Difference between revisions of "2009 Summer Project Week Slicer3 XNAT usecases"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
= General comments/questions = | = General comments/questions = | ||
| + | == XNAT Enterprise == | ||
* Can you have templates for creating directory structures on XNE? Dan recommends using script using webservices API to implement that template. | * Can you have templates for creating directory structures on XNE? Dan recommends using script using webservices API to implement that template. | ||
* Can we upload other formats besides DICOM> Dan demonstrates how to create a new folder with custom name (NRRD) into which we can subsequently upload. This may also be done using a script, using webservices API or using XNDesktop. | * Can we upload other formats besides DICOM> Dan demonstrates how to create a new folder with custom name (NRRD) into which we can subsequently upload. This may also be done using a script, using webservices API or using XNDesktop. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
* How are web forms integrated (need to author screen class/template/action, maybe other java classes too for something more complicated, for each web form and install in your instance of XNATE) | * How are web forms integrated (need to author screen class/template/action, maybe other java classes too for something more complicated, for each web form and install in your instance of XNATE) | ||
* Options menu (within search) can be extended for processing (batchmake, loni pipeline) | * Options menu (within search) can be extended for processing (batchmake, loni pipeline) | ||
| + | ==XNAT Desktop== | ||
= Use Case 1: Image Guided Therapy Planning and in OR = | = Use Case 1: Image Guided Therapy Planning and in OR = | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 24 June 2009
Home < 2009 Summer Project Week Slicer3 XNAT usecasesContents
XNAT interface Worksheet
Goals:
- Determine User Interface Requirements for representative use cases
- Determine Webservices API Requirements for representative use cases
- Determine sufficiency of XNAT Data Model for representative use cases
NOTES
Group looks at XNAT Enterprise and XNAT Desktop user interfaces
General comments/questions
XNAT Enterprise
- Can you have templates for creating directory structures on XNE? Dan recommends using script using webservices API to implement that template.
- Can we upload other formats besides DICOM> Dan demonstrates how to create a new folder with custom name (NRRD) into which we can subsequently upload. This may also be done using a script, using webservices API or using XNDesktop.
- Can share data with another project-- new project contains *links* to data from parent project. How do permissions work in this case? Bound by permissions of parent project.
- Sharing: multi-site projects -- each site have their own project; each site shares its data with collaborating sites. (this can be done now using REST API).
- Scientists in multi-site study download data from a single site's shared project. Work on that data.
- Want to upload new/derived data to that single site's shared project and then
- Want to share them back with other sites. Possible? This requires some clarification.
- Confusion about difference between assessors and reconstructions (reconstruction doesn't have concept of additional values yielded by processing -- assessors (like a FreeSurfer analysis) have their own XML specifications to contain specialized values ).
- XNAT Desktop: are their paradigms for setting tags? XND has its own set of default tags, and lets you set your own. But not clear what tags you need to set. Misha is working on this for now. For instance, there is a modality tag, but easy to forget to provide it.
- XNE GUI lets you store a search -- convenient to use as a template to grab data of interest.
- Are stored searches associated to project, to user? Now associated to a user; a user can share these with other users.
- How are web forms integrated (need to author screen class/template/action, maybe other java classes too for something more complicated, for each web form and install in your instance of XNATE)
- Options menu (within search) can be extended for processing (batchmake, loni pipeline)
XNAT Desktop
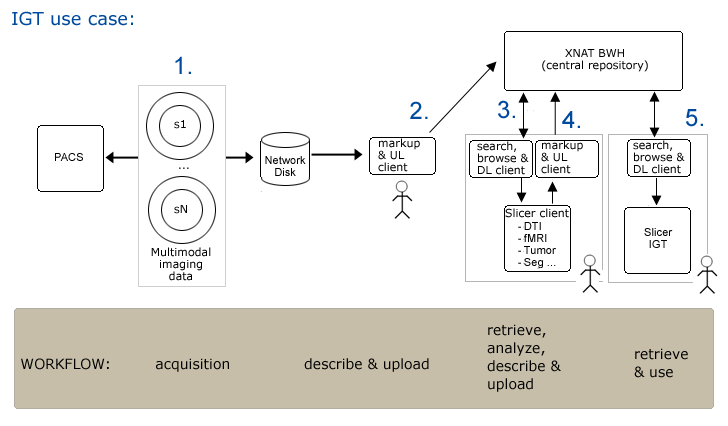
Use Case 1: Image Guided Therapy Planning and in OR
Workflow
Step1. Subject is scanned and data is pushed to a networked disk (and referenced by a PACS system) automatically.
