Difference between revisions of "Projects:DTIModeling"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | = Discription = | ||
| + | |||
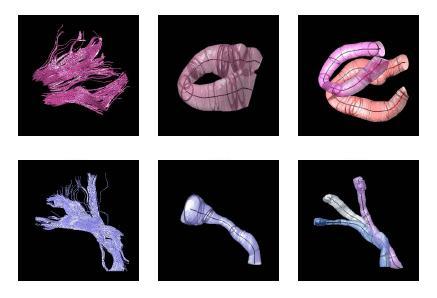
| + | We present a novel approach for joint clustering and point-by-point mapping of white matter fiber pathways. Knowledge of the point correspondence along the fiber pathways is not only necessary for accurate clustering of the trajectories into fiber bundles, but also crucial for any tract-oriented quantitative analysis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We employ an expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm to cluster the trajectories in a Gamma mixture model context. The result of clustering is the probabilistic assignment of the fiber trajectories to each cluster and an estimate of the cluster parameters, i.e. spatial mean and variance, and point correspondences. The fiber bundles are modeled by the mean trajectory and its spatial variation. Point-by-point correspondence of the trajectories within a bundle is obtained by constructing a distance map and a label map from each cluster center at every iteration of the EM algorithm. This offers a time-efficient alternative to pairwise curve matching of all trajectories with respect to each cluster center. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The proposed method has the potential to benefit from an anatomical atlas of fiber tracts by incorporating it as prior information in the EM algorithm. The algorithm is also capable of handling outliers in a principled way. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:models.jpg|Model of fiber tracts]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:clusters.jpg|clustering results]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
= Publications = | = Publications = | ||
Revision as of 22:14, 23 April 2007
Home < Projects:DTIModelingDiscription
We present a novel approach for joint clustering and point-by-point mapping of white matter fiber pathways. Knowledge of the point correspondence along the fiber pathways is not only necessary for accurate clustering of the trajectories into fiber bundles, but also crucial for any tract-oriented quantitative analysis.
We employ an expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm to cluster the trajectories in a Gamma mixture model context. The result of clustering is the probabilistic assignment of the fiber trajectories to each cluster and an estimate of the cluster parameters, i.e. spatial mean and variance, and point correspondences. The fiber bundles are modeled by the mean trajectory and its spatial variation. Point-by-point correspondence of the trajectories within a bundle is obtained by constructing a distance map and a label map from each cluster center at every iteration of the EM algorithm. This offers a time-efficient alternative to pairwise curve matching of all trajectories with respect to each cluster center.
The proposed method has the potential to benefit from an anatomical atlas of fiber tracts by incorporating it as prior information in the EM algorithm. The algorithm is also capable of handling outliers in a principled way.
Publications
[1] M. Maddah, W. M. Wells, S. K. Warfield, C.-F. Westin, and W. E. L. Grimson, Probabilistic Clustering and Quantitative Analysis of White Matter Fiber Tracts,IPMI 2007, Netherlands.
[2] M. Maddah, W. M. Wells, S. K. Warfield, C-F. Westin, and W. E. L. Grimson, A Spatial Model of White Matter Fiber Tracts to be presented at ISMRM 2007, Berlin.
[3] M. Maddah, W. E. L. Grimson, and S. Warfield, Statistical Modeling and EM Clustering of White Matter Fiber Tracts 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Macro to Nano (ISBI) 2006, pp. 53-56.
[4] D. Goldberg-Zimring, A. U. J. Mewes, M. Maddah, S. K. Warfield, Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis J Neuroimaging, vol. 15, pp. 68S-81S, 2005.
[5] M. Maddah, A. Mewes, S. Haker, W. E. L. Grimson, and S. Warfield, Automated Atlas-Based Clustering of White Matter Fiber Tracts from DTMRI. MICCAI05, Palm Spring, CA, pp. 188-195, 2005.
Software
Currently, all of the codes are implemented in MATLAB.