Difference between revisions of "Project Week 25/Surgical Planning In Stereotaxy"
m (Fill progress and next steps section) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
|<!-- Progress and Next steps (fill out at the end of project week), bullet points --> | |<!-- Progress and Next steps (fill out at the end of project week), bullet points --> | ||
| − | + | * Segmentations have been integrated in the core of the toolbox | |
| + | * GUI has been improved, but there's still some work to do: | ||
| + | ** Get inspiration from commercial consoles | ||
| + | ** Ask neurosurgeons for feedback | ||
| + | * A [https://github.com/Slicer/Slicer/pull/741 pull request] for a new colormap has been created | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Illustrations== | ==Illustrations== | ||
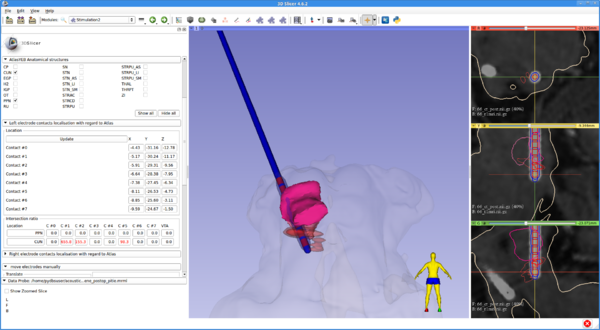
| + | [[File:Pydbs module.png|600px|thumb|left|Post-operative scene in Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)]] | ||
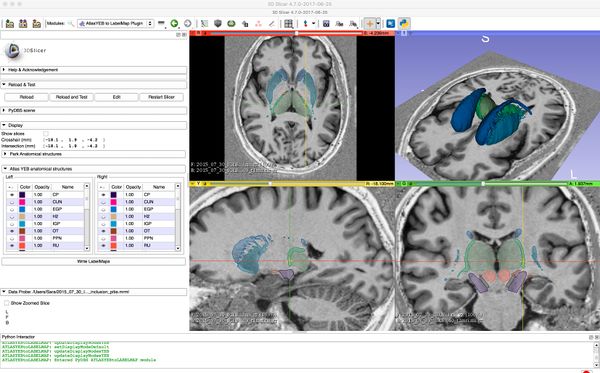
| + | [[File:YeB atlas segmentation.jpg|600px|thumb|left|Segmentation representing a histological atlas of the basal ganglia and segments tables included in the GUI]] | ||
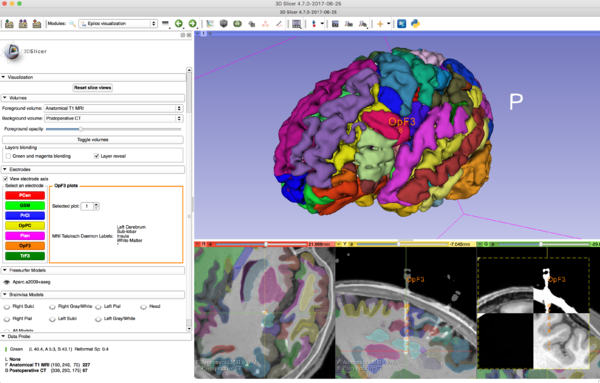
| + | [[File:FreeSurfer segmentation epilepsy.png|600px|thumb|left|Visualization of FreeSurfer segmentation for the assessment of stereotactic surgery in epilepsy]] | ||
| + | [[File:Diverging colormap for Jacobian visualization.png|600px|thumb|left|Different colormaps used to visualize compression and expansion after a non-linear deformation]] | ||
| − | |||
==Background and References== | ==Background and References== | ||
Revision as of 10:15, 30 June 2017
Home < Project Week 25 < Surgical Planning In Stereotaxy
Back to Projects List
Key Investigators
- Sara Fernández-Vidal (Brain & Spine Institute, Paris, France)
- Fernando Pérez-García (Brain & Spine Institute, Paris, France)
- Csaba Pinter (Queen's University, Canada)
- Andras Lasso (Queen's University, Canada)
- Steve Pieper (Isomics Inc., USA)
Project Description
PyDBS is an automated image processing workflow for planning and postoperative assessment of deep brain stimulation interventions. It takes as input patient-specific data (i.e. patient images and patient clinical data) and generic models (i.e. an anatomical atlas, a model of the stereotactic frame and a model of the implanted electrodes) and provides as output a patient-specific model for planning and postoperative assessment of DBS surgery. This patient-specific model is composed of patient images, segmented anatomical structures (volumetric binary masks and triangular surface meshes) and geometrical transformations (registration matrices and deformation fields). All images, masks and meshes are mapped to a common reference space and fused in geometrical 3D scenes that can be readily visualized by the surgeon.
The software used for visualization and surgical planning is 3D Slicer. PyDBS includes several modules used for targeting and surgery assessment.
| Objective | Approach and Plan | Progress and Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Illustrations