Projects:ShapeAnalysis
Project Description
In contrast to shape-based segmentation that utilizes a statistical model of the shape variability in one population (typically based on the Principal Component Analysis), we are interested in identifying and characterizing differences between two sets of shape examples. We use the discriminative framework to characterize the differences in shape by training a classifier function and studying its sensitivity to small perturbations in the input data. An additional benefit of employing the classification approach is that the resulting classifier function can be used to label new examples into one of the two populations, e.g., for early detection in population screening or prediction in longitudinal studies. We estimate the expected accuracy of the classifier in a jackknife procedure. We have also adapted a non-parametric permutation test to the classification setting to estimate the statistical significance of the detected differences and the observed classification accuracy.
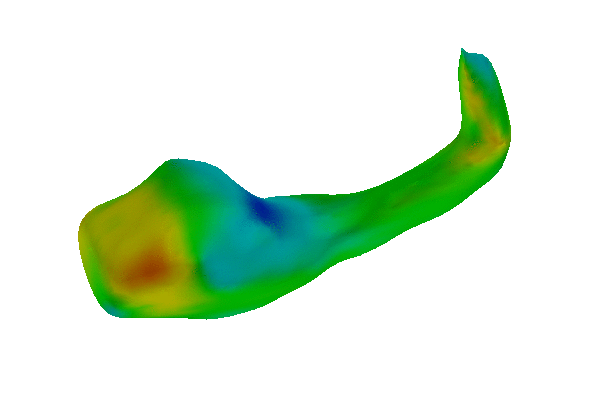
Example: Study of Hippocampal Shape in Schizophrenia.
Recent Update
We have also started exploring alternative, surface-based descriptors for objects of spherical topology based on hierarchical decomposition of the surface functions into an over-complete basis. This work is still preliminary, but promises to improve our ability to detect and characterize subtle differences int he shape of anatomical structures due to diseases such as schizophrenia.
Publications
B.T. T. Yeo, W. Ou, P. Golland. Invertible Filter Banks on the 2-Sphere. Accepted to the Internation Conference in Image Processing (ICIP) 2006. (pdf)
B.T. T. Yeo, W. Ou, P. Golland. Invertible Filter Banks on the 2-Sphere. Technical Report, February 2006. (pdf)
P. Golland, W.E.L. Grimson, M.E. Shenton, R. Kikinis. Detection and Analysis of Statistical Differences in Anatomical Shape. Medical Image Analysis, 9(1):69-86, 2005. (pdf)
P. Golland and B. Fischl. Permutation Tests for Classification: Towards Statistical Significance in Image-Based Studies. In Proc. IPMI'2003: The 18th International Conference on Information Processing and Medical Imaging, LNCS 2732:330-341, 2003.
P. Golland, B. Fischl, M. Spiridon, N. Kanwisher, R.L. Buckner, M.E. Shenton, R. Kikinis, A. Dale, W.E.L. Grimson. Discriminative Analysis for Image-Based Studies. In Proc. MICCAI'2002: Fifth International Conference on Medical Image Computing And Computer Assisted Intervention. LNCS 2488:508-515, 2002.
Software
- Stand alone code for training a classifier, jackknifing and permutation testing.
- Current plans include integration within the shape analysis pipeline, in collaboration with UNC (Martin Styner).
- We are currently also porting the software into ITK.