Difference between revisions of "Algorithm:UNC"
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
<font color="red">'''New: '''</font> User-friendly GUI interface and statistical result visualization via automatically generated Slicer MRML scenes | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> User-friendly GUI interface and statistical result visualization via automatically generated Slicer MRML scenes | ||
| − | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Available on NITRC either | + | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Available on NITRC either [http://www.nitrc.org/projects/shape_mancova separately (ShapeAnalysisMANCOVA)] or as part of the SPHARM-PDM shape analysis package |
* Paniagua B., Styner M., Macenko M., Pantazis D., Niethammer M, Local Shape Analysis using MANCOVA, Insight Journal, 2009 July-December, http://hdl.handle.net/10380/3124 | * Paniagua B., Styner M., Macenko M., Pantazis D., Niethammer M, Local Shape Analysis using MANCOVA, Insight Journal, 2009 July-December, http://hdl.handle.net/10380/3124 | ||
Revision as of 18:24, 30 March 2011
Home < Algorithm:UNCBack to NA-MIC Algorithms
Overview of UNC Algorithms (PI: Martin Styner)
At UNC, we are interested in a range of algorithms and solutions for the surface based analysis of brain structures and the cortex. We pioneered the use of spherical harmonics based shape analysis for comparing brain structures across objects. We are now working on incorporating various data sources on the entire cortical surface for improving the correspondence computation. Furthermore, validation and evaluation of methods is highly relevant within our core.
UNC Projects
|
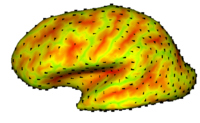
Cortical Correspondence using Particle SystemIn this project, we want to compute cortical correspondence on populations, using various features such as cortical structure, DTI connectivity, vascular structure, and functional data (fMRI). This presents a challenge because of the highly convoluted surface of the cortex, as well as because of the different properties of the data features we want to incorporate together. This correspondence method has been included in our NAMIC cortical thickness framework GAMBIT More... New: Vachet, C., Hazlett, H., Niethammer, M., Oguz, I., Cates, J., Whitaker, R., Piven, J., Styner, M., “Group-wise automatic mesh-based analysis of cortical thickness“. Medical Imaging 2011: Image Processing (2011) vol. 7962 (1) pp. 796227 1 - 10 New: Lee J, Ehlers C, Crews F, Niethammer M, Budin F, Paniagua B, Sulik K, Johns J, Styner M, Oguz I. Automatic cortical thickness analysis on rodent brain. Medical Imaging 2011: Image Processing (2011) vol. 7962 (1) pp. 796248 |

|
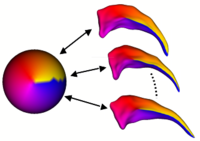
Shape Analysis Framework using SPHARM-PDMThe UNC shape analysis is based on an analysis framework of objects with spherical topology, described mainly by sampled spherical harmonics SPHARM-PDM. The input of the shape analysis framework is a set of binary segmentations of a single brain structure, such as the hippocampus or caudate. These segmentations are converted into a shape description (SPHARM-PDM) with correspondence and tested via statistical point-wise analysis. More...
New: automatic generation of Slicer MRML scenes for result visualization New: Mark Walterfang, Jeffrey Chee Leong Looi, Martin Styner, Ruth H Walker, Adrian Danek, Marc Neithammer, Andrew Evans, Katya Kotschet, Guilherme R Rodrigues, Andrew Hughes, Dennis Velakoulis. Shape alterations in the striatum in chorea-acanthocytosis. Psychiatry research (2011) preprint online New: Beatriz Paniagua, Lucia Cevidanes, David Walker, Hongtu Zhu, Ruixin Guo, Martin Styner. Clinical application of SPHARM-PDM to quantify temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Computerized medical imaging and graphics : the official journal of the Computerized Medical Imaging Society (2010) pp. New: Beatriz Paniagua, Lucia Cevidanes, Hongtu Zhu, Martin Styner. Outcome quantification using SPHARM-PDM toolbox in orthognathic surgery. International journal of computer assisted radiology and surgery (2010) pp. New: Jeffrey Chee Leong Looi, Mark Walterfang, Martin Styner, Leif Svensson, Olof Lindberg, Per Ostberg, Lisa Botes, Eva Orndahl, Phyllis Chua, Rajeev Kumar, Dennis Velakoulis, Lars-Olof Wahlund. Shape analysis of the neostriatum in frontotemporal lobar degeneration, Alzheimer's disease, and controls. Neuroimage (2010) vol. 51 (3) pp. 970-86
|
|
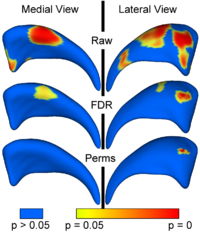
Local Statistical Analysis via Permutation TestsWe have further developed a set of statistical testing methods that allow the analysis of local shape differences via group differences tests as well interaction tests. Resulting significance maps (both raw and corrected for multiple comparisons) are easily visualized. Additional visualization of the group tests are provided via mean difference magnitude and vector maps, as well as maps of the group covariance information. Additional visualization of the interaction tests include Pearson and Spearman correlation maps. More... New: User-friendly GUI interface and statistical result visualization via automatically generated Slicer MRML scenes New: Available on NITRC either separately (ShapeAnalysisMANCOVA) or as part of the SPHARM-PDM shape analysis package
|
|
Evaluation and Comparison of Medical Image Analysis MethodsIn this project, we want to focus on the evaluation of medical image analysis methods for specific clinical applications in respect to development of evaluation methodology and the organization of venues promoting such comparison and validation studies. New: DTI fiber tractography challenge at MICCAI 2011 |
|
Population Based CorrespondenceWe are developing methodology to automatically find dense point correspondences between a collection of polygonal genus 0 meshes. The advantage of this method is independence from indivisual templates, as well as enhanced modeling properties. The method is based on minimizing a cost function that describes the goodness of correspondence. Apart from a cost function derived from the description length of the model, we also employ a cost function working with arbitrary local features. We extended the original methods to use surface curvature measurements, which are independent to differences of object aligment. More...
|