Difference between revisions of "2012 Winter Project Week:TBIValidation"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
| − | * | + | * Define manual segmentation protocol for MR images of TBI |
| − | * | + | * Validate the segmentation of the algorithm |
| − | * | + | * Visualize volume changes, deformation field |
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 13 January 2012
Home < 2012 Winter Project Week:TBIValidation- Visualization and validation of segmentation
Key Investigators
- Utah: Bo Wang, Marcel Prastawa, and Guido Gerig
- UCLA: Andrei Irimia, Micah Chambers, Jack Van Horn and Paul M. Vespa
- Kitware: Danielle Pace, Stephen Aylward
Objective
- Define manual segmentation protocol for MR images of TBI
- Validate the segmentation of the algorithm
- Visualize volume changes, deformation field
Approach, Plan
Our plan for the project week:
- Working with collaborators to define manual segmentation protocol
- Comparing the independent segmentation and joint segmentation
- Visualizing volume changes and deformation field according to clinicians' requirements.
Progress
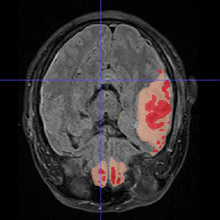
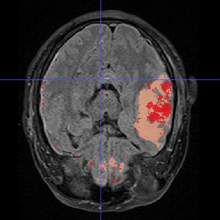
- Summarized the rule the clinician used to do manual segmentation
- Compared the result of the algorithm with clinician's manual segmentation
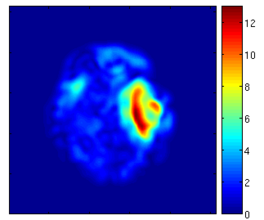
- Explored different ways to visualize the volume changes/deformation field, we tried the following methods.
- Jacobian determinant
- Vector magnitude
References
- Bo Wang, Marcel Prastawa, Andrei Irimia, Micah C. Chambers, Paul M. Vespa, John D. van Horn, Guido Gerig, A Patient-Specific Segmentation Framework for Longitudinal MR Images of Traumatic Brain Injury, SPIE Medical Imaging 2012.
- Andrei Irimia, Micah C. Chambers, Jeffry R. Alger, Maria Filippou, Marcel W. Prastawa, Bo Wang, David A. Hovda, Guido Gerig, Arthur W. Toga, Ron Kikinis, Paul M. Vespa, John D. van Horn (2011) Comparison of acute and chronic traumatic brain injury using semi-automatic multimodal segmentation of MR volumes. Journal of Neurotrauma