NA-MIC Internal Collaborations:StructuralImageAnalysis
Back to NA-MIC Internal Collaborations
Structural Image Analysis
Image Segmentation
|
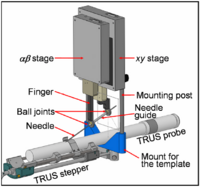
Brachytherapy Needle Positioning Robot IntegrationThe Queen’s/Hopkins team is developing novel devices and procedures for cancer interventions, including biopsy and therapies. Our goal for the programming week is to design and start implementing software for the new MRI Brachytherapy needle positioning robot. More... New: Meeting at JHU on July 17-19, 2007. |

|
Tubular Surface Segmentation FrameworkWe have proposed a new model for tubular surfaces that transforms the problem of detecting a surface in 3D space, to detecting a curve in 4D space. Besides allowing us to impose a "soft" tubular shape prior, this also leads to computational efficiency over conventional surface segmentation approaches. More... New: V. Mohan, G. Sundaramoorthi and A. Tannenbaum. Tubular Surface Segmentation for identifying anatomical structures from medical imagery. September 2008.
|
|
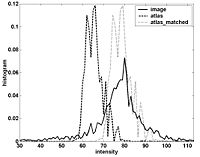
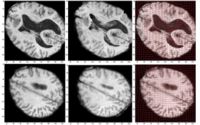
Atlas Renormalization for Improved Brain MR Image Segmentation across Scanner PlatformsAtlas-based approaches have demonstrated the ability to automatically identify detailed brain structures from 3-D magnetic resonance (MR) brain images. Unfortunately, the accuracy of this type of method often degrades when processing data acquired on a different scanner platform or pulse sequence than the data used for the atlas training. In this paper, we improve the performance of an atlas-based whole brain segmentation method by introducing an intensity renormalization procedure that automatically adjusts the prior atlas intensity model to new input data. Validation using manually labeled test datasets has shown that the new procedure improves the segmentation accuracy (as measured by the Dice coefficient) by 10% or more for several structures including hippocampus, amygdala, caudate, and pallidum. The results verify that this new procedure reduces the sensitivity of the whole brain segmentation method to changes in scanner platforms and improves its accuracy and robustness, which can thus facilitate multicenter or multisite neuroanatomical imaging studies. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 |
Image Registration
|
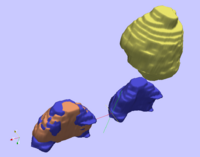
Optimal Mass Transport RegistrationThe goal of this project is to implement a computationaly efficient Elastic/Non-rigid Registration algorithm based on the Monge-Kantorovich theory of optimal mass transport for 3D Medical Imagery. Our technique is based on Multigrid and Multiresolution techniques. This method is particularly useful because it is parameter free and utilizes all of the grayscale data in the image pairs in a symmetric fashion and no landmarks need to be specified for correspondence. More... New: Tauseef ur Rehman, A. Tannenbaum. Multigrid Optimal Mass Transport for Image Registration and Morphing. SPIE Conference on Computational Imaging V, Jan 2007. |
|
Particle Filter Registration of Medical Imagery3D volumetric image registration is performed. The method is based on registering the images through point sets, which is able to handle long distance between as well as registration between Supine and Prone pose prostate. More... New: Will be put into Slicer3.
|
|
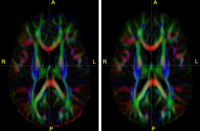
Diffusion Tensor Image Processing ToolsWe implement the diffusion weighted image (DWI) registration model from the paper of G.K.Rohde et al. Patient head motion and eddy currents distortion cause artifacts in maps of diffusion parameters computer from DWI. This model corrects these two distortions at the same time including brightness correction. New: We have recently developed software for eddy current correction. |

|
Non-Rigid EPI RegistrationOur Objective is to identify optimal ITK method and parameter settings for non-rigid intrasubject registration of T2 EPI, the raw building block images of DTI, to T1 conventional images. Provide software devliverable. More... New: Project Week Results: Jan 2006 |
|
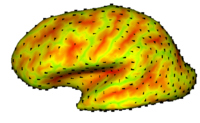
Cortical Correspondence using Particle SystemIn this project, we want to compute cortical correspondence on populations, using various features such as cortical structure, DTI connectivity, vascular structure, and functional data (fMRI). This presents a challenge because of the highly convoluted surface of the cortex, as well as because of the different properties of the data features we want to incorporate together. More... New:
|
|
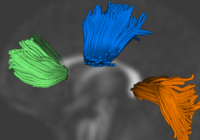
Population Analysis from Deformable RegistrationAnalysis of populations of diffusion images typically requires time-consuming manual segmentation of structures of interest to obtain correspondance for statistics. This project uses non-rigid registration of DTI images to produce a common coordinate system for hypothesis testing of diffusion properties. More... New: Command line DTI tools available as part of UNC NeuroLib |
|
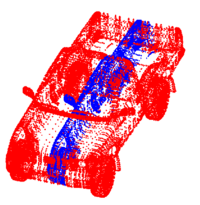
