Difference between revisions of "2010 Summer Project Week Primate image analysis using the standard Slicer pipeline"
(Created page with '__NOTOC__ <gallery> Image:PW-MIT2010.png|Projects List </gallery> ==Key Investigators== * University of Iowa: Nicole Grosland, Vince Magno…') |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
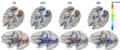
| − | Image: | + | Image:Slide1.png |
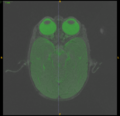
| + | Image:snapshot0001.png | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Key Investigators== | ==Key Investigators== | ||
| − | * | + | * UNC: Yundi(Wendy) Shi, Clement Vachet, Martin Styner |
| − | * | + | * Emory: Mar Sanchez |
| + | * BWH: Andriy Fedorov | ||
<div style="margin: 20px;"> | <div style="margin: 20px;"> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
| − | + | To build an open-source software (mainly involving Slicer3) based pipeline for primate imaging, including skull stripping of T1,T2 and DTI images, tissue segmentation, cortical thickness analysis, atlas building and fiber tracing and tract-based analysis. This is part of a longitudinal study of rhesus macaque monkeys | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | <h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | ||
| − | + | * Skull stripping and Tissue segmentation | |
| + | ABC (developed by Marcel Prastawa, SCI, Utah) is currently used for skull stripping and tissue segmentation of the 3 months, 6 months and 12 months T1 and T2 images. | ||
| + | Challenge include: Application of ABC or neoseg for the same task on 2 weeks old monkey images, due to the different anatomical structures during early ages and small brain size of the monkeys | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Cortical thickness analysis | ||
| + | Will work with Clement Vachet and adapt the tools for human data to primate data | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Affine alignment | ||
| + | RVIEW is currently used for affine alignment of the monkey images. Working on testing the data with the Slicer tools and replace rview tools with them. We need to work with ?? for the special challenge in registration of the monkey brains. | ||
| − | + | * Atlas building | |
| + | AtlasWerks is the tool for atlas building with fWarp (developed by Sarang Joshi, SCI, UTAH). We would like to start using open source tools like the deamons registration in Slicer for the same task. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 45: | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| − | + | * Attended the DTI breakout session, and identified the problem/challenge of the commonly used tools in the pipeline used by people in the community and the tools we usually use (DicomtoNrrdConvert...) | |
| + | |||
| + | * Work with Hans, and tested BrainsFit for the "affine alignment" task in tissue segmentation, which includes rigid registration of T1 and T2 images, as well as the alignment of subject with template using affine registration. Parameters were selected for monkey data with good results. | ||
| − | + | * Testing Demons for warping the subjects to atlas, instead of fWarp. | |
| + | |||
| + | * Meeting with Steve for using the color module for visualization of fiber bundles with scalars with custom min and max and workaround to visualize fibers as tubes with scalar values written in the vtk lookup table. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 60: | ||
==Delivery Mechanism== | ==Delivery Mechanism== | ||
| − | This work will be delivered | + | This work will be delivered as open-source software and open dataset |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | * | + | *M. Styner, R. Knickmeyer, S. Joshi, C. Coe, S. J. Short, and J. Gilmore. Automatic brain segmentation in rhesus monkeys. In Proc SPIE Vol 6512, Medical Imaging, 2007, pp. 65122 L1-8. |
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:32, 25 June 2010
Home < 2010 Summer Project Week Primate image analysis using the standard Slicer pipeline
Key Investigators
- UNC: Yundi(Wendy) Shi, Clement Vachet, Martin Styner
- Emory: Mar Sanchez
- BWH: Andriy Fedorov
Objective
To build an open-source software (mainly involving Slicer3) based pipeline for primate imaging, including skull stripping of T1,T2 and DTI images, tissue segmentation, cortical thickness analysis, atlas building and fiber tracing and tract-based analysis. This is part of a longitudinal study of rhesus macaque monkeys
Approach, Plan
- Skull stripping and Tissue segmentation
ABC (developed by Marcel Prastawa, SCI, Utah) is currently used for skull stripping and tissue segmentation of the 3 months, 6 months and 12 months T1 and T2 images. Challenge include: Application of ABC or neoseg for the same task on 2 weeks old monkey images, due to the different anatomical structures during early ages and small brain size of the monkeys
- Cortical thickness analysis
Will work with Clement Vachet and adapt the tools for human data to primate data
- Affine alignment
RVIEW is currently used for affine alignment of the monkey images. Working on testing the data with the Slicer tools and replace rview tools with them. We need to work with ?? for the special challenge in registration of the monkey brains.
- Atlas building
AtlasWerks is the tool for atlas building with fWarp (developed by Sarang Joshi, SCI, UTAH). We would like to start using open source tools like the deamons registration in Slicer for the same task.
Progress
- Attended the DTI breakout session, and identified the problem/challenge of the commonly used tools in the pipeline used by people in the community and the tools we usually use (DicomtoNrrdConvert...)
- Work with Hans, and tested BrainsFit for the "affine alignment" task in tissue segmentation, which includes rigid registration of T1 and T2 images, as well as the alignment of subject with template using affine registration. Parameters were selected for monkey data with good results.
- Testing Demons for warping the subjects to atlas, instead of fWarp.
- Meeting with Steve for using the color module for visualization of fiber bundles with scalars with custom min and max and workaround to visualize fibers as tubes with scalar values written in the vtk lookup table.
Delivery Mechanism
This work will be delivered as open-source software and open dataset
References
- M. Styner, R. Knickmeyer, S. Joshi, C. Coe, S. J. Short, and J. Gilmore. Automatic brain segmentation in rhesus monkeys. In Proc SPIE Vol 6512, Medical Imaging, 2007, pp. 65122 L1-8.