zhao Z., Taylor W., Styner M., Steffens D., Krishnan R., Macfall J. , Hippocampus shape analysis and late-life depression. PLoS ONE. 2008 Mar 19;3(3):e1837. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | [[Image:BasePair3DModel.JPG|200px|]] | ||
| + | | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == [[Projects:NonParametricClustering|Non Parametric Clustering for Biomolecular Structural Analysis]] == | ||
| + | |||
| + | High accuracy imaging and image processing techniques allow for collecting structural information of biomolecules with atomistic accuracy. Direct interpretation of the dynamics and the functionality of these structures with physical models, is yet to be developed. Clustering of molecular conformations into classes seems to be the first stage in recovering the formation and the functionality of these molecules. [[Projects:NonParametricClustering|More...]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> E. Hershkovits, A. Tannenbaum, and R. Tannenbaum. Adsorption of Block Copolymers from Selective Solvents on Curved Surfaces. Macromolecules. 2008. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 16:38, 2 September 2009
Home < NA-MIC Internal Collaborations:StructuralImageAnalysisBack to NA-MIC Internal Collaborations
Structural Image Analysis
Image Segmentation
Kernel PCA for SegmentationSegmentation performances using active contours can be drastically improved if the possible shapes of the object of interest are learnt. The goal of this work is to use Kernel PCA to learn shape priors. Kernel PCA allows for learning non linear dependencies in data sets, leading to more robust shape priors. More... New: S. Dambreville, Y. Rathi, and A. Tannenbaum. A Framework for Image Segmentation using Image Shape Models and Kernel PCA Shape Priors. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2008 Aug;30(8):1385-99 |
Image Registration
|
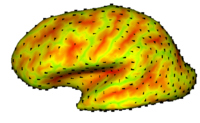
Cortical Correspondence using Particle SystemIn this project, we want to compute cortical correspondence on populations, using various features such as cortical structure, DTI connectivity, vascular structure, and functional data (fMRI). This presents a challenge because of the highly convoluted surface of the cortex, as well as because of the different properties of the data features we want to incorporate together. More... New: Oguz I, Niethammer M, Cates J, Whitaker R, Fletcher T, Vachet C, Styner M. “Cortical Correspondence with Probabilistic Fiber Connectivity”. Proc. Information Processing in Medical Imaging, 2009. |
|
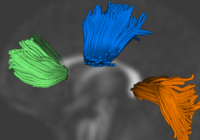
Population Analysis from Deformable RegistrationAnalysis of populations of diffusion images typically requires time-consuming manual segmentation of structures of interest to obtain correspondance for statistics. This project uses non-rigid registration of DTI images to produce a common coordinate system for hypothesis testing of diffusion properties. More... New: Casey B. Goodlett, P. Thomas Fletcher, John H. Gilmore, Guido Gerig. Group Analysis of DTI Fiber Tract Statistics with Application to Neurodevelopment. NeuroImage 45 (1) Supp. 1, 2009. p. S133-S142. |
|
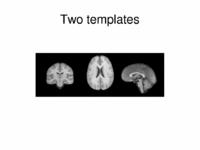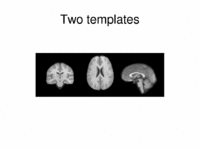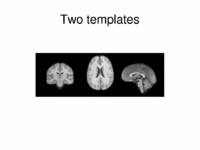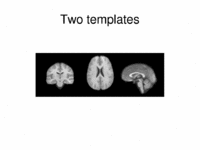
Multimodal AtlasIn this work, we propose and investigate an algorithm that jointly co-registers a collection of images while computing multiple templates. The algorithm, called iCluster, is used to compute multiple atlases for a given population. More... NEW: Image-driven Population Analysis through Mixture-Modeling, M.R. Sabuncu, S.K. Balci, M.E. Shenton and P. Golland. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. Accepted for Publication, 2009. |
Morphometric Measures and Shape Analysis
|
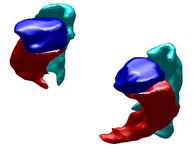
Label Space: A Coupled Multi-Shape RepresentationMany techniques for multi-shape representation may often develop inaccuracies stemming from either approximations or inherent variation. Label space is an implicit representation that offers unbiased algebraic manipulation and natural expression of label uncertainty. We demonstrate smoothing and registration on multi-label brain MRI. More... New: J. Malcolm, Y. Rathi, A. Tannenbaum. "Label Space: A Multi-Object Shape Representation." In Combinatorial Image Analysis, 2008. |

|
Shape Analysis Framework using SPHARM-PDMThe UNC shape analysis is based on an analysis framework of objects with spherical topology, described mainly by sampled spherical harmonics SPHARM-PDM. The input of the shape analysis framework is a set of binary segmentations of a single brain structure, such as the hippocampus or caudate. These segmentations are converted into a shape description (SPHARM) with correspondence and analyzed via Hotelling T^2 two sample metric. More... New: Zhao Z., Taylor W., Styner M., Steffens D., Krishnan R., Macfall J. , Hippocampus shape analysis and late-life depression. PLoS ONE. 2008 Mar 19;3(3):e1837. |
|
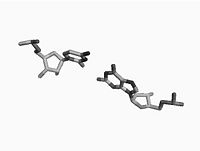
Non Parametric Clustering for Biomolecular Structural AnalysisHigh accuracy imaging and image processing techniques allow for collecting structural information of biomolecules with atomistic accuracy. Direct interpretation of the dynamics and the functionality of these structures with physical models, is yet to be developed. Clustering of molecular conformations into classes seems to be the first stage in recovering the formation and the functionality of these molecules. More... New: E. Hershkovits, A. Tannenbaum, and R. Tannenbaum. Adsorption of Block Copolymers from Selective Solvents on Curved Surfaces. Macromolecules. 2008. |