Difference between revisions of "Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C10"
From NAMIC Wiki
(Created page with 'Back to ARRA main page <br> Back to Registration main page <br> [[Projects:RegistrationDocumentation:UseCaseInv…') |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
{| style="color:#bbbbbb; background-color:#333333;" cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="0" | {| style="color:#bbbbbb; background-color:#333333;" cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
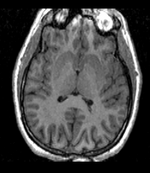
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:RegLib_C10_EMAtlas1.png|150px|lleft|this is the fixed reference image. All images are aligned into this space]] |
|[[Image:Arrow_left_gray.jpg|100px|lleft]] | |[[Image:Arrow_left_gray.jpg|100px|lleft]] | ||
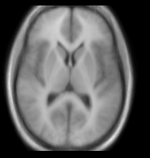
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:RegLib_C10_EMAtlas2.png|150px|lleft|this is the moving image. The transform is calculated by matching this to the reference image]] |
| − | |||
|align="left"|LEGEND<br><small><small> | |align="left"|LEGEND<br><small><small> | ||
[[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the reference image that is fixed and does not move. All other images are aligned into this space and resolution<br> | [[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the reference image that is fixed and does not move. All other images are aligned into this space and resolution<br> | ||
[[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the moving image that determines the registration transform. <br> | [[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the moving image that determines the registration transform. <br> | ||
| − | [ | + | [</small></small> |
| − | </small></small> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|40px|lleft]] Target Brain | |[[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|40px|lleft]] Target Brain | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |[[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|40px|lleft]] | + | |[[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|40px|lleft]] Tissue Atlas |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|0.46 x 0.46 x 3.0 mm axial <br> 512 x 512 x 46<br>RAS | |0.46 x 0.46 x 3.0 mm axial <br> 512 x 512 x 46<br>RAS | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |1.0 x 1.0 x 3.3 mm <br> axial oblique<br> 256 x 256 x 36 | + | |1.0 x 1.0 x 3.3 mm <br> axial oblique<br> 256 x 256 x 36 <br>RAS |
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
===Objective / Background === | ===Objective / Background === | ||
| − | This is | + | This is an example of sparse atlas co-registration. Not all atlases have an associated reference image that can be used for registration. Because the atlas represents a map of a particular tissue class probability, its contrast differs significantly from the target image. |
=== Keywords === | === Keywords === | ||
| − | MRI, brain, head, | + | MRI, brain, head, inter-subject, probabilistic atlas, atlas-based segmentation |
===Input Data=== | ===Input Data=== | ||
| − | *[[Image:Button_red_fixed_white.jpg|20px]]reference/fixed : | + | *[[Image:Button_red_fixed_white.jpg|20px]]reference/fixed : T1w axial, 1mm resolution in plane, 3mm slices |
| − | *[[Image:Button_green_moving_white.jpg|20px]] moving: | + | *[[Image:Button_green_moving_white.jpg|20px]] moving: Probabilistic Tissue atlas, |
| − | + | x 36 x 9 | |
=== Registration Results=== | === Registration Results=== | ||
| Line 64: | Line 60: | ||
=== Discussion: Registration Challenges === | === Discussion: Registration Challenges === | ||
| − | * | + | *Because the atlas represents a map of a particular tissue class probability, its contrast differs significantly from the target image. |
| − | * | + | *The two images may have strong differences in voxel sizes and voxel anisotropy. If the orientation of the highest resolution is not the same in both images, finding a good match can be difficult. |
| − | * | + | *The two images represent different anatomies, a non-rigid registration is required |
=== Discussion: Key Strategies === | === Discussion: Key Strategies === | ||
| − | * | + | *Because of the strong differences in image contrast, Mutual Information is recommended as the most robust metric. |
| − | * | + | *masking (skull stripping) is highly recommended to obtain good results. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*because speed is not that critical, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%. | *because speed is not that critical, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%. | ||
| − | *we also expect larger differences in scale & distortion than with regular structural | + | *we also expect larger differences in scale & distortion than with regular structural scans: so we significantly (2x-3x) increase the expected values for scale and skew from the defaults. |
*a good affine alignment is important before proceeding to non-rigid alignment to further correct for distortions. | *a good affine alignment is important before proceeding to non-rigid alignment to further correct for distortions. | ||
=== Acknowledgments === | === Acknowledgments === | ||
Revision as of 22:44, 16 February 2010
Home < Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C10Back to ARRA main page
Back to Registration main page
Back to Registration Use-case Inventory
Slicer Registration Library Exampe #10: Co-registration of probabilistic tissue atlas for subsequent EM segmentation
Objective / Background
This is an example of sparse atlas co-registration. Not all atlases have an associated reference image that can be used for registration. Because the atlas represents a map of a particular tissue class probability, its contrast differs significantly from the target image.
Keywords
MRI, brain, head, inter-subject, probabilistic atlas, atlas-based segmentation
Input Data
 reference/fixed : T1w axial, 1mm resolution in plane, 3mm slices
reference/fixed : T1w axial, 1mm resolution in plane, 3mm slices moving: Probabilistic Tissue atlas,
moving: Probabilistic Tissue atlas,
x 36 x 9
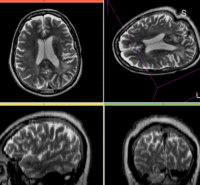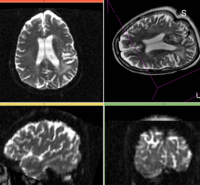
Registration Results
Download
- download entire package (Data,Presets,Tutorial, Solution, zip file 33.7 MB) (to be added: tutorial + presets)
- Presets
- Tutorial only
- Image Data only
Discussion: Registration Challenges
- Because the atlas represents a map of a particular tissue class probability, its contrast differs significantly from the target image.
- The two images may have strong differences in voxel sizes and voxel anisotropy. If the orientation of the highest resolution is not the same in both images, finding a good match can be difficult.
- The two images represent different anatomies, a non-rigid registration is required
Discussion: Key Strategies
- Because of the strong differences in image contrast, Mutual Information is recommended as the most robust metric.
- masking (skull stripping) is highly recommended to obtain good results.
- because speed is not that critical, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%.
- we also expect larger differences in scale & distortion than with regular structural scans: so we significantly (2x-3x) increase the expected values for scale and skew from the defaults.
- a good affine alignment is important before proceeding to non-rigid alignment to further correct for distortions.