Difference between revisions of "Non-rigid MR-CT Image Registration"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Image:nonrigid.png |NON-RIGID MR-CT IMAGE REGISTRATION: This tutorial demonstrates how to perform MR-CT and CT-CT non-rigid registrations. In a CT-guided cryoablation of liver case, we can see a tumor on pre-operated MRI. However, on intra-operated CT image, the tumor can not be seen though cryoproves can be seen. | + | [[Image:nonrigid.png |NON-RIGID MR-CT IMAGE REGISTRATION: This tutorial demonstrates how to perform MR-CT and CT-CT non-rigid registrations. In a CT-guided cryoablation of liver case, we can see a tumor on pre-operated MRI. However, on intra-operated CT image, the tumor can not be seen though cryoproves can be seen. The non-rigid registration method can enhance visualization of tumor margins and location as shown in this figure. |500px|thumb|right]] |
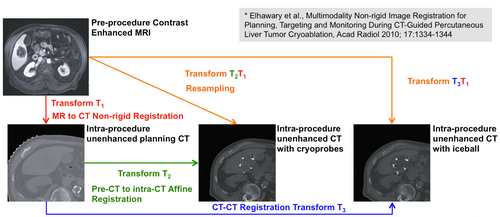
[[Image:nonrigid-cryo.png |PROCESS OF IMAGE REGISTRATION IN CRYOABLATION OF LIVER CASE: Registration process between MR and CT images in cryoablation of a liver case is shown. (1) A transformation matrix T1 was used to deform the pre-procedure contrast enhanced MR image on to the planning CT image. (2) T2 was used to deform the planning CT image on to the intra procedure CT image with cryoprobes. (3) The matrix T2 was combined with T1 to deform the MR image onto the CT image with cryoprobe. |500px|thumb|right]] | [[Image:nonrigid-cryo.png |PROCESS OF IMAGE REGISTRATION IN CRYOABLATION OF LIVER CASE: Registration process between MR and CT images in cryoablation of a liver case is shown. (1) A transformation matrix T1 was used to deform the pre-procedure contrast enhanced MR image on to the planning CT image. (2) T2 was used to deform the planning CT image on to the intra procedure CT image with cryoprobes. (3) The matrix T2 was combined with T1 to deform the MR image onto the CT image with cryoprobe. |500px|thumb|right]] | ||
Revision as of 01:48, 4 June 2011
Home < Non-rigid MR-CT Image Registration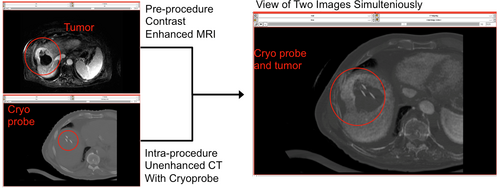
Contents
Non-rigid MR-CT Image Registration Tutorial
Overview
This tutorial demonstrates how to perform MR-CT and Ct-CT non-rigid image registrations. The case study is CT-guided liver tumor cryoablation. The clinical significants are as follows.
- Non-rigid registrations desirable to compensate for liver deformation caused by patient positioning, respiratory motion, and interventional manipulation.
- A multi-modality non-rigid registration method can enhance visualization of tumor margins and location during the planning, targeting, and monitoring phases of CT imaging-guided cryoablation procedure.
In this tutorial, the three steps are performed as shown the figure on right side.
- (1) In the image registration between MR image and planning CT image, we can obtain the moved and deformed MR image and the Bspline transformation matrix T1 by using pre-procedure contrast enhanced MRI and mask image.
- (2) In the image registration between plannning CT image and intra-procedure CT image, we can obtain the moved and deformed planning CT image and the Bspline transformation matrix T2.
- (3) In the image registration between MR image and intra-procedure CT image, we can obtain the moved and deformed MR image by using T1 and T2 BSpline transformation matrices.
For non-rigid registration, BRAINSFitIGT and BRAINSResamle modules are used. In this tutorial, we will show that 3D Slicer with BRAINSFitIGT module allows performing non-rigid image registration and BRAINSResample module allows performing non-rigid image deformation using Bspline transform matrix. We also shows the non-rigid registration method can enhance visualization of tumor margins and location during the planning, targeting, and monitoring phases of CT imaging-guided cryoablation procedure.
Tutorials
Non-rigid MR-CT Image Registration Module tutorial : to perform MR-CT and CT-CT image registration [ppt] [pdf]
Tutorial materials
Material data:
People
Atsushi Yamada, Ph.D. (Research Associate, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School)
Dominik S. Meier, Ph.D. (Assistant Professor, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School)
Nobuhiko Hata, Ph.D. (Associate Professor, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School)