Step2. Researcher1 uses an XND client (on a laptop or a desktop system) to
- apply metadata (DICOM rule sufficient?)
- upload data to XNAT repository
Step3. Researcher2 opens slicer and querieswebservices for a list of subjects.
- Query for all subjects on system
- Choose a subject, query for available data...
- Browse results
- download data of interest
Step4. Completed neurosurgical planning analysis
- apply metadata (need custom metadata) --must be quick/easy to do
- and upload results -- must be quick/easy to do (drag/drop, with confirmation0).
Step5. In IGT, search for and download scene for patient (subject)
Clinician cuts network link to remote repository (all files are locally cached so OR system is self sufficient).
GUI Requirements
Webservices API Requirements
Metadata Requirements or Data Model modifications
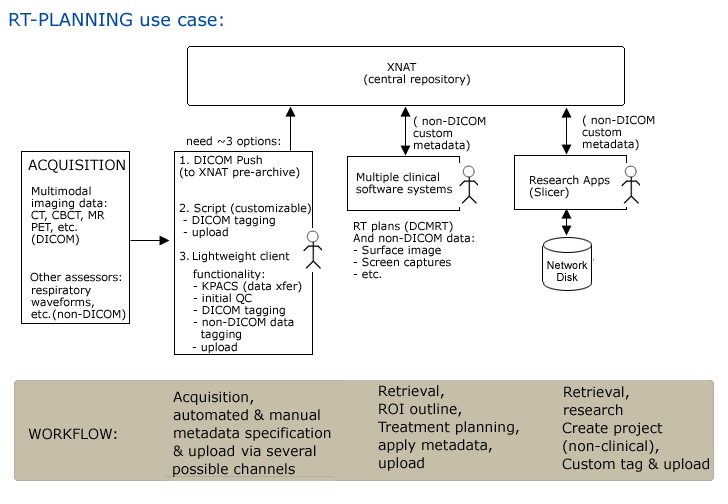
Use Case 2: Radiation Treatment Planning
Workflow
Step1. Patient is scanned and data is pushed to XNAT (and referenced by a PACS system) automatically.
- possibly DICOM DCMRT metadata automatically applied
- other assessors may be collected and described manually, uploaded to XNAT using client GUI.
Step2. Scientist/Clinician queries for patient data & browses results using GUI, downloads to RT planning software
Step3. Scientist/Clinician uploads plan in progress (drag & drop?). DICOM DCMRT metadata automatically applied at upload.
Step4. Researcher queries for case data & browses results using GUI, downloads to local disk for study.
GUI Requirements
- Interface to commercial systems?
- Appropriateness of XND for tagging & upload of non-imaging assessors?
- Specific user requirements for metadata authoring and upload client software?
Webservices API Requirements
Metadata Requirements or Data Model modifications
- DCMRT supported by DICOM rule?
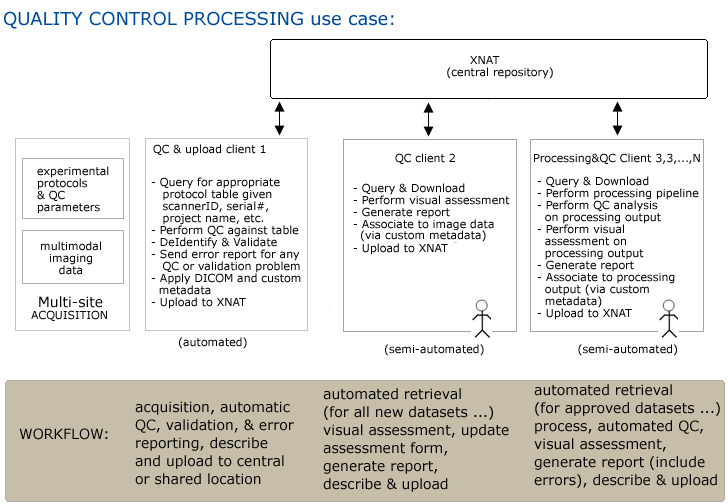
Use Case 3: Quality Control Processing of Large Studies
Workflow
Step 1. Multiple study sites acquire imaging data and other assessors
Step 2. Combination of automatic (DICOM) and manual (custom?) markup of data and upload to central repository
Step 3. QC batch client 1 automatically queries for (site/subject/scanID), retrieves, processes data, generates report and notifies any site of errors in (or missing) datasets. Additional processing may be performed (de-identification of data)...
Step4. Additional metadata may be automatically applied (provenance?) and data is uploaded.
Step5. QC batch client 2 (automatically?) queries for (site/subject/scanID), retrieves, allows visual inspection of data and report generation.