Point Set Rigid RegistrationIn this work, we propose a particle filtering approach for the problem of registering two point sets that differ by a rigid body transformation. Experimental results are provided that demonstrate the robustness of the algorithm to initialization, noise, missing structures or differing point densities in each sets, on challenging 2D and 3D registration tasks. More... New: R. Sandhu, S. Dambreville, A. Tannenbaum. Particle Filtering for Registration of 2D and 3D Point Sets with Stochastic Dynamics. In CVPR, 2008. |
|
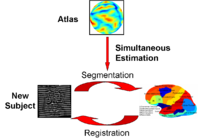
Optimal Atlas Regularization in Image SegmentationWe propose a unified framework for computing atlases from manually labeled data sets at various degrees of “sharpness” and the joint registration and segmentation of a new brain with these atlases. Using this framework, we investigate the tradeoff between warp regularization and image fidelity, i.e. the smoothness of the new subject warp and the sharpness of the atlas in a segmentation application. More... New: B.T.T. Yeo, M.R. Sabuncu, R. Desikan, B. Fischl, P. Golland. Effects of Registration Regularization and Atlas Sharpness on Segmentation Accuracy. In Proceedings of MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 683-691, 2007. MICCAI Young Scientist Award. |
|
Multimodal AtlasIn this work, we propose and investigate an algorithm that jointly co-registers a collection of images while computing multiple templates. The algorithm, called iCluster, is used to compute multiple atlases for a given population. More... New: M.R. Sabuncu, M.E. Shenton, P. Golland. Joint Registration and Clustering of Images. In Proceedings of MICCAI 2007 Statistical Registration Workshop: Pair-wise and Group-wise Alignment and Atlas Formation, 47-54, 2007. |
|
Groupwise RegistrationWe extend a previously demonstrated entropy based groupwise registration method to include a free-form deformation model based on B-splines. We provide an efficient implementation using stochastic gradient descents in a multi-resolution setting. We demonstrate the method in application to a set of 50 MRI brain scans and compare the results to a pairwise approach using segmentation labels to evaluate the quality of alignment. More... New: S.K. Balci, P. Golland, M.E. Shenton, W.M. Wells III. Free-Form B-spline Deformation Model for Groupwise Registration. In Proceedings of MICCAI 2007 Statistical Registration Workshop: Pair-wise and Group-wise Alignment and Atlas Formation, 23-30, 2007. |
Morphometric Measures and Shape Analysis
|
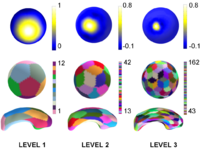
Multiscale Shape AnalysisWe present a novel method of statistical surface-based morphometry based on the use of non-parametric permutation tests and a spherical wavelet (SWC) shape representation. More... New: D. Nain, M. Styner, M. Niethammer, J. J. Levitt, M E Shenton, G Gerig, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. Statistical Shape Analysis of Brain Structures using Spherical Wavelets. Accepted in The Fourth IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI ’07) that will be held April 12-15, 2007 in Metro Washington DC, USA. |
|
Population Analysis of Anatomical VariabilityOur goal is to develop mathematical approaches to modeling anatomical variability within and across populations using tools like local shape descriptors of specific regions of interest and global constellation descriptors of multiple ROI's. More... New: Mert R Sabuncu and Polina Golland. Structural Constellations for Population Analysis of Anatomical Variability. |
|
Shape Analysis With Overcomplete WaveletsIn this work, we extend the Euclidean wavelets to the sphere. The resulting over-complete spherical wavelets are invariant to the rotation of the spherical image parameterization. We apply the over-complete spherical wavelet to cortical folding development More... New: B.T.T. Yeo, W. Ou, P. Golland. On the Construction of Invertible Filter Banks on the 2-Sphere. Yeo, Ou and Golland. Accepted to the IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. P. Yu, B.T.T. Yeo, P.E. Grant, B. Fischl, P. Golland. Cortical Folding Development Study based on Over-Complete Spherical Wavelets. In Proceedings of MMBIA: IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis, 2007. |
Shape Based Level SegmentationThis class of algorithms explicitly manipulates the representation of the object boundary to fit the strong gradients in the image, indicative of the object outline. Bias in the boundary evolution towards the likely shapes improves the robustness of the segmentation results when the intensity information alone is insufficient for boundary detection. More... | |
|
Shape Based Segmentation and RegistrationThis type of algorithm assigns a tissue type to each voxel in the volume. Incorporating prior shape information biases the label assignment towards contiguous regions that are consistent with the shape model. More... New: K.M. Pohl, J. Fisher, S. Bouix, M. Shenton, R. W. McCarley, W.E.L. Grimson, R. Kikinis, and W.M. Wells. Using the Logarithm of Odds to Define a Vector Space on Probabilistic Atlases. Medical Image Analysis,11(6), pp. 465-477, 2007. Best Paper Award MICCAI 2006 |
|
