Difference between revisions of "Algorithm:Utah2"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Casey B. Goodlett, P. Thomas Fletcher, John H. Gilmore, Guido Gerig. Group Analysis of DTI Fiber Tract Statistics with Application to Neurodevelopment. NeuroImage 45 (1) Supp. 1, 2009. p. S133-S142. | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Casey B. Goodlett, P. Thomas Fletcher, John H. Gilmore, Guido Gerig. Group Analysis of DTI Fiber Tract Statistics with Application to Neurodevelopment. NeuroImage 45 (1) Supp. 1, 2009. p. S133-S142. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | [[Image:LesionSegmentation.png|200px]] | ||
| + | | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == [[Projects:LesionSegmentation|Lesion Segmentation]] == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Quantification, analysis and display of brain pathology such as white matter lesions as observed in MRI is important for diagnosis, monitoring of disease progression, improved understanding of pathological processes and for developing new therapies. | ||
| + | [[Projects:LesionSegmentation|More...]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Marcel Prastawa and Guido Gerig. Automatic MS Lesion Segmentation by Outlier Detection and Information Theoretic Region Partitioning. 3D Segmentation in the Clinic: A Grand Challenge II Workshop at Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2008. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 39: | Line 51: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:14, 27 August 2009
Home < Algorithm:Utah2Back to NA-MIC Algorithms
Overview of Utah 2 Algorithms (PI: Guido Gerig)
At Utah, we are interested in a range of algorithms and solutions for the analysis of DTI and the segmentation of healthy brains and brains with lupus lesions from structural MRI.
Utah 2 Projects
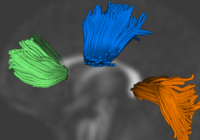
|
Group Analysis of DTI Fiber TractsAnalysis of populations of diffusion images typically requires time-consuming manual segmentation of structures of interest to obtain correspondance for statistics. This project uses non-rigid registration of DTI images to produce a common coordinate system for hypothesis testing of diffusion properties. More... New: Casey B. Goodlett, P. Thomas Fletcher, John H. Gilmore, Guido Gerig. Group Analysis of DTI Fiber Tract Statistics with Application to Neurodevelopment. NeuroImage 45 (1) Supp. 1, 2009. p. S133-S142. |
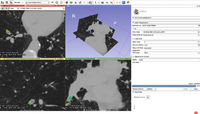
|
Lesion SegmentationQuantification, analysis and display of brain pathology such as white matter lesions as observed in MRI is important for diagnosis, monitoring of disease progression, improved understanding of pathological processes and for developing new therapies. More... New: Marcel Prastawa and Guido Gerig. Automatic MS Lesion Segmentation by Outlier Detection and Information Theoretic Region Partitioning. 3D Segmentation in the Clinic: A Grand Challenge II Workshop at Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2008. |
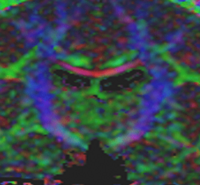
|
Influence of Imaging Noise on DTI StatisticsClinical acquisition of diffusion weighted images with high signal to noise ratio remains a challenge. The goal of this project is to understand the impact of MR noise on quantiative statistics of diffusion properties such as anisotropy measures, trace, etc. More... |
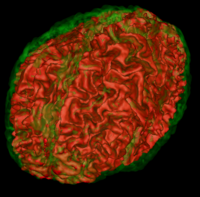
|
Atlas Based Brain SegmentationAutomatic segmentation can be performed reliably using priors from brain atlases and an image generative model. We have developed a tool that provides an automatic segmentation pipeline in a modular framework. More... |