NA-MIC Internal Collaborations:StructuralImageAnalysis
Back to NA-MIC Internal Collaborations
Image Segmentation
|
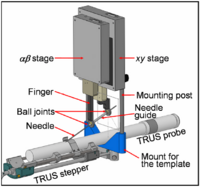
Brachytherapy Needle Positioning Robot IntegrationThe Queen’s/Hopkins team is developing novel devices and procedures for cancer interventions, including biopsy and therapies. Our goal for the programming week is to design and start implementing software for the new MRI Brachytherapy needle positioning robot. More... New: Meeting at JHU on July 17-19, 2007. |
|
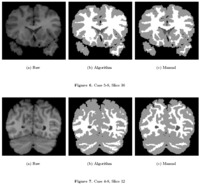
Knowledge-Based Bayesian SegmentationThis ITK filter is a segmentation algorithm that utilizes Bayes's Rule along with an affine-invariant anisotropic smoothing filter. More... New: J. Melonakos, Y. Gao, and A. Tannenbaum. Tissue Tracking: Applications for Brain MRI Classification. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2007. |
|
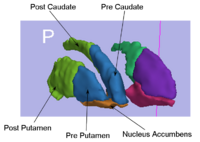
Rule-Based Striatum SegmentationIn this work, we provide software to semi-automate the implementation of segmentation procedures based on expert neuroanatomist rules for the striatum. More... New: Al-Hakim, et al. Parcellation of the Striatum. SPIE MI 2007. |
|
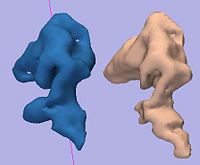
Rule-Based DLPFC SegmentationIn this work, we provide software to semi-automate the implementation of segmentation procedures based on expert neuroanatomist rules for the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. More... New: Al-Hakim, et al. A Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Semi-Automatic Segmenter. SPIE MI 2006. |
|
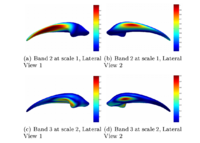
Multiscale Shape Segmentation TechniquesTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More... New: Delphine Nain won the best student paper at MICCAI 2006 in the category "Segmentation and Registration" for her paper entitled "Shape-driven surface segmentation using spherical wavelets" by D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. |
|
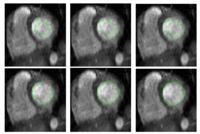
Stochastic Methods for SegmentationNew stochastic methods for implementing curvature driven flows for various medical tasks such as segmentation. More... New: Currently under investigation. |
|
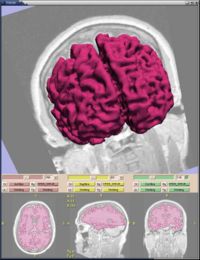
Statistical/PDE Methods using Fast Marching for SegmentationThis Fast Marching based flow was added to Slicer 2. More... |
Tissue Classification with Neighborhood StatisticsWe have implemented an MRI tissue classification algorithm based on unsupervised non-parametric density estimation of tissue intensity classes. More... T Tasdizen, S Awate, R Whitaker, A nonparametric, entropy-minimizing MRI tissue classification algorithm implementation using ITK, MICCAI 2005 Open-Source Workshop. | |
|
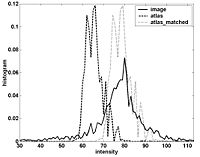
Atlas Renormalization for Improved Brain MR Image Segmentation across Scanner PlatformsAtlas-based approaches have demonstrated the ability to automatically identify detailed brain structures from 3-D magnetic resonance (MR) brain images. Unfortunately, the accuracy of this type of method often degrades when processing data acquired on a different scanner platform or pulse sequence than the data used for the atlas training. In this paper, we improve the performance of an atlas-based whole brain segmentation method by introducing an intensity renormalization procedure that automatically adjusts the prior atlas intensity model to new input data. Validation using manually labeled test datasets has shown that the new procedure improves the segmentation accuracy (as measured by the Dice coefficient) by 10% or more for several structures including hippocampus, amygdala, caudate, and pallidum. The results verify that this new procedure reduces the sensitivity of the whole brain segmentation method to changes in scanner platforms and improves its accuracy and robustness, which can thus facilitate multicenter or multisite neuroanatomical imaging studies. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 |