Adaptive, Particle-Based Sampling for Shapes and ComplexesThis research is a new method for constructing compact statistical point-based models of ensembles of similar shapes that does not rely on any specific surface parameterization. The method requires very little preprocessing or parameter tuning, and is applicable to a wider range of problems than existing methods, including nonmanifold surfaces and objects of arbitrary topology. More... New: J Cates, PT Fletcher, M Styner, M Shenton, R Whitaker, Shape modeling and analysis with entropy-based particle systems, IPMI 2007, pp. 333-345. |

|
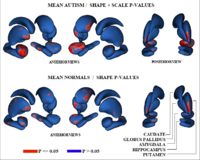
Shape Analysis Framework using SPHARM-PDMThe UNC shape analysis is based on an analysis framework of objects with spherical topology, described mainly by sampled spherical harmonics SPHARM-PDM. The input of the shape analysis framework is a set of binary segmentations of a single brain structure, such as the hippocampus or caudate. These segmentations are converted into a shape description (SPHARM) with correspondence and analyzed via Hotelling T^2 two sample metric. More... New:
|
|
Shape Analysis of the HippocampusOur objective is to examine hippocampal shape in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls. More... New: Styner M, Lieberman JA, McClure RK, Weinberger DR, Jones DW, Gerig G.: Morphometric analysis of lateral ventricles in schizophrenia and healthy controls regarding genetic and disease-specific factors, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005 Mar 29;102(13):4872-7. Epub 2005 Mar 16. |
|
Population Based CorrespondenceWe are developing methodology to automatically find dense point correspondences between a collection of polygonal genus 0 meshes. The advantage of this method is independence from indivisual templates, as well as enhanced modeling properties. The method is based on minimizing a cost function that describes the goodness of correspondence. Apart from a cost function derived from the description length of the model, we also employ a cost function working with arbitrary local features. We extended the original methods to use surface curvature measurements, which are independent to differences of object aligment. More... New:
|

|
Spherical WaveletsCortical Surface Shape Analysis Based on Spherical Wavelets. We introduce the use of over-complete spherical wavelets for shape analysis of 2D closed surfaces. Bi-orthogonal spherical wavelets have been proved to be powerful tools in the segmentation and shape analysis of 2D closed surfaces, but unfortunately they suffer from aliasing problems and are therefore not invariant to rotation of the underlying surface parameterization. In this paper, we demonstrate the theoretical advantage of over-complete wavelets over bi-orthogonal wavelets and illustrate their utility on both synthetic and real data. In particular, we show that the over-complete spherical wavelet transform enjoys significant advantages for the analysis of cortical folding development in a newborn dataset. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 |
Topology CorrectionGeometrically-Accurate Topology-Correction of Cortical Surfaces using Non-Separating Loops. We propose a technique to accurately correct the spherical topology of cortical surfaces. Specifically,we construct a mapping from the original surface onto the sphere to detect topological defects as minimal nonhomeomorphic regions. The topology of each defect is then corrected by opening and sealing the surface along a set of nonseparating loops that are selected in a Bayesian framework. The proposed method is a wholly self-contained topology correction algorithm, which determines geometrically accurate, topologically correct solutions based on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) intensity profile and the expected local curvature. Applied to real data, our method provides topological corrections similar to those made by a trained operator. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 | |
|
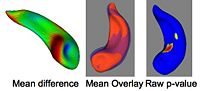
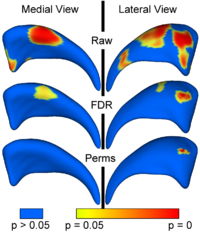
Local Statistical Analysis via Permutation TestsWe have further developed a set of statistical testing methods that allow the analysis of local shape differences using the Hotelling T 2 two sample metric. Permutatioin tests are employed for the computation of statistical p-values, both raw and corrected for multiple comparisons. Resulting significance maps are easily visualized. Additional visualization of the group tests are provided via mean difference magnitude and vector maps, as well as maps of the group covariance information. Ongoing research focuses on incorporating covariates such as clinical scores into the testing scheme. More... New:
|
|
Automatic Outlining of sulci on the brain surfaceWe present a method to automatically extract certain key features on a surface. We apply this technique to outline sulci on the cortical surface of a brain. More... |
|
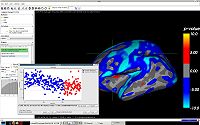
QDEC: An easy to use GUI for group morphometry studiesQdec is a application included in the Freesurfer software package intended to aid researchers in performing inter-subject / group averaging and inference on the morphometry data (cortical surface and volume) produced by the Freesurfer processing stream. The functionality in Qdec is also available as a processing module within Slicer3, and XNAT. More... See: Qdec user page |