Projects:DiffeoMixedEffects
Back to Utah 2 Algorithms
Ongoing Work
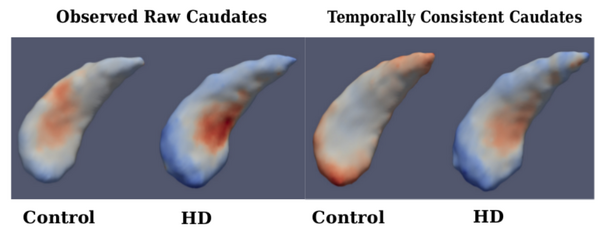
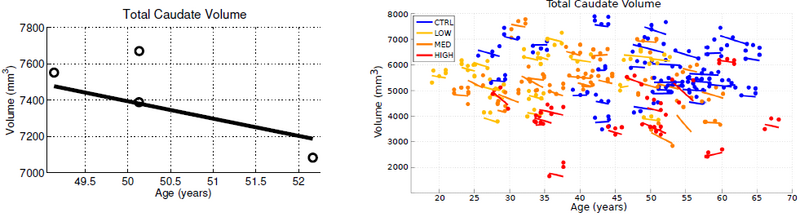
Diffeomorphic Shape Trajectories for Improved Longitudinal Segmentation and Statistics
Longitudinal image data has several sources of variability. First, there is inherent biological variability, both within a subject changing over time and also between subjects in a population. The goal of longitudinal analysis is to quantify this variability and make inferences about changes over time in a population. However, longitudinal imaging data also include unwanted sources of variability, such as noise in image acquisition, segmentation and registration errors, and human expert judgment, among others. These extraneous errors tend to dampen statistical power, especially when trying to distinguish between trajectories of two different populations, e.g., healthy and diseased.

Literature
[1] Muralidharan, P., Fishbaugh, J., Johnson, H., Durrleman, S., Paulsen, J., Gerig, G., Fletcher, P.T. Diffeomorphic shape trajectories for improved longitudinal segmentation and statistics. Proc. of Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI '14). (2014).
Key Investigators
- Utah: Prasanna Muralidharan, James Fishbaugh, P.T. Fletcher, Guido Gerig
- INRIA/ICM, Pitie Salpetriere Hospital: Stanley Durrleman
- Department of Psychiatry, Carver College of Medicine, University of Iowa: Jane Paulsen, Hans Johnson