Difference between revisions of "2013 Summer Project Week: Computer Assisted Surgery"
Kfritscher76 (talk | contribs) |
Kfritscher76 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* MGH/BWH/UMIT: Karl Fritscher | * MGH/BWH/UMIT: Karl Fritscher | ||
* GATECH: Peter Karasev | * GATECH: Peter Karasev | ||
| − | * BWH: Ron Kikinis | + | * BWH: Ron Kikinis, Steve Pieper |
<div style="margin: 20px;"> | <div style="margin: 20px;"> | ||
Revision as of 18:18, 17 June 2013
Home < 2013 Summer Project Week: Computer Assisted Surgery
Key Investigators
- MGH/BWH/UMIT: Karl Fritscher
- GATECH: Peter Karasev
- BWH: Ron Kikinis, Steve Pieper
Objective
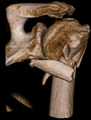
The repositioning of fracture fragments during a surgical intervention often requires a trial and error approach, which leads to a significant prolongation of the surgery and causes additional trauma to the fragments and the surrounding soft tissue. Wound healing failure, infections, or joint stiffness can be the consequence. Therefore, there is a clear trend towards the development of less invasive techniques to reconstruct complex fractures. In order to support this trend, software tools for calculating and visualizing the optimal way of repositioning fracture fragments based on the usage of segmented CT images as input data have been developed. In several studies, they have successfully demonstrated their potential to decrease operation times and increase reduction accuracy. However, existing software tools are often restricted to particular types of fractures and require a large amount of user interaction. Hence, the main objective of the project is to overcome these limitations by developing an algorithmic pipeline that is calculating and visualizing the optimal way of repositioning fracture fragments with a minimal amount of user interaction and without restrictions to particular types of fractures.
Plan
Novel concepts like the usage of prior knowledge about the shape of the healthy (=non-fractured) bone during the reconstruction process will be applied. Moreover, information coming from CT volumes will be combined with information on geometric surface properties in order to identify corresponding (fragment) surface points.
Progress/Goals
A slicer command line module + loadable module has been created. Until the project week they will be available as an extension. Different implmentation details like usage of CUDA code and improved manual interactions shall be discussed in the project week.
Delivery Mechanism
The code for automated fracture reconstruction will be provided as Slicer extension.