Difference between revisions of "DBP2:Harvard"
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
== [[Projects:MultiscaleShapeAnalysis| Shape Analysis of the Caudate]] == | == [[Projects:MultiscaleShapeAnalysis| Shape Analysis of the Caudate]] == | ||
| − | Multiscale shape analysis | + | Multiscale shape analysis |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
== [[Projects:ShapeBasedSegmentationAndRegistration|Shape Based Segmentation and Registration]] == | == [[Projects:ShapeBasedSegmentationAndRegistration|Shape Based Segmentation and Registration]] == | ||
We use this segmentation algorithm to process our entire data set. [[http://pnl.bwh.harvard.edu/pub/papers_html/PohlIEEE07.html| Reference: A Hierarchical Algorithm for MR Brain Image Parcellation, K. Pohl, S. Bouix, M. Nakamura, T. Rohlfing, R. McCarley, R. Kikinis, W. Grimson, M. E. Shenton, W. Wells, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Volume 26, Number 9, Pages 1201-1212, 2007 ]] | We use this segmentation algorithm to process our entire data set. [[http://pnl.bwh.harvard.edu/pub/papers_html/PohlIEEE07.html| Reference: A Hierarchical Algorithm for MR Brain Image Parcellation, K. Pohl, S. Bouix, M. Nakamura, T. Rohlfing, R. McCarley, R. Kikinis, W. Grimson, M. E. Shenton, W. Wells, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Volume 26, Number 9, Pages 1201-1212, 2007 ]] | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 81: | Line 82: | ||
== [[Projects:GroupwiseRegistration| Groupwise Registration]] == | == [[Projects:GroupwiseRegistration| Groupwise Registration]] == | ||
The goal is to create unbiased atlases throught nonlinear (b-spline) group wise registration. | The goal is to create unbiased atlases throught nonlinear (b-spline) group wise registration. | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 15 December 2008
Home < DBP2:HarvardBack to NA-MIC DBP 2
Overview of Harvard DBP 2
Velocardiofacial Syndrome (VCFS) as a Genetic Model for Schizophrenia
VCFS is a genetic disorder characterized by a deletion of a small piece of chromosome-22. The features of this syndrome include deficits in neurological psychomotor and perceptual skills, as well as in cognitive domains such as learning and memory. Most importantly, up to 30% of VCFS patients develop schizophrenia, making it the most commonly known single risk factor for the development of psychosis and a unique model for studying neurodevelopmental changes leading to psychotic deficits. We plan to collect new, high resolution DTI, structural and fMRI data, and apply existing NAMIC tools, as well as help to develop new tools to investigate the contribution of genetic variation to brain and behavioral/cognitive abnormalities, thus bridging the gap between neuroimaging studies and genetics. The NAMIC community will gain access to de-identified imaging data (new, high resolution structural and diffusion data acquired on the 3T magnet at Brigham and Women’s Hospital). Unlike in schizophrenia, subjects with VCFS have concrete cognitive abnormalities, in addition to a well defined chromosomal abnormality, which, taken together, will make it easier to establish scientific protocols that reveal associated anatomical and functional brain abnormalities in this disorder. Interestingly, some anatomical abnormalities will be shared between VCFS and schizophrenia (e.g., connections within working memory circuits), and some will be not (e.g., sensory and motor paths). Neuropsychological and genetic data will also be collected for each individual as part of separate collaboration between PI and the Children's Hospital("Investigation of Genotype/Phenotype Correlations in Velocardiofacial and DiGeorge Syndromes”) and de-dentified dataset containing neuropsychological tests, clinical evaluations and genetic data will be provided to the PI. The NAMIC project with thus enable the PI to apply NAMIC tools to imaging VCFS data, a genetic disorder that is viewed as a genetically mediated subtype of schizophrenia. To date, there have only been a small number of neuroimaging studies of this disorder and no studies have combined neurocognitive, neuroimaging, and genetic investigations in the same study. Importantly, this research will also increase our understanding of schizophrenia, and will help establish a multimodal research project involving an important collaboration between computer scientists, cognitive neuroscientists, radiologists, psychiatrists, and geneticists. The focus on imaging and genes also affords a new window of opportunity for defining further the new area of “imaging genomics”. More...
