Projects:ProbabilisticCorpusCallosumAnalysis
Back to NA-MIC_Collaborations
Objectives:
To measure differences in fractional anisotropy (FA) of probabilistically derived subdivisions of the corpus callosum in schizophrenic patients vs. normal controls using previously published UNC method.
Key Investigators:
Harvard PNL: Marek Kubicki, Mark Dreusicke, Sylvain Bouix, Marc Niethammer, Martha Shenton; UNC: Martin Styner
Progress:
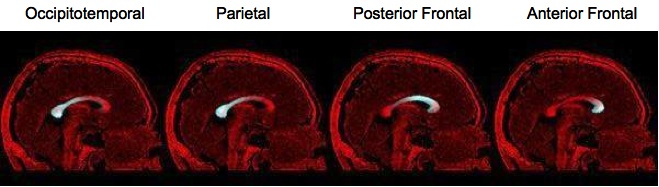
We are using sagittal LSDI scans that are characterized by high in-plane resolution (1.7 x 1.7 mm), and high resolution structural scans. DTI and structural MRI scans were already obtained from 32 schizophrenic subjects and 42 controls. Corpus Callosum cross sectional area and its probabilistic subdivisions were determined automatically from the structural MRI scans using a model based deformable contour segmentation. The subdivision employs a previously generated probabilistic subdivision atlas, based on the distance to trans-callosal DTI fibers associated with an anatomical lobe subdivision. The structural scan was then co-registered with the DTI scan and the anatomical corpus callosum subdivisions were propagated to the associated FA map.
Results revealed decreased FA within the parts of the corpus interconnecting anterior (P=0.03) and posterior (P=0.008) frontal regions in schizophrenia compared with controls, but no significant changes within the callosal fibers interconnecting parietal (P=0.12) and temporo-occipital (P=0.07) brain regions.
References:
Styner M, Gimpel Smith R, Cascio C, Oguz I, Jomier M. Corpus Callosum Subdivision based on a Probabilistic Model of Inter-hemispheric Connectivity. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions MICCAI. 2005 LNCS 3750;765-772