2013 Summer Project Week:Epilepsy Surgery
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < 2013 Summer Project Week:Epilepsy Surgery
The Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (TLE) with hippocampal sclerosis affects other mesial temporal lobe structures, showing the change in signal intensity of white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in patients with TLE.
Such abnormalities of signal intensity changes in the temporal lobes, or loss of marking between WM and GM are referred as blurring in literature.
TLE is the most common type of refractory epilepsy in adults, and thus strong candidate to surgery.
Purpose To provide a better quality of life for those with TLE, a surgical procedure is usually proposed for extracting the brain region that is the focus of epilepsy.
This project aims to implment a semi-automated method capable of locating lesions, that is difficult to be detected by visual inspection, is built to help experts identify tissues presenting blurring in temporal lobes.
The proposed software tool was developed in C + +, using three toolkits to support: VTK, ITK and QT.
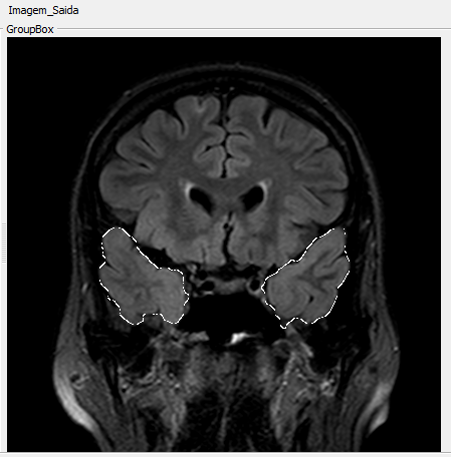
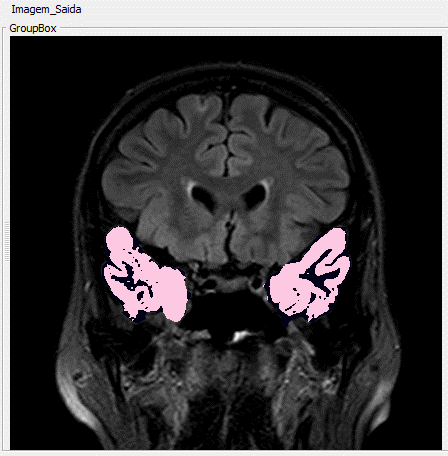
To provide segmentation of the temporal lobes, we used the Geodesic Active Contour method combined with the anomalous anisotropic diffusion filter.
Once segmented, the images are analyzed using texture descriptors from the intensity histogram and local pixels dependence measures proposed by Haralick were extracted.
Subsequently, the set of feature vectors from the segmented images is evaluated using three classifiers in WEKA environment.
Images of 32 patients with TLE were used, 15 of those exhibiting blurring phenomenon in TL and 17 do not.
In total, a set of 98 planar images was segmented, and 51 are classified in "with blurring" category and 47 "without blurring" category.
Of all three classifiers:
artificial neural network;
nearest neighbour;
and decision tree
tested, the one based on "J48" decision tree had the best, and most interesting results.
In the construction of the feature vectors of the images 32 have been used to describe the characteristics segmented images:
24 are extracted from the co-occurrence matrix using Haralick texture descriptors and
8 intensity histogram statistics.
When evaluating the performance of the three classifiers selected for the learning process, as a basis of 70 training samples and 28 test.
It was found that, for "J48" decision tree, the area under the ROC curve were 71.42 % and 69.30 %, respectively.
Key Investigators
- USP - Luiz Murta
Objective
This project will investigate the presence and location of the epileptogenic focus in temporal lobe by analyzing patterns of texture in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) after segmentation using anisotropic diffusion filters anomalous and geodesic active contour.
Purpose
Progress
Examples:
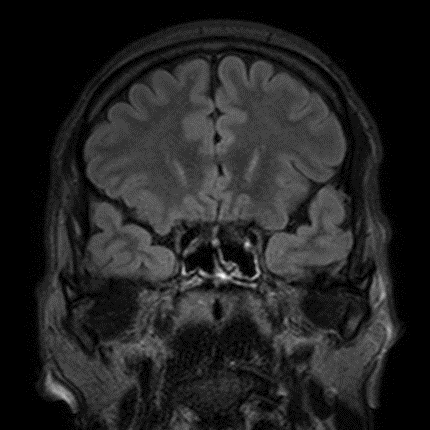
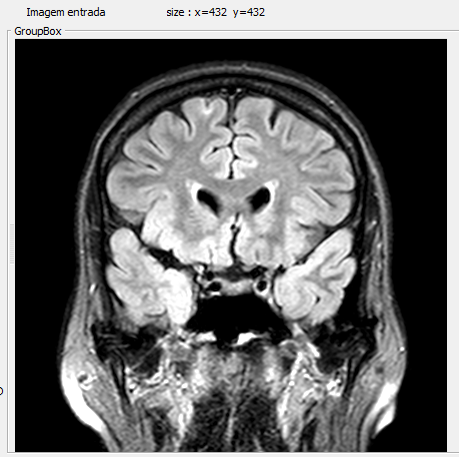
Normal MRI at mesial temporal lobe
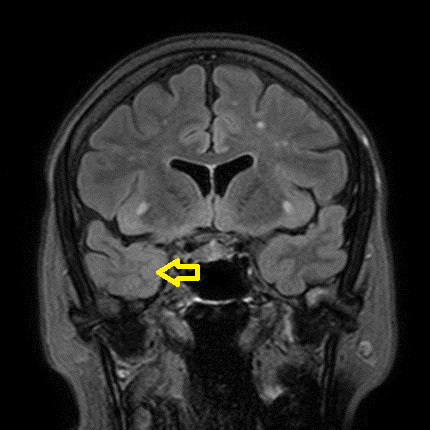
MRI containing blurring phenomena on right side as indicated by the yellow arrow
Results
Classifier
References
- Shaker, M. & Soltanian-Zadeh, H., 2008. Voxel-Based Morphometric Study of Brain Regions from Magnetic Resonance Images in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Image Analysis and Interpretation, 2008. SSIAI 2008. IEEE Southwest Symposium on, 209-212.