Difference between revisions of "DBP3:Utah:RegSegPipeline"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
::*'''Input''': MRI_pre_n4 (fixed) and MRI_post_n4 (moving) ; '''Output:''' MRI_pre_n4_cropped, MRI_post_n4_cropped | ::*'''Input''': MRI_pre_n4 (fixed) and MRI_post_n4 (moving) ; '''Output:''' MRI_pre_n4_cropped, MRI_post_n4_cropped | ||
::*'''Module used:''' [http://www.slicer.org/slicerWiki/index.php/Modules:CropVolume-Documentation-3.6 Crop Volume] | ::*'''Module used:''' [http://www.slicer.org/slicerWiki/index.php/Modules:CropVolume-Documentation-3.6 Crop Volume] | ||
| + | ::*''Comments:'' the [http://www.slicer.org/slicerWiki/index.php/Modules:VolumeRendering-Documentation-3.6 volume rendering module] may help in obtaining a good cropping ROI. Because of the high contrast, the MRA provides a good source for volume rendering. | ||
5. registration post -> pre: phase 2: nonrigid / BSPLINE | 5. registration post -> pre: phase 2: nonrigid / BSPLINE | ||
::*'''Input''': MRI_pre_n4_cropped (fixed) and MRI_post_n4_cropped (moving) ; '''Output:''' Xf4_pre-post_BSpline.tfm" | ::*'''Input''': MRI_pre_n4_cropped (fixed) and MRI_post_n4_cropped (moving) ; '''Output:''' Xf4_pre-post_BSpline.tfm" | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 5 April 2011
Home < DBP3:Utah:RegSegPipelineback to DBP3 home
Contents
The CARMA DBP: MRI-based study and treatment of atrial fibrillation
Pilot Studies on a Registration & Segmentation Pipeline & Workflow
Alex Zaitsev, Dominik Meier, Ron Kikinis
Main processing pipeline
To facilitate the workflow, we can place all the automated steps at the beginning and cluster interactive elements at the end. Exception is the cropping step required as input for nonrigid registration.
1. N4 bias field correction for the MRI (surface coils):
- Input: MRI_pre and MRI_post, each run separately with the same parameters below; Output: MRI_pre_n4 and MRI_post_n4
- Module used: N4 ITK; Parameters: convergence: 1e-5, iterations: 50,40,30,20, shrink factor: 3
- Comments: a run on entire image gives some benefit that may be improved with masking: again the dominant intensity dropoff from the surface coil occurs along the chest wall and ribcage. Even if that is not the structure of interest, it is the low-freq. variation the bias correction algorithm is searching for, and masking that out can be counter-productive: via masking we may end up with a smoother image, but the intensity variations removed were not caused by the coil but are actually true signal.
2. affine registration MRA ->MRI (both pre and post)
- Input: MRI_pre_n4 (fixed) and MRA_pre ; Output: Xf1_pre_MRA-MRI.tfm"
- Input: MRI_post_n4 (fixed) and MRA_post ; Output: Xf2_post_MRA-MRI.tfm"
- Module used: BRAINSfit
- Parameters: no initialization; samples: 200k, convergence: 1e-5, iterations:
- Comments: from the example dataset (P1) we infer that the two scans tend to have little initial alignment, hence initialization steps are not recommended. We choose registration parameters such that the chance of the registration making the alignment worse is minimized. Decide in a subsequent review/QC step if we keep the transform or the original pose. The MRA contains the same FOV and has surrounding structures (liver, chest, spine etc) visible also, despite lower intensities. A global affine is thus not necessarily going to benefit from masking the heart, unless the relative motion of the heart becomes the dominant reason for misalignment. We tried masking with both BrainsFit and RobustMultires modules. Both failed to provide better alignment with masking.
3. registration post -> pre: phase 1: AFFINE
- Input: MRI_pre_n4 (fixed) and MRI_post_n4 (moving) ; Output: Xf3_pre-post_affine.tfm
- Module used: BRAINSfit
- Parameters: DOF: rigid+similarity+affine (possibly rigid only); initialization: Moments align ; samples: 200k, convergence: 1e-5, iterations:
- Comments: done on the entire image. The surrounding structures are useful in constraining the solution transform and should provide a more robust behavior. Cropping down to the cardiac only ROI is deferred to the nonrigid registration in phase 2. The inferior-superior FOV can differ, e.g. how much of the liver is included. If the two exams differ significantly (>30%) in that content, the above affine could fail and a prior cropping step is then suggested to better match image content before registration. Resampling to isotropic voxel size at this stage is also advantageous but will generate very large files > 100MB due to the full FOV.
4. Cropping to VOI:
- Input: MRI_pre_n4 (fixed) and MRI_post_n4 (moving) ; Output: MRI_pre_n4_cropped, MRI_post_n4_cropped
- Module used: Crop Volume
- Comments: the volume rendering module may help in obtaining a good cropping ROI. Because of the high contrast, the MRA provides a good source for volume rendering.
5. registration post -> pre: phase 2: nonrigid / BSPLINE
- Input: MRI_pre_n4_cropped (fixed) and MRI_post_n4_cropped (moving) ; Output: Xf4_pre-post_BSpline.tfm"
- Module used: BRAINSfit or CMTK
- Parameters: DOF: BSpline only; initialization: Xf3_pre-post_affine.tfm ; samples: 200k, convergence: 1e-5, iterations:
- Comments: crop to volume of interest: CropVolume module, use Resample to isotropic voxelsize option.
6. resample MRA: apply above BSpline to the pre MRA
- Input Volume: MRA_post_n4_cropped
- Input Transform: above Xf4_pre-post_BSpline.tfm; Output Volume: MRA_post_n4_cropped_Xf4
- Module used: ResampleScalarVectorDWIVolume
- Parameters: output-to-input box checked, interpolation: linear
7. ROI definition (manual box ROI or automated via atlas)
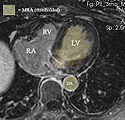
8. segmentation of LA from MRA -> inner wall
- Module used: Robust Statistics module or Editor: thresholding for thresholding within CMTK
- Comments: as a dynamic image the MRA contains significant spread and likely requires interactive segmentation/thresholding to yield a satisfactory LA volume. For validation/visualization, use the :Volumes thresholding option within Display tab, use iron colormap & low alpha setting to check for ventricular wall borders.
9. LA wall segmentation
- Module used: Atrium Cardiac Wall Segmentation (Extension Module, no documentation yet, authors: Yi Gao, Behnood Gholami, Allen Tannenbaum)
10. segmentation of enhancement
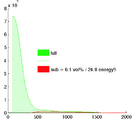
- Module used: Editor: thresholding ::*Comments:'; operate only on ROI within LA wall. Based on proper intensity statistics. An atlas-based set of intensity distributions may be more meaningful here than a simple Otsu, because both amount and location of enhancement is unknown and can in theory be 0.
Example Cases
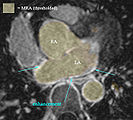
- Example Case P2 : pre-post registration
- This example contains significant MRI (motion?) artifacts that require dedicated processing to isolate the structures of interest
- E.g. FOV includes much more of liver on pre exam, which needs to be cropped to amount matching the follow-up