Difference between revisions of "Projects:BrainManifold"
From NAMIC Wiki
m |
m |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
* The low dimensional parametrization simplifies statistical analysis of populations. | * The low dimensional parametrization simplifies statistical analysis of populations. | ||
* Applications to searching and browsing large database | * Applications to searching and browsing large database | ||
| − | * The manifold represents a localized Atlas. Alternative to template based applications | + | * The manifold represents a localized Atlas. Alternative to template based applications, for example as a segmentation prior. |
* Aid in clinical diagnosis. Different regions on the manifold can indicate different pathologies. | * Aid in clinical diagnosis. Different regions on the manifold can indicate different pathologies. | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 7 October 2009
Home < Projects:BrainManifoldBack to Utah Algorithms
Brain Manifold Learning
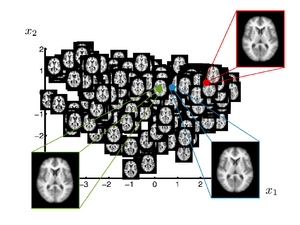
This work investigates the use of manifold learning approaches in the context of brain population analysis. The goal is to construct a manifold model from a set of brain images that captures variability in shape, a parametrization of the shape space. Such a manifold model is interesting in several ways
- The low dimensional parametrization simplifies statistical analysis of populations.
- Applications to searching and browsing large database
- The manifold represents a localized Atlas. Alternative to template based applications, for example as a segmentation prior.
- Aid in clinical diagnosis. Different regions on the manifold can indicate different pathologies.
Description
Key Investigators
- Utah: Samuel Gerber, Tolga Tasdizen, Sarang Joshi, Tom Fletcher, Ross Whitaker
Publications
Published in MICCAI and ICCV