Supervised Fissure Enhancement
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < Supervised Fissure Enhancement
Key Investigators
- James Ross (Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston)
- German Gonzalez (Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston)
- Rola Harmouche (Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston)
Project Description
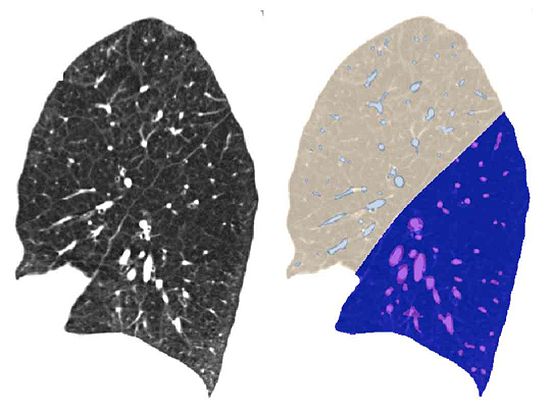
The Chest Imaging Platform provides automatic tools for lung lobe segmentation. These rely in part on detecting pulmonary fissures, which can be difficult due to poor signal-to-noise ratios and/or lung pathologies.
Objective
- Use positive and negative examples of fissures to train a classifier that can be used to detect/enhance fissures
Approach, Plan
- Guided by approach described in van Rikxoort et al: 'Supervised enhancement filters: application to fissure detection in chest CT scans'
- Use itkDiscreteHessianGaussianImageFunction and itkDiscreteGaussianDerivativeImageFunction for point-wise computation of Hessian and gradient features
- Use logistic regression as classifier. Investigate different feature subsets for best classification results.
Progress
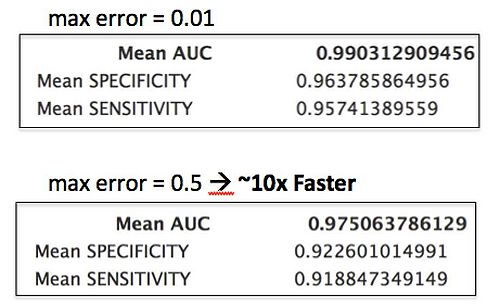
- Early experiments are promising. Would like to speed up gradient and Hessian computations.
- Results: Increased itkDiscreteHessianGaussianImageFunction and itkDiscreteGaussianDerivativeImageFunction max error parameter from 0.01 to 0.5. Noticed a factor of ten speed-up with negligible impact on logistic regression classifier