2011 Winter Project Week:MeshCurvolver
Key Investigators
- Georgia Tech: Peter Karasev, Karol Chudy, Allen Tannenbaum
- BWH: Ron Kikinis
Objective
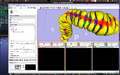
We are developing methods for segmentation of surfaces defined by polygonal meshes. In image or volume-slice segmentation, 'information' comes from image intensity, while in mesh surface segmentation the information is purely geometric. The goal of this project is to develop algorithms allowing a user to quickly and robustly segment one or several regions on a surface. Specifically, it is required to reconcile some concepts in classical differential geometry and embedded curves with the numerical and discrete-space constraints of polygon meshes.
Approach, Plan
Surface Geometry Computation
Closest Path Between Initial Points
Fast Level Set Implementation for Unstructured Mesh
Support 'global geometry' estimation for statistical analysis versus local-only for fast segmentation
Extend Functionality in VTK and ITK to perform needed operations
The module pipeline now contains three classes that extend vtkPolyDataAlgorithm. It now makes use of vtkSmartPointer.
- vtkInitClosedPath : take in poly data and set of fiducial points, create a closed path including the closest points on the mesh to the given fiducials. Searches for pre-existence of geometry information, pass-through if it already exists.
- vtkComputeLocalGeometry : take in poly data, compute curvature, its derivatives, and related differential geometric quantities. Uses its own version of curvature computation- vtk versions are not useable because they only consider 1-neighborhood. Searches for pre-existence of geometry information, pass-through if it already exists.
- vtkLevelSetMeshEvolver : take in poly data with a scalar array defining the current region boundaries. Update the boundaries with curve evolution and return poly data with updated scalar array.
References
P.A. Karasev, J.G. Malcolm, M. Niethammer, R. Kikinis, A. Tannenbaum. User-Driven 3D Mesh Region Targeting. SPIE Medical Imaging 2010.