Validation of Defined Regions of Interest Using Surface Scanning
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < Validation of Defined Regions of Interest Using Surface Scanning
Objective:
- To evaluate manual and automated segmentation routines using surface scans of disected bones from cadaveric specimens
Progress:
- CT images of the hand and wrist have been obtained
- Four hands have been disected and bones extracted
- Surface scanning for these disected bones is completed using a Roland LPX-250 Laser Scanner
- Manual tracing of the CT images is completed
- Evaluate reliability of the manual tracers is complete using relative overlap
- Tools have been developed to reorient surface axes and to register the manually defined model and the surface resulting from laser scanning
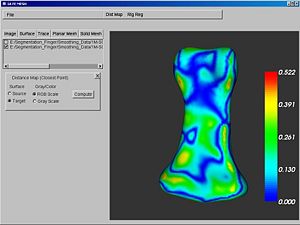
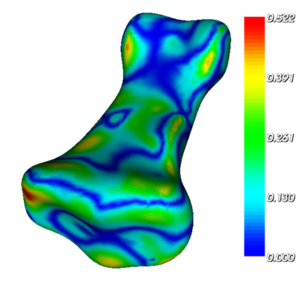
- Distance maps for the manual segmentation have been generated.
- The effect of various post processing routines have been studied relative to changes in the surface geometry relative to the laser scan.
To Do:
- Evaluate automated segmentation algorithms to the Physical laser scans
- Neural network segmentation
- EM Segmenter
- Integrate surface orientation and registration tools into Slicer3
- Integrate surface distance map tools into Slicer3 - These could be useful for other applications as well.
Key Investigators:
- Iowa: Nicole Grosland, Vincent Magnotta, Nicole DeVries
Links:
References:
- Validation of Phalanx Bone 3D Surface Segmentation from CT Images Using Laser Scanning, Skeletal Radiology, In press.
Figures: