NA-MIC Internal Collaborations:StructuralImageAnalysis
Back to NA-MIC Internal Collaborations
Structural Image Analysis
Image Segmentation
|
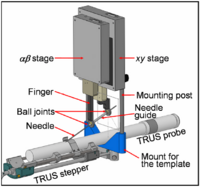
Brachytherapy Needle Positioning Robot IntegrationThe Queen’s/Hopkins team is developing novel devices and procedures for cancer interventions, including biopsy and therapies. Our goal for the programming week is to design and start implementing software for the new MRI Brachytherapy needle positioning robot. More... New: Meeting at JHU on July 17-19, 2007. |

|
Tubular Surface Segmentation FrameworkWe have proposed a new model for tubular surfaces that transforms the problem of detecting a surface in 3D space, to detecting a curve in 4D space. Besides allowing us to impose a "soft" tubular shape prior, this also leads to computational efficiency over conventional surface segmentation approaches. More... New: V. Mohan, G. Sundaramoorthi and A. Tannenbaum. Tubular Surface Segmentation for identifying anatomical structures from medical imagery. September 2008.
|
Image Registration
|
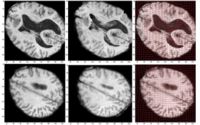
Optimal Mass Transport RegistrationThe goal of this project is to implement a computationaly efficient Elastic/Non-rigid Registration algorithm based on the Monge-Kantorovich theory of optimal mass transport for 3D Medical Imagery. Our technique is based on Multigrid and Multiresolution techniques. This method is particularly useful because it is parameter free and utilizes all of the grayscale data in the image pairs in a symmetric fashion and no landmarks need to be specified for correspondence. More... New: Tauseef ur Rehman, A. Tannenbaum. Multigrid Optimal Mass Transport for Image Registration and Morphing. SPIE Conference on Computational Imaging V, Jan 2007. |
|
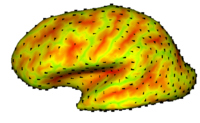
Cortical Correspondence using Particle SystemIn this project, we want to compute cortical correspondence on populations, using various features such as cortical structure, DTI connectivity, vascular structure, and functional data (fMRI). This presents a challenge because of the highly convoluted surface of the cortex, as well as because of the different properties of the data features we want to incorporate together. More... New: Oguz I, Niethammer M, Cates J, Whitaker R, Fletcher T, Vachet C, Styner M. “Cortical Correspondence with Probabilistic Fiber Connectivity”. Proc. Information Processing in Medical Imaging, 2009. |
|
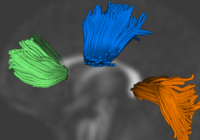
Population Analysis from Deformable RegistrationAnalysis of populations of diffusion images typically requires time-consuming manual segmentation of structures of interest to obtain correspondance for statistics. This project uses non-rigid registration of DTI images to produce a common coordinate system for hypothesis testing of diffusion properties. More... New: Casey B. Goodlett, P. Thomas Fletcher, John H. Gilmore, Guido Gerig. Group Analysis of DTI Fiber Tract Statistics with Application to Neurodevelopment. NeuroImage 45 (1) Supp. 1, 2009. p. S133-S142. |
|
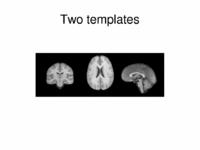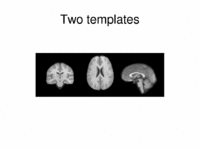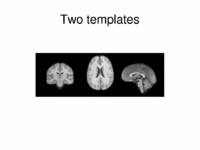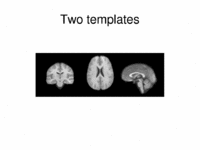
Multimodal AtlasIn this work, we propose and investigate an algorithm that jointly co-registers a collection of images while computing multiple templates. The algorithm, called iCluster, is used to compute multiple atlases for a given population. More... NEW: Image-driven Population Analysis through Mixture-Modeling, M.R. Sabuncu, S.K. Balci, M.E. Shenton and P. Golland. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. Accepted for Publication, 2009. |
Morphometric Measures and Shape Analysis
|
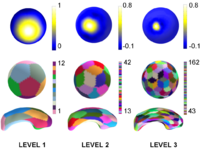
Multiscale Shape AnalysisWe present a novel method of statistical surface-based morphometry based on the use of non-parametric permutation tests and a spherical wavelet (SWC) shape representation. More... New: D. Nain, M. Styner, M. Niethammer, J. J. Levitt, M E Shenton, G Gerig, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. Statistical Shape Analysis of Brain Structures using Spherical Wavelets. Accepted in The Fourth IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI ’07) that will be held April 12-15, 2007 in Metro Washington DC, USA. |

|
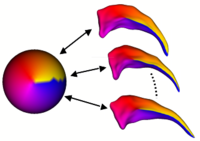
Shape Analysis Framework using SPHARM-PDMThe UNC shape analysis is based on an analysis framework of objects with spherical topology, described mainly by sampled spherical harmonics SPHARM-PDM. The input of the shape analysis framework is a set of binary segmentations of a single brain structure, such as the hippocampus or caudate. These segmentations are converted into a shape description (SPHARM) with correspondence and analyzed via Hotelling T^2 two sample metric. More... New:
|
|
Shape Analysis of the HippocampusOur objective is to examine hippocampal shape in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls. More... New: Styner M, Lieberman JA, McClure RK, Weinberger DR, Jones DW, Gerig G.: Morphometric analysis of lateral ventricles in schizophrenia and healthy controls regarding genetic and disease-specific factors, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005 Mar 29;102(13):4872-7. Epub 2005 Mar 16. |
|
Population Based CorrespondenceWe are developing methodology to automatically find dense point correspondences between a collection of polygonal genus 0 meshes. The advantage of this method is independence from indivisual templates, as well as enhanced modeling properties. The method is based on minimizing a cost function that describes the goodness of correspondence. Apart from a cost function derived from the description length of the model, we also employ a cost function working with arbitrary local features. We extended the original methods to use surface curvature measurements, which are independent to differences of object aligment. More... New:
|

|
Spherical WaveletsCortical Surface Shape Analysis Based on Spherical Wavelets. We introduce the use of over-complete spherical wavelets for shape analysis of 2D closed surfaces. Bi-orthogonal spherical wavelets have been proved to be powerful tools in the segmentation and shape analysis of 2D closed surfaces, but unfortunately they suffer from aliasing problems and are therefore not invariant to rotation of the underlying surface parameterization. In this paper, we demonstrate the theoretical advantage of over-complete wavelets over bi-orthogonal wavelets and illustrate their utility on both synthetic and real data. In particular, we show that the over-complete spherical wavelet transform enjoys significant advantages for the analysis of cortical folding development in a newborn dataset. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 |
Topology CorrectionGeometrically-Accurate Topology-Correction of Cortical Surfaces using Non-Separating Loops. We propose a technique to accurately correct the spherical topology of cortical surfaces. Specifically,we construct a mapping from the original surface onto the sphere to detect topological defects as minimal nonhomeomorphic regions. The topology of each defect is then corrected by opening and sealing the surface along a set of nonseparating loops that are selected in a Bayesian framework. The proposed method is a wholly self-contained topology correction algorithm, which determines geometrically accurate, topologically correct solutions based on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) intensity profile and the expected local curvature. Applied to real data, our method provides topological corrections similar to those made by a trained operator. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 | |
|
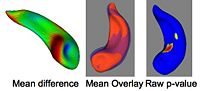
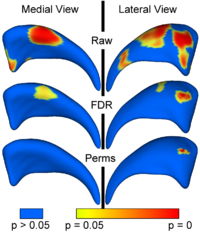
Local Statistical Analysis via Permutation TestsWe have further developed a set of statistical testing methods that allow the analysis of local shape differences using the Hotelling T 2 two sample metric. Permutatioin tests are employed for the computation of statistical p-values, both raw and corrected for multiple comparisons. Resulting significance maps are easily visualized. Additional visualization of the group tests are provided via mean difference magnitude and vector maps, as well as maps of the group covariance information. Ongoing research focuses on incorporating covariates such as clinical scores into the testing scheme. More... New:
|
|
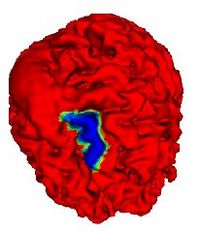
Automatic Outlining of sulci on the brain surfaceWe present a method to automatically extract certain key features on a surface. We apply this technique to outline sulci on the cortical surface of a brain. More... |
|
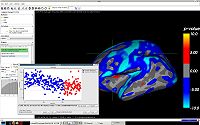
QDEC: An easy to use GUI for group morphometry studiesQdec is a application included in the Freesurfer software package intended to aid researchers in performing inter-subject / group averaging and inference on the morphometry data (cortical surface and volume) produced by the Freesurfer processing stream. The functionality in Qdec is also available as a processing module within Slicer3, and XNAT. More... See: Qdec user page |