Difference between revisions of "Projects:CorpusCallosumRegionalFAAnalysis"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | = Corpus Callosum Regional FA analysis in Schizophrenia = | ||
| + | |||
Back to [[NA-MIC_Collaborations|NA-MIC_Collaborations]] | Back to [[NA-MIC_Collaborations|NA-MIC_Collaborations]] | ||
| − | '''Objective | + | '''Objective''' |
| + | |||
| + | To quantify diffusion fractional anisotropy (FA) differences between controls and schizophrenia subjects within anatomicaly defined portions of the corpus callosum. | ||
| − | '''Progress | + | '''Progress''' |
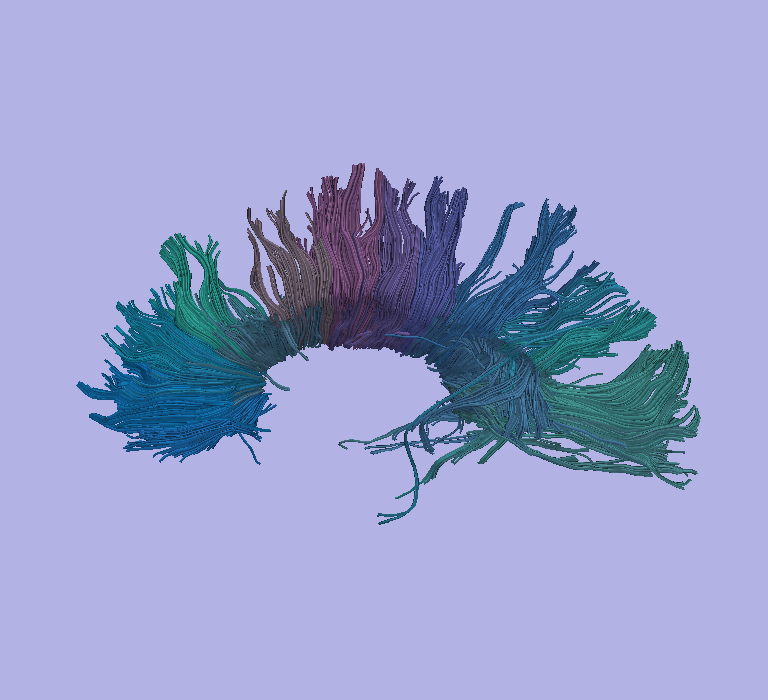
* We are in the process of applying population clustering algorythm to the NAMIC chronic schizophrenia data. Corpus callosum masks have been already drawn manually in slicer, and combined with fiber tractography clustering output. Several clusters of fiber tracts going through the corpus callosum have been identified, and now corpus masks will be back-painted and separated according to clusters. | * We are in the process of applying population clustering algorythm to the NAMIC chronic schizophrenia data. Corpus callosum masks have been already drawn manually in slicer, and combined with fiber tractography clustering output. Several clusters of fiber tracts going through the corpus callosum have been identified, and now corpus masks will be back-painted and separated according to clusters. | ||
* In a separate analysis, a probabilistic regional parcellation shape model derived by tracking inter-hemispheric lobar DTI connections has been applied. The corpus callosum contours and respective 4 probabilistic parcellations were computed from the structural MRI automatically using a Fourier descriptor based active shape segmentation. The probabilistic masks were non-rigidly registered to the DTI base image and used for probabilistic histogram computation of the FA. A paper is currently being written up with significant findings of differences between healthy and schizophrenics. | * In a separate analysis, a probabilistic regional parcellation shape model derived by tracking inter-hemispheric lobar DTI connections has been applied. The corpus callosum contours and respective 4 probabilistic parcellations were computed from the structural MRI automatically using a Fourier descriptor based active shape segmentation. The probabilistic masks were non-rigidly registered to the DTI base image and used for probabilistic histogram computation of the FA. A paper is currently being written up with significant findings of differences between healthy and schizophrenics. | ||
| − | + | ''References'' | |
M. Styner, R. Gimpel Smith, C. Cascio, I. Oguz, M. JomierL: Corpus Callosum Subdivision based on a Probabilistic Model of Inter-hemispheric Connectivity, Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions 2005, LNCS 3750, pp. 765-772. | M. Styner, R. Gimpel Smith, C. Cascio, I. Oguz, M. JomierL: Corpus Callosum Subdivision based on a Probabilistic Model of Inter-hemispheric Connectivity, Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions 2005, LNCS 3750, pp. 765-772. | ||
| − | '''Key Investigators | + | '''Key Investigators''' |
* Harvard PNL: Marek Kubicki, Mark Dreusicke, Doug Markant, Martha Shenton | * Harvard PNL: Marek Kubicki, Mark Dreusicke, Doug Markant, Martha Shenton | ||
Revision as of 18:12, 3 September 2007
Home < Projects:CorpusCallosumRegionalFAAnalysisCorpus Callosum Regional FA analysis in Schizophrenia
Back to NA-MIC_Collaborations
Objective
To quantify diffusion fractional anisotropy (FA) differences between controls and schizophrenia subjects within anatomicaly defined portions of the corpus callosum.
Progress
- We are in the process of applying population clustering algorythm to the NAMIC chronic schizophrenia data. Corpus callosum masks have been already drawn manually in slicer, and combined with fiber tractography clustering output. Several clusters of fiber tracts going through the corpus callosum have been identified, and now corpus masks will be back-painted and separated according to clusters.
- In a separate analysis, a probabilistic regional parcellation shape model derived by tracking inter-hemispheric lobar DTI connections has been applied. The corpus callosum contours and respective 4 probabilistic parcellations were computed from the structural MRI automatically using a Fourier descriptor based active shape segmentation. The probabilistic masks were non-rigidly registered to the DTI base image and used for probabilistic histogram computation of the FA. A paper is currently being written up with significant findings of differences between healthy and schizophrenics.
References
M. Styner, R. Gimpel Smith, C. Cascio, I. Oguz, M. JomierL: Corpus Callosum Subdivision based on a Probabilistic Model of Inter-hemispheric Connectivity, Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions 2005, LNCS 3750, pp. 765-772.
Key Investigators
- Harvard PNL: Marek Kubicki, Mark Dreusicke, Doug Markant, Martha Shenton
- MIT: Lauren O'Donnell, Carl-Fredrik Westin
- UNC: Martin Styner
Links: