Difference between revisions of "DBP2:UNC:Local Cortical Thickness Pipeline"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
*** Tool: FixImage (UNC Slicer3 external module) | *** Tool: FixImage (UNC Slicer3 external module) | ||
*** Go back to step 5 | *** Go back to step 5 | ||
| − | ** '''1.7. | + | ** '''1.7. Cortical thickness computation''' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*** Asymmetric local cortical thickness or Laplacian cortical thickness | *** Asymmetric local cortical thickness or Laplacian cortical thickness | ||
*** Tool: UNCCortThick or measureThicknessFilter (UNC Slicer3 external modules) | *** Tool: UNCCortThick or measureThicknessFilter (UNC Slicer3 external modules) | ||
| − | ** '''1. | + | ** '''1.8. Sulcal depth''' |
| − | *** Sulcal depth computation using genus zero surface and inflated one | + | *** Sulcal depth computation using genus-zero surface and inflated one |
*** Tool: MeshMath (UNC module) | *** Tool: MeshMath (UNC module) | ||
| − | ** '''1. | + | ** '''1.9. Surface area computation''' |
*** Lobar surface area measurement on smoothed genus-zero surface | *** Lobar surface area measurement on smoothed genus-zero surface | ||
*** Tool: MeshMath (UNC module) | *** Tool: MeshMath (UNC module) | ||
| − | ** '''1. | + | ** '''1.10. Particles initialization for cortical correspondence''' |
| − | *** Initializing particles on inflated surface using 98-lobe parcellation map and genus zero surface | + | *** Initializing particles on inflated genus-zero surface using 98-lobe parcellation map and genus zero surface |
| − | *** | + | *** Tool: ParticleInitializer (UNC Slicer3 external module) |
| − | * '''2. | + | * '''2. Particle-based shape correspondence''' |
** Correspondence on inflated surfaces using particle system | ** Correspondence on inflated surfaces using particle system | ||
| − | ** | + | ** '''2.1. Preprocessing''' |
| + | ** Distance maps creation from inflated genus-zero surfaces with slight gaussian blurring | ||
| + | ** Tool: ParticleCorrespondencePreProcessing (UNC Slicer3 external module) | ||
| + | ** '''2.2. Correspondence optimization''' | ||
| + | ** Particle-based shape correspondence optimization (using sulcal depth) with Procrustes alignement | ||
| + | ** Tool: ShapeWorksRun (Slicer3 external module) | ||
| + | ** '''2.3. Postprocessing''' | ||
| + | ** Re-meshing using template | ||
| + | ** Tool: ParticleCorrespondencePostProcessing (UNC Slicer3 external module) | ||
| + | ** '''2.4. Cortical thickness interpolation''' | ||
| + | ** Cortical thickness interpolation on surface in correspondence | ||
| + | ** Tool: MeshMath (UNC module) | ||
* '''3. Group statistical analysis''' | * '''3. Group statistical analysis''' | ||
** Tool: QDEC Slicer module or StatNonParamPDM | ** Tool: QDEC Slicer module or StatNonParamPDM | ||
Revision as of 21:58, 9 March 2010
Home < DBP2:UNC:Local Cortical Thickness PipelineBack to UNC Cortical Thickness Roadmap
Contents
Objective
We would like to create end-to-end applications within Slicer3 allowing individual and group analysis of mesh-based local cortical thickness.
Pipeline overview
Input: RAW images (T1-weighted, T2-weighted, PD-weighted images)
- 1. Individual pipeline
- 1.1. Tissue segmentation
- Probabilistic atlas-based automatic tissue segmentation via an Expectation-Maximization scheme
- Tool: itkEMS (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- 1.2. Atlas-based ROI segmentation: subcortical structures, lateral ventricles, parcellation
- 1.2.1. Skull stripping using previously computed tissue segmentation label image
- Tool: SegPostProcess (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- 1.2.2. T1-weighted atlas deformable registration
- B-spline pipeline registration
- Tool: RegisterImages (Slicer3 module)
- 1.2.3. Applying transformations to the structures
- Tool: ResampleVolume2 (Slicer3 module)
- 1.2.1. Skull stripping using previously computed tissue segmentation label image
- 1.3. White matter map creation
- Brainstem and cerebellum extraction
- Adding subcortical structures except amygdala and hippocampus
- Tool: ImageMath (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- 1.4. White matter map post-processing
- Largest component computation
- Smoothing: Level set smoothing or weighted average filter
- Connectivity enforcement (6-connectivity)
- White matter filling
- Tool: WMSegPostProcess (UNC Slicer3 external module)
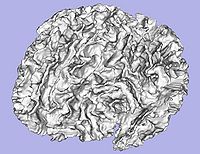
- 1.5. Genus zero white matter map image and surface creation
- Tool: GenusZeroImageFilter (UNC Slicer3 external module)
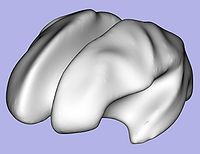
- 1.6. White matter surface inflation
- Iterative smoothing using relaxation operator (considering average vertex) and L2 norm of the mean curvature as a stopping criterion
- Iteration stopped if vertices that have too high curvature (some extremities)
- Tool: MeshInflation (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- 1.6 bis(Optional). White matter image fixing if necessary
- Correction of the white matter map image (corresponding to vertices that have high curvature) with connectivity enforcement
- Tool: FixImage (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- Go back to step 5
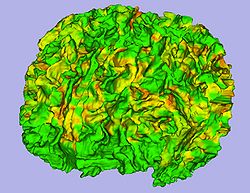
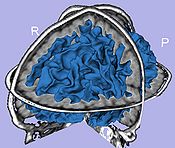
- 1.7. Cortical thickness computation
- Asymmetric local cortical thickness or Laplacian cortical thickness
- Tool: UNCCortThick or measureThicknessFilter (UNC Slicer3 external modules)
- 1.8. Sulcal depth
- Sulcal depth computation using genus-zero surface and inflated one
- Tool: MeshMath (UNC module)
- 1.9. Surface area computation
- Lobar surface area measurement on smoothed genus-zero surface
- Tool: MeshMath (UNC module)
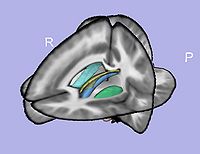
- 1.10. Particles initialization for cortical correspondence
- Initializing particles on inflated genus-zero surface using 98-lobe parcellation map and genus zero surface
- Tool: ParticleInitializer (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- 1.1. Tissue segmentation
- 2. Particle-based shape correspondence
- Correspondence on inflated surfaces using particle system
- 2.1. Preprocessing
- Distance maps creation from inflated genus-zero surfaces with slight gaussian blurring
- Tool: ParticleCorrespondencePreProcessing (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- 2.2. Correspondence optimization
- Particle-based shape correspondence optimization (using sulcal depth) with Procrustes alignement
- Tool: ShapeWorksRun (Slicer3 external module)
- 2.3. Postprocessing
- Re-meshing using template
- Tool: ParticleCorrespondencePostProcessing (UNC Slicer3 external module)
- 2.4. Cortical thickness interpolation
- Cortical thickness interpolation on surface in correspondence
- Tool: MeshMath (UNC module)
- 3. Group statistical analysis
- Tool: QDEC Slicer module or StatNonParamPDM
Download
Brain atlases
Four brain atlases are available on MIDAS and on NITRC:
- Pediatric atlas: http://www.insight-journal.org/midas/item/view/2277
- Adult atlas: http://www.insight-journal.org/midas/item/view/2328
- Elderly atlas: http://www.insight-journal.org/midas/item/view/2330
- Primate atlas: http://www.insight-journal.org/midas/item/view/2283
Pipeline validation
Analysis on a small pediatric dataset
Tests will be computed on a small pediatric dataset which includes 2 year-old and 4 year-old cases.
- 16 autistic cases
- 1 developmental delay
- 3 normal control
Comparison to state of the art
We would like to compare our pipeline with FreeSurfer. We will thus perform a regional statistical analysis using Pearson's correlation coefficient on an adult dataset (FreeSurfer's publicly available tutorial dataset) including 40 cases.
Planning
Done
Steps 1 to 11:
- Development of UNC Slicer3 modules
- Modules applied on small pediatric dataset from the Autism study
- Symmetric atlases generation (pediatric, adult, elderly):
- T1-weighted atlas
- Tissue segmentation probability maps
- Subcortical structures probability maps
In progress
- Step 1.6: Parameter exploration on autism dataset to improve inflation-fixing steps
- Step 2: Particle correspondence testing with pediatric surfaces (Meeting with Josh Cates at UNC - February 2010)
- Automatization of several steps using ShapeWorksRun and parameter files
Future work
- Full pipeline working on pediatric dataset
- Workflow for individual analysis as a Slicer3 high-level module using BatchMake
- Workflow for group analysis
References
- I. Oguz, M. Niethammer, J. Cates, R. Whitaker, T. Fletcher, C. Vachet, and M. Styner, Cortical Correspondence with Probabilistic Fiber Connectivity, Information Processing in Medical Imaging, IPMI 2009, LNCS, in print.
- H.C. Hazlett, C. Vachet, C. Mathieu, M. Styner, J. Piven, Use of the Slicer3 Toolkit to Produce Regional Cortical Thickness Measurement of Pediatric MRI Data, presented at the 8th Annual International Meeting for Autism Research (IMFAR) Chicago, IL 2009.
- C. Mathieu, C. Vachet, H.C. Hazlett, G. Geric, J. Piven, and M. Styner, ARCTIC – Automatic Regional Cortical ThICkness Tool, UNC Radiology Research Day 2009 abstract
- C. Vachet, H.C. Hazlett, M. Niethammer, I. Oguz, J.Cates, R. Whitaker, J. Piven, M. Styner, Mesh-based Local Cortical Thickness Framework, UNC Radiology Research Day 2009 abstract