Difference between revisions of "Projects:MultiscaleShapeSegmentation"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Back to [[NA-MIC_Collaborations|NA-MIC_Collaborations]] | ||
| + | |||
== Objective == | == Objective == | ||
To represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. | To represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. | ||
Revision as of 14:57, 31 July 2007
Home < Projects:MultiscaleShapeSegmentationBack to NA-MIC_Collaborations
Contents
Objective
To represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus.
Overview
Shape Representation and Prior
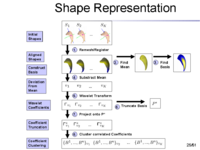
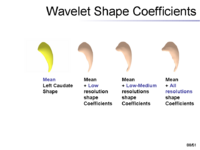
The overview of our shape representation is given in Figure 1. Our technique defines a multiscale parametric model of surfaces belonging to the same population using a compact set of spherical wavelets targeted to that population (Figure 2). We further refine the shape representation by separating into groups wavelet coefficients that describe independent global and/or local biological variations in the population, using spectral graph partitioning. We then learn a prior probability distribution induced over each group to explicitly encode these variations at different scales and spatial locations (Figure 4) [1].
Segmentation
Based on this representation, we derive a parametric active surface evolution using the multiscale prior coefficients as parameters for our optimization procedure to naturally include the prior for segmentation. Additionally, the optimization method can be applied in a coarse-to-fine manner.
Results
We applied our algorithm to the caudate nucleus, a brain structure of interest in the study of schizophrenia [2]. Our validation shows our algorithm is computationally efficient and outperforms the Active Shape Model (ASM) algorithm, by capturing finer shape details.
References
- [1] Nain D, Haker S, Bobick A, Tannenbaum A. Multiscale 3D Shape Analysis using Spherical Wavelets. Proc MICCAI, Oct 26-29 2005; p 459-467 [1]
- [2] Nain D, Haker S, Bobick A, Tannenbaum A. Shape-driven 3D Segmentation using Spherical Wavelets. Proc MICCAI, Oct 2-5, 2006. PDF of paper
Key Investigators
- Core 1:
- Georgia Tech: Delphine Nain, Aaron Bobick, Allen Tannenbaum
- Harvard SPL: Steven Haker
Collaborators
- Core 1: Martin Styner (UNC)
- Core 2: Jim Miller (GE), Luis Ibanez (Kitware)
- Core 3: James Levitt, Marc Niethammer, Sylvain Bouix, Martha Shenton (Harvard PNL)