Data is provided at the following link: Harvard Data.
Harvard Roadmap Project
|
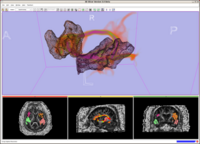
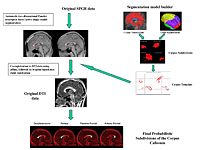
Stochastic Tractography for VCSFThe main goal of this project is to develop end-to-end application that would be used to characterize anatomical connectivity abnormalities in the brain of patients with velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS), and to link this information with deficits in schizophrenia. More... New: 12/10/2008 official release of the python Slicer 3 stochastic tractography module New: Collaborative Publication: "Reduced interhemispheric connectivity in schizophrenia-tractography based segmentation of the corpus callosum. Kubicki M, Styner M, Bouix S, Gerig G, Markant D, Smith K, Kikinis R, McCarley RW, Shenton ME. Schizophr Res. 2008 Dec;106(2-3):125-131. Epub 2008 Sep 30. |
|
Harvard Collaborations
- GA Tech
EPI distortion correction using optimal mass transport.EPI distortion correction using optimal mass transport. (baseline vs. strct t2w). Goal is to use optimal registration for EPI distortion correction in diffusion weigthed scans. | |
Geodesic Tractography SegmentationWe are currently investigating Cingulum Bundle fractional anisotropy (FA) differences between a population of 12 schizophrenics and 12 normal controls using this new methodology. | |
A Coupled Multi-Shape RepresentationWe are currently using this technique to build an unbiased atlas for segmentation. | |
Shape Analysis of the CaudateMultiscale shape analysis |
- MIT
Shape Based Segmentation and RegistrationWe use this segmentation algorithm to process our entire data set. [Reference: A Hierarchical Algorithm for MR Brain Image Parcellation, K. Pohl, S. Bouix, M. Nakamura, T. Rohlfing, R. McCarley, R. Kikinis, W. Grimson, M. E. Shenton, W. Wells, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Volume 26, Number 9, Pages 1201-1212, 2007 ] | |
Groupwise RegistrationThe goal is to create unbiased atlases throught nonlinear (b-spline) group wise registration. | |
DTI Fiber Clustering and Fiber Based AnalysisThe goal of this project is to provide structural description of the white matter architecture as a partition into coherent fiber bundles and clusters, and to use these bundles for quantitative measurement. We use this method in two ongoing projects- corpus callosum segmentation in chronic schizophrenia sample, and whole brain clustering in sample of first episode psychosis subjects. | |
Fiber Tract Modeling, Clustering, and Quantitative AnalysisThe goal of this project is to segment and parametrize fiber bundles for more precise group comparison. We use this method to segment and compare between controls and chronic schizophrenia population tracts belonging to inferior semantic processing stream (Inferior Longitudinal fasciculus, Uncinate Fasciculus and Inferior Occipito-Frontal Fasciculus). Manuscript is in preparation. | |
fMRI clusteringThe goal of this project is to use resting state fMRI data and clustering algorythm to detect and separate specific functional brain networks. We are in the process of runing the method on group of chronic schizophrenia and matched control subjects. |
- UNC
Shape Analysis Framework using SPHARM-PDMThe manuscript, "Shape Abnormalities of Caudate Nucleus in Schizotypal Personality Disorder" has been accepted by Schizophrenia Research. |
- Utah 1
Diffusion Tensor Image Processing ToolsTesting and use of eddy current correction for our DWI scans. |
- Utah 2
Population Analysis from Deformable RegistrationThis project uses non-rigid registration of DTI images to produce a common coordinate system for hypothesis testing of diffusion properties. |