Step6. Report is automatically uploaded and associated with image data.
GUI Requirements
Webservices API Requirements
Metadata Requirements or Data Model modifications
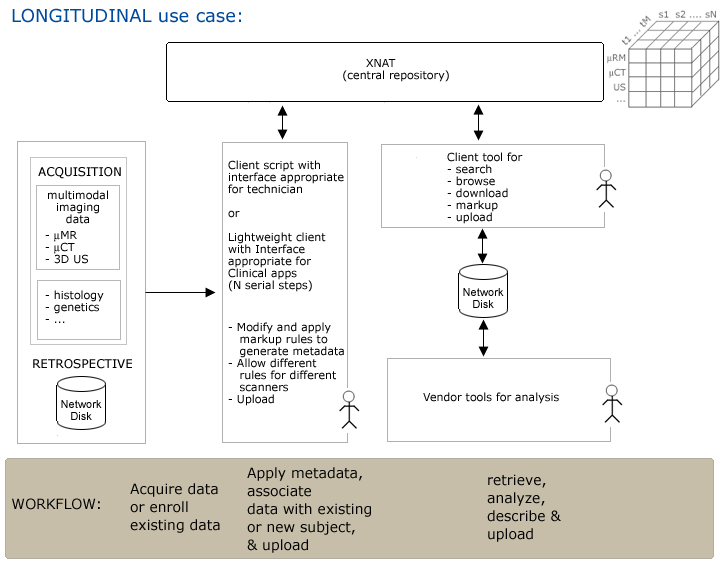
Use Case 4: Longitudinal Studies
Workflow
Step1. Imaging data and other assessors (induced pathology, etc.) are acquired and saved to a network disk.
Step2. Research assistant uses GUI to apply metadata at capture, or subsequently & uploads to XNAT.
- Need to specify whether subject is control or experimental
- Imagedata is typically in non-standard DICOM format.
- Need to associate new data to existing (or new) subject in longitudinal study -- need entities for:
- modality
- subject
- timepoint
- ...?
Step3. Researcher queries for data using GUI, browses results and downloads to vendor tools for analysis.
Step4. Researcher generates derived data,
- applies metadata (provenance? and maybe notable parameters of interest).
- associates to subject or study (population)
- and uploads via GUI
GUI Requirements
Webservices API Requirements
Metadata Requirements or Data Model modifications
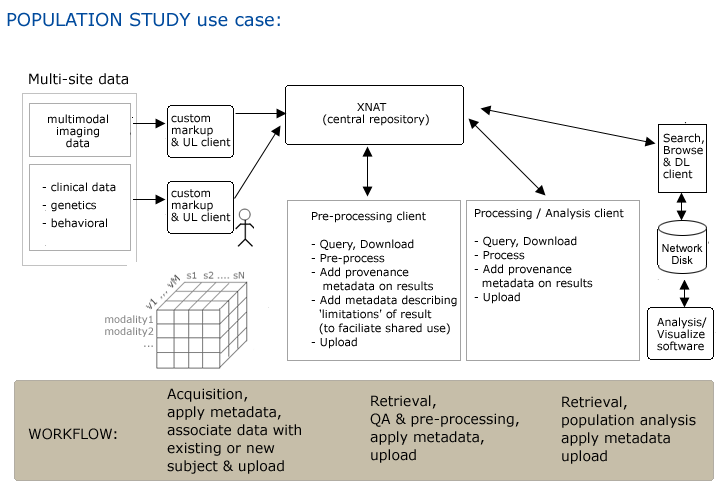
Use Case 5: Population Studies
Step 1. Multiple sites acquire multi-modal imagedata, across multiple visits for multiple subjects.
Step 2. All acquired data has metadata applied (combination manual and automatic) Metadata enables association of all collected data with individual subject. Among other important descriptions, subjects must be distinguished as either controls or experimental
Step 3. Data is uploaded to XNAT, either automatically or manually via a GUI.
Step 4. Pre-processing (& QA?) client automatically queries for datastes, downloads, pre-processes data.
Step 5. Client software adds custom metadata that includes provenance, descriptions of any 'limitations' of data that may affect its shared use & automatcially uploads data/metadata back to XNAT.
Step 6. Processing/Analysis client automatically queries for datasets, downloads, processes and generates derived data.
Step 7. Client software adds custom metadata that includes provenance, descriptions that associate metadata with subject or study & automatically uploads to XNAT.
Step 8. Scientist using Analysis/Visualization client searches for data of interest, browses results & downloads using client GUI. May derive new data, apply metadata & upload using client GUI.
GUI Requirements
Webservices API Requirements
Metadata Requirements or Data Model modifications