Difference between revisions of "Projects:DTIFiberRegistration"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
'''Registration of Fiber Bundles''' | '''Registration of Fiber Bundles''' | ||
| − | To align the bundles from two subjects, we | + | To align the bundles from two subjects, we utilize the corresponce information |
| − | + | from the segmentation results in order to compute a non-linear warp field. More details | |
| − | + | will be posted once this work is accepted for publication. | |
| − | the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | non-linear | ||
| − | this | ||
[[Image:FiberBundleReg.jpg]] | [[Image:FiberBundleReg.jpg]] | ||
| Line 58: | Line 48: | ||
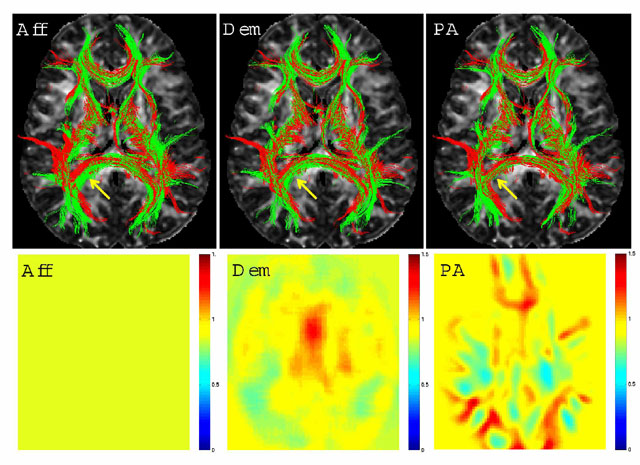
template. ''Aff'' (left) stands for the FA based global affine, | template. ''Aff'' (left) stands for the FA based global affine, | ||
''Dem'' (middle) for the demons algorithm and ''PA'' (right) for the | ''Dem'' (middle) for the demons algorithm and ''PA'' (right) for the | ||
| − | + | proposed framework in this work. Arrows point to an | |
area of differing qualities of registration. Overlapping of the red and | area of differing qualities of registration. Overlapping of the red and | ||
green fibers is indicative of better registration. Bottom Row: | green fibers is indicative of better registration. Bottom Row: | ||
| Line 66: | Line 56: | ||
The Jacobian of the global affine registration is constant. The | The Jacobian of the global affine registration is constant. The | ||
Jacobian of the demons algorithm is smooth due to the Gaussian | Jacobian of the demons algorithm is smooth due to the Gaussian | ||
| − | regularization. The Jacobian of the | + | regularization. The Jacobian of the new algorithm reflects |
the underlying anatomy because of the fiber bundle-based definition | the underlying anatomy because of the fiber bundle-based definition | ||
of the deformation. | of the deformation. | ||
Revision as of 21:11, 20 April 2007
Home < Projects:DTIFiberRegistrationDescription
Collaborators: Ulas Ziyan (MIT), Lauren O'Donnell (BWH), Mert Sabuncu (MIT), Carl-Fredrik Westin (BWH)
Image registration is necessary to compare and combine information from a group of subjects. Affine registration (e.g. Talairach normalization) is common for group analysis, but this typically yields poor alignment accuracy in certain local regions of interest.
To address this, there has been interest in developing nonlinear registration methods. In nonlinear registration, the description and regularization of the deformation is critical, since an unconstrained registration algorithm suffers form the potential problem of overfitting to the images, which may undermine consecutive analyses. A popular approach is to employ a model-based regularization which may have no biological meaning. Yet, we believe that the regularization and description of the deformation should be grounded in the application.
In this project, we explore the use of anatomical structures (called fiber bundles) extracted from Diffusion MR Images of a group of subjects for regularizing a non-linear registration algorithm.
Segmentation
Organization of tract fibers into bundles, in the entire white matter, reveals anatomical connections such as the corpus callosum and corona radiata. By clustering fibers from multiple subjects into bundles, these common white matter structures can be discovered in an automatic way, and the bundle models can be saved with expert anatomical labels to form an atlas. In this work, we take advantage of automatically segmented tractography that has been labeled (as bundles) with such an atlas.
Registration of Fiber Bundles
To align the bundles from two subjects, we utilize the corresponce information from the segmentation results in order to compute a non-linear warp field. More details will be posted once this work is accepted for publication.
Top Row: 3D renderings of the registered tracts of a subject (in green) and the template (in red) within 5mm of the central axial slice overlayed on the central FA slice of the template. Aff (left) stands for the FA based global affine, Dem (middle) for the demons algorithm and PA (right) for the proposed framework in this work. Arrows point to an area of differing qualities of registration. Overlapping of the red and green fibers is indicative of better registration. Bottom Row: Jacobian determinant images from the central slice of the volume: Yellow represents areas with small changes in size, and the shades of red and blue represent enlargement and shrinking, respectively. The Jacobian of the global affine registration is constant. The Jacobian of the demons algorithm is smooth due to the Gaussian regularization. The Jacobian of the new algorithm reflects the underlying anatomy because of the fiber bundle-based definition of the deformation.
Publications
Submitted for publication.
Software
The algorithms now are implemented in matlab.