Difference between revisions of "Projects:UtahAtlasSegmentation"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
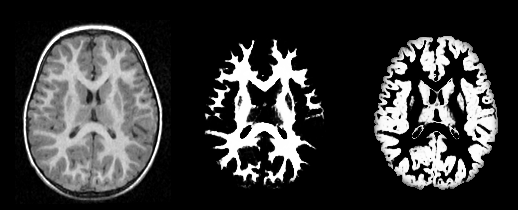
Our tool generates bias corrected images, fuzzy classification maps, and discrete segmentation labels. The tool has been used to automatically segment thousands of adult and toddler images from the University of North Carolina (UNC), and is also being used as a skull stripping mechanism for DTI processing at UNC and Utah. An example of the output of the tool is shown below. | Our tool generates bias corrected images, fuzzy classification maps, and discrete segmentation labels. The tool has been used to automatically segment thousands of adult and toddler images from the University of North Carolina (UNC), and is also being used as a skull stripping mechanism for DTI processing at UNC and Utah. An example of the output of the tool is shown below. | ||
[[Image:UtahSegPlugin_result.png|thumb|center|600px|Output of the segmentation plugin, showing the bias corrected image and the probabilities for white and gray matter.]] | [[Image:UtahSegPlugin_result.png|thumb|center|600px|Output of the segmentation plugin, showing the bias corrected image and the probabilities for white and gray matter.]] | ||
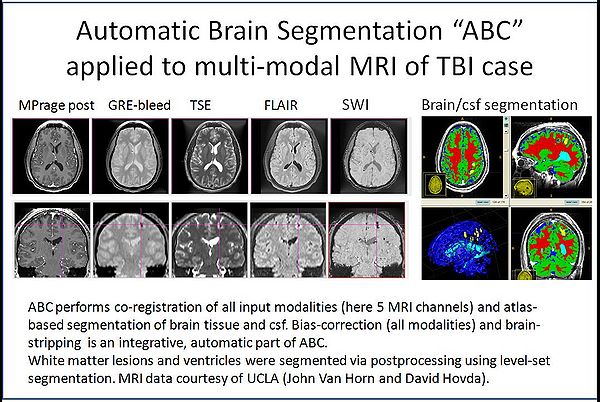
| + | [[Image:TBI-seg.jpg|thumb|center|600px|ABC tool applied to TBI MRI data.]] | ||
| + | |||
The tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc | The tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc | ||
Revision as of 14:22, 11 May 2010
Home < Projects:UtahAtlasSegmentationBack to Utah 2 Algorithms
Atlas Based Brain Segmentation
Automatic segmentation can be performed reliably using priors from brain atlases and an image generative model. We have developed a tool that provides an automatic segmentation pipeline in a modular framework. The processing pipeline is composed tasks such as filtering the input images, registering the multimodal input images and the brain atlas to a common space, followed by iterative steps which interleave segmentation, inhomogeneity correction, and atlas warping.
Our tool generates bias corrected images, fuzzy classification maps, and discrete segmentation labels. The tool has been used to automatically segment thousands of adult and toddler images from the University of North Carolina (UNC), and is also being used as a skull stripping mechanism for DTI processing at UNC and Utah. An example of the output of the tool is shown below.
The tool has been integrated into Slicer as an extension, and it can also be executed as a stand-alone application. Both versions are available for download through NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/abc
The bias correction module that we develop as part of our tool is available separately from NITRC: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/probbiascor.
- Marcel Prastawa, John H. Gilmore, Weili Lin, and Guido Gerig. Automatic Segmentation of MR Images of the Developing Newborn Brain. Medical Image Analysis (MedIA). Vol 9, Issue 5, October 2005, Pages 457-466.
- Marcel Prastawa, Elizabeth Bullitt, Sean Ho, and Guido Gerig. A Brain Tumor Segmentation Framework Based on Outlier Detection . Medical Image Analysis (MedIA). Vol 8, Issue 3, September 2004, Pages 275-283.
- Marcel Prastawa, John Gilmore, Weili Lin, and Guido Gerig. Automatic Segmentation of Neonatal Brain MRI. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS) 3216, Pages 10-17.
- Marcel Prastawa, Elizabeth Bullitt, Nathan Moon, Koen van Leemput, and Guido Gerig. Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation by Subject Specific Modification of Atlas Priors. Academic Radiology. Vol 10, Issue 12, December 2003, Pages 1341-1348.
- Marcel Prastawa, Elizabeth Bullitt, Sean Ho, and Guido Gerig. Robust Estimation for Brain Tumor Segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS) 2879, Pages 530-537.
Key Investigators
- Utah Algorithms: Marcel Prastawa, Guido